Penis is an external male reproductive organ. In men and most other male mammals, both urine and a sperm-carrying fluid called semen leave the body through the penis. The penis is shaped somewhat like a finger. It hangs between the legs and is attached to the pelvic bones by connective tissues.
Thin, hairless skin covers the penis. Inside are three adjoining cylinders of spongy tissue that contains many blood vessels. These cylinders are bound together by a fibrous sheath. One of them encloses the urethra, a passageway for semen and urine. The urethra ends as an opening in the tip of the penis. The tip, called the head or glans, is slightly enlarged and has highly sensitive nerve endings. A fold of skin called the foreskin or prepuce, covers the glans. In many males, the foreskin has been removed by a surgical procedure called circumcision (see Circumcision ).
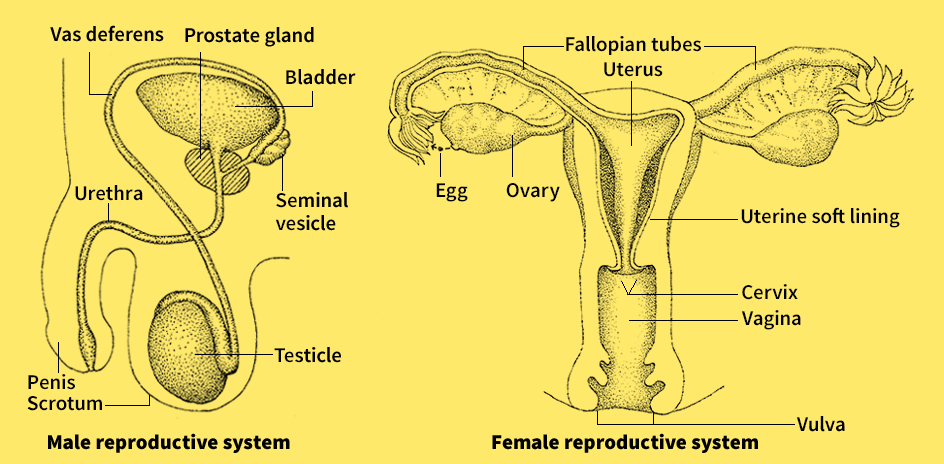
The penis is usually soft and limp. Sexual excitement increases the flow of blood to the organ, filling its tissues and making it stiff and erect. The stiffened penis, called an erection, enables the male to have sexual intercourse. In a sexually mature male, stimulation of the erect penis leads to ejaculation, the discharge of semen that accompanies sexual climax. After ejaculation, blood drainage returns the penis to its normal state.
