Pepper is a common spice used in cooking. The spice comes from the fruit of a trailing or climbing vine native to Asia. The two most common forms of pepper are black pepper and white pepper, but other forms are also made. It was partly the demand for black pepper and other spices that led the Italian navigator Christopher Columbus to seek a sea route to Asia on the famous voyage that instead brought him to the Caribbean region. Today, most black pepper and white pepper come from Brazil, India, Indonesia, Vietnam, and other countries with hot climates.
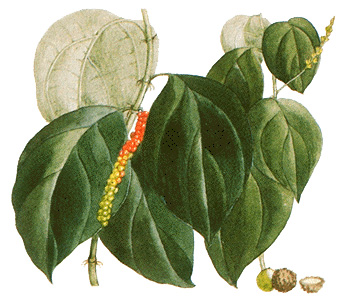
The pepper plant bears a small green berry, which turns red as it ripens. The berries are gathered when they begin to change color. They are cleaned, then dried in the sun or near a fire. In drying, the berries turn black. After they are ground and sifted, they form the black pepper known in most households.
White pepper is made from the ripe berries of the same plant. These are bruised, then washed until the seeds are free from pulpy matter and bits of stalk. The seeds are then dried. White pepper has a finer flavor than black but is not so strong.
Pepper contains a substance called piperine that gives the spice its sharp, biting taste. Pepper also contains a mixture of oils that produce its aroma.
Other spices are sometimes called pepper but are made from different plants. For example, a spice called red pepper, or cayenne pepper, is not true pepper and is made from an unrelated plant. Allspice, sometimes called Jamaica pepper, is not true pepper either.
