Mouth is the part of the body that is adapted for taking in food and liquids. The lips at the mouth opening help us drink and pick up our food. Inside are two rows of teeth, one above the other, to grind and crush food into a bolus (lump) to be swallowed. Salivary glands in the walls and floor of the mouth produce saliva, which mixes with food as we chew it. Saliva helps us swallow dry foods and begins the digestion of sugars. See Saliva.
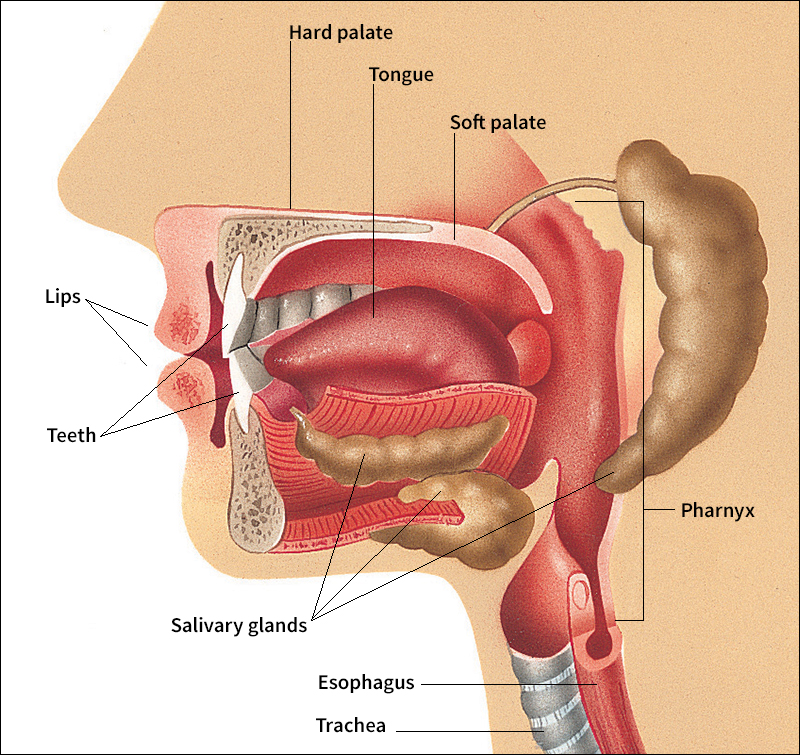
The inside of the mouth, called the oral cavity, is lined with a mucous membrane. The roof of the mouth consists of a bony front part, called the hard palate, and a soft part in the rear, the soft palate. The hard palate forms a partition between the oral and nasal passages. The soft palate arches at the back of the mouth to form a curtain between the mouth and pharynx (back part of the throat). During swallowing, the soft palate closes the nasal passages from the throat to prevent food from entering the nose. The pharynx connects the mouth and nose with both the esophagus (tube that carries food to the stomach) and the trachea (windpipe that carries air to the lungs). A flexible bundle of muscles extends from the floor of the mouth to form the tongue. The tongue not only helps us to eat, swallow, and talk, but also has almost all the sense organs of taste (see Taste).
Harmful germs may enter the body through the mouth. The mouth should be kept clean to help ward off disease. The mouth cavity is an excellent breeding place for germs because it is warm and moist.
The teeth should be cleaned thoroughly at least twice a day. They should be brushed lengthwise as well as crosswise, to remove particles of food. Jagged teeth may damage the mucous membrane and lead to infection. Periodontitis (diseased gums) causes bone loss around the teeth, which may eventually make teeth become loose and fall out. Disease of the teeth may cause the body to become infected by bacteria. Trench mouth, also called Vincent’s infection, is an infection of the mouth. Painful cankers may also attack the mucous membrane that lines the mouth.
