Nut is the popular name for many kinds of edible, dry seeds or fruits that grow in a woody shell. The word nut can refer to both the shell and the nutmeat, or kernel, inside or to the kernel alone. Nut-bearing plants grow in almost every part of the world.
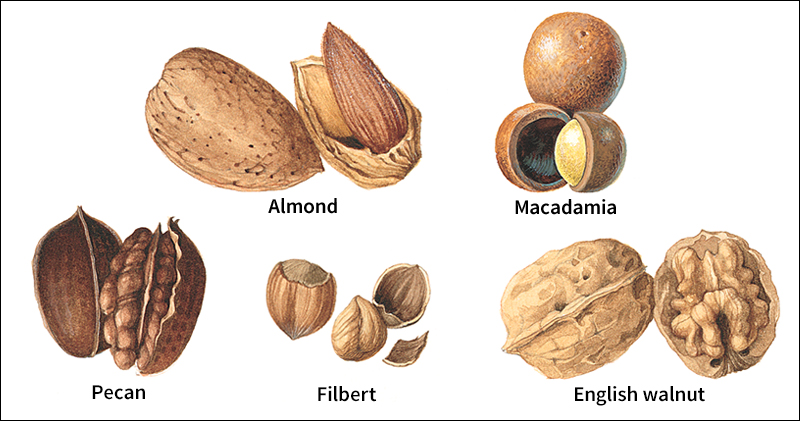
Botanists define a nut as a dry, one-seed fruit surrounded by a hard shell that does not open on its own. Some edible nuts, including chestnuts and filberts, fit this definition of a true nut. But people also eat other kinds of “nuts,” including almonds, coconuts, and peanuts, that are not true nuts. In fact, peanuts are related to peas (see Peanut).
Uses of nuts.
People commonly eat nuts as snacks or use them as flavoring in cooking. For example, food processing companies use peanuts in peanut butter, candies, and cookies. Most nuts provide rich sources of protein and fat, though chestnuts and a few others have more starch than protein. In Italy, bakers sometimes produce bread from flour made from chestnuts.
Prehistoric human beings probably ate nuts as a regular part of their diet, and many people today still rely on nuts for this purpose. Some scientists believe that nuts will become more widely used as a source of protein in parts of the world that have food shortages.
In addition to their value as food, certain nuts provide useful oil. For example, peanut oil and walnut oil are used in cooking. Walnut oil is also used to clean and polish wooden furniture. Jojoba nuts furnish a valuable lubricant for precision instruments. Tung oil is used in paints and varnishes.
Kinds of nuts.
Hundreds of shrub and tree species produce nuts. But growers raise only about 25 kinds of nuts as crops. Peanuts rank among the most important and widespread nut crops. Leading peanut-growing countries include China, India, Nigeria, and the United States. Growers in Australia, California, Iran, and the Mediterranean region produce much of the world’s almonds. The United States is the leading grower of pecans, a type of hickory nut. Australia, Mexico, South Africa, and the Middle East also raise pecans.
Leading walnut-producing countries include China, Iran, Turkey, and the United States. Filberts grow on large shrubs or small trees and rank as a major crop in Italy, Turkey, and the northwestern United States. Pistachios are grown in Iran, the United States, and the Mediterranean region. These nuts have a delicate flavor and a distinctive green color. Processors often use them in ice cream.

Various species of chestnuts are produced throughout the world. Many people roast sweet chestnuts and eat them whole, and others turn them into sauces. During the early 1900’s, a disease called chestnut blight almost wiped out the American chestnut trees of eastern North America. Though some of these diseased trees still sprout from old stumps, they do not produce seeds.
A number of important nuts grow in tropical regions, including macadamia nuts, Brazil nuts, cashews, and coconuts. Macadamia nuts come from macadamia trees, which are native to Australian rain forests. Australia, South Africa, and the United States rank among the leading producers of these nuts. Most U.S. macadamia nut production occurs in Hawaii. Brazil nuts are native to the Amazon rain forest in South America. Harvesting of these nuts ranks as a major economic activity in the Amazon region. Cashew nuts originally came from Brazil, and people now cultivate them in Brazil, India, the Philippines, Vietnam, and sub-Saharan Africa. Cashews have a sweet flavor and are rich in protein. Coconuts grow primarily in Southeast Asia and Brazil. They contain a crisp, sweet-tasting meat and a sugary liquid called coconut milk.
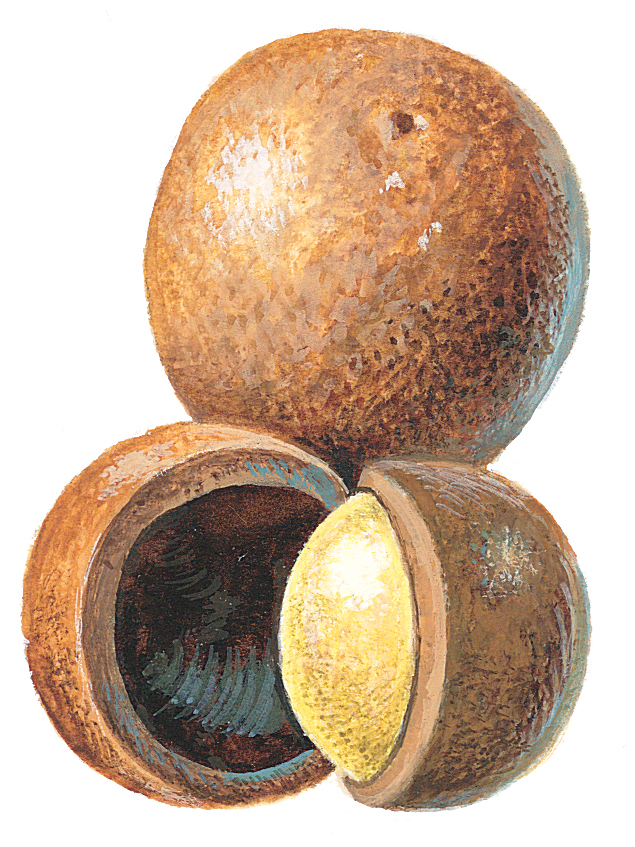
Nut growing.
Most kinds of nut trees produce nuts only if they have been cross-pollinated—that is, pollinated by flowers from another tree of the same species. Nut growers raise new trees by grafting certain parts of one tree to the roots of another (see Grafting).
Nut trees—and nuts themselves—may be damaged by a number of pests and diseases. For example, mice, squirrels, weevils, and some species of birds eat nuts and feed on nut crops. Nut trees can be harmed by certain insects and diseases that attack the leaves, stems, or nuts. Nut growers commonly protect their crops from insects and diseases by spraying the trees with pesticides. They use firearms, mechanical barriers, poisons, repellents, traps, and various other means to control birds and rodents. Breeding programs also help growers develop disease-resistant varieties of trees.
