Polyhedron, << `pol` ee HEE druhn, >> is a solid figure bounded by four or more flat surfaces called faces. Each face of a polyhedron is a polygon. The sides of the polygons form the edges of the polyhedron. The points at which the edges meet are called vertexes or vertices. Examples of polyhedrons include cubes and pyramids. A polyhedron is convex if it lies entirely on one side of each of the planes determined by the faces.
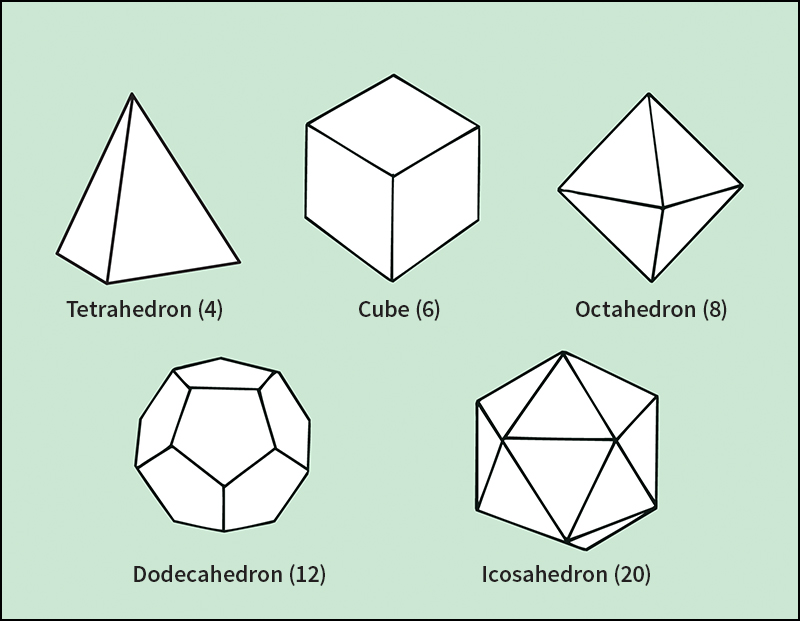
A regular polyhedron, or Platonic solid, is a convex polyhedron in which each face is a regular polygon and is identical to all the other faces. A regular polygon has equal sides and equal angles. The five regular polyhedrons are tetrahedrons (4 faces), cubes (6 faces), octahedrons (8 faces), dodecahedrons (12 faces), and icosahedrons (20 faces).
