Rhodes, << rohdz, >> is the largest of the Dodecanese Islands in the Aegean Sea. It lies 12 miles (19 kilometers) off the southwestern coast of Turkey. Rhodes (also called Rodhos) has an area of 540 square miles (1,398 square kilometers) and a population of about 125,000. A range of mountains runs lengthwise across the island and rises to a height of 3,986 feet (1,215 meters) above the sea. Tourism is the island’s chief industry. Rhodes produces cigarettes, food products, machinery, and textiles. The major crops of Rhodes include citrus fruits, olives, tobacco, and vegetables.
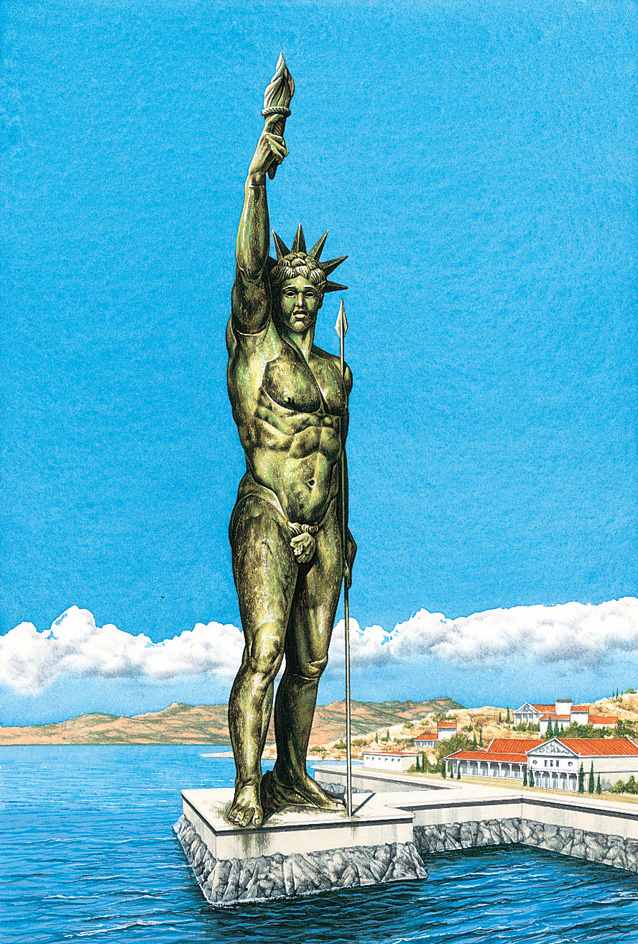
In early days, Rhodes was a wealthy and independent state of Greece. Rhodes was the home of numerous poets, artists, and philosophers. A great statue of Helios, called the Colossus of Rhodes, was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World (see Seven Wonders of the Ancient World). In 1310, the Knights Hospitallers occupied Rhodes. In 1522, the Turks captured it. Then Rhodes declined in glory and grandeur.

Italy occupied Rhodes during the Turko-Italian War of 1911-1912. Italy held Rhodes and the rest of the Dodecanese Islands until 1947. It then ceded them to Greece. The capital of the island is the city of Rhodes (or Rodhos). It is a major tourist attraction.
See also Dodecanese Islands.
