Salt Lake City (pop. 199,723; met. area pop. 1,257,936) is the capital and largest city of Utah. Salt Lake City is a center of culture, industry, commerce, and transportation. Snow-capped mountains provide a beautiful natural setting for the city. It lies in the Salt Lake Valley at the foot of the Wasatch Range of the Rocky Mountains. Salt Lake City is about 15 miles (24 kilometers) southeast of Great Salt Lake. For location, see Utah.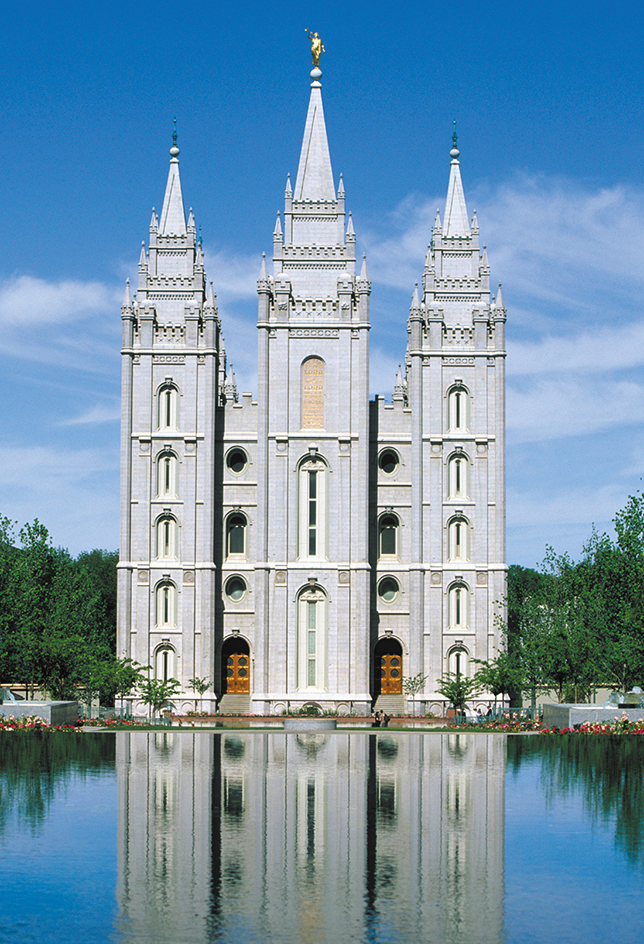 
Salt Lake City is the world headquarters of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. The church’s members are known as Mormons. Mormons make up about half of the city’s population.
Mormon pioneers, led by Brigham Young, founded Salt Lake City in 1847. According to an account from the time, Young chose the location for the scenic land. He said, “This is the right place.” Today, the state celebrates the day of Young’s arrival, July 24, as Pioneer Day. The Mormons called their settlement Great Salt Lake City. The name became simply Salt Lake City in 1868.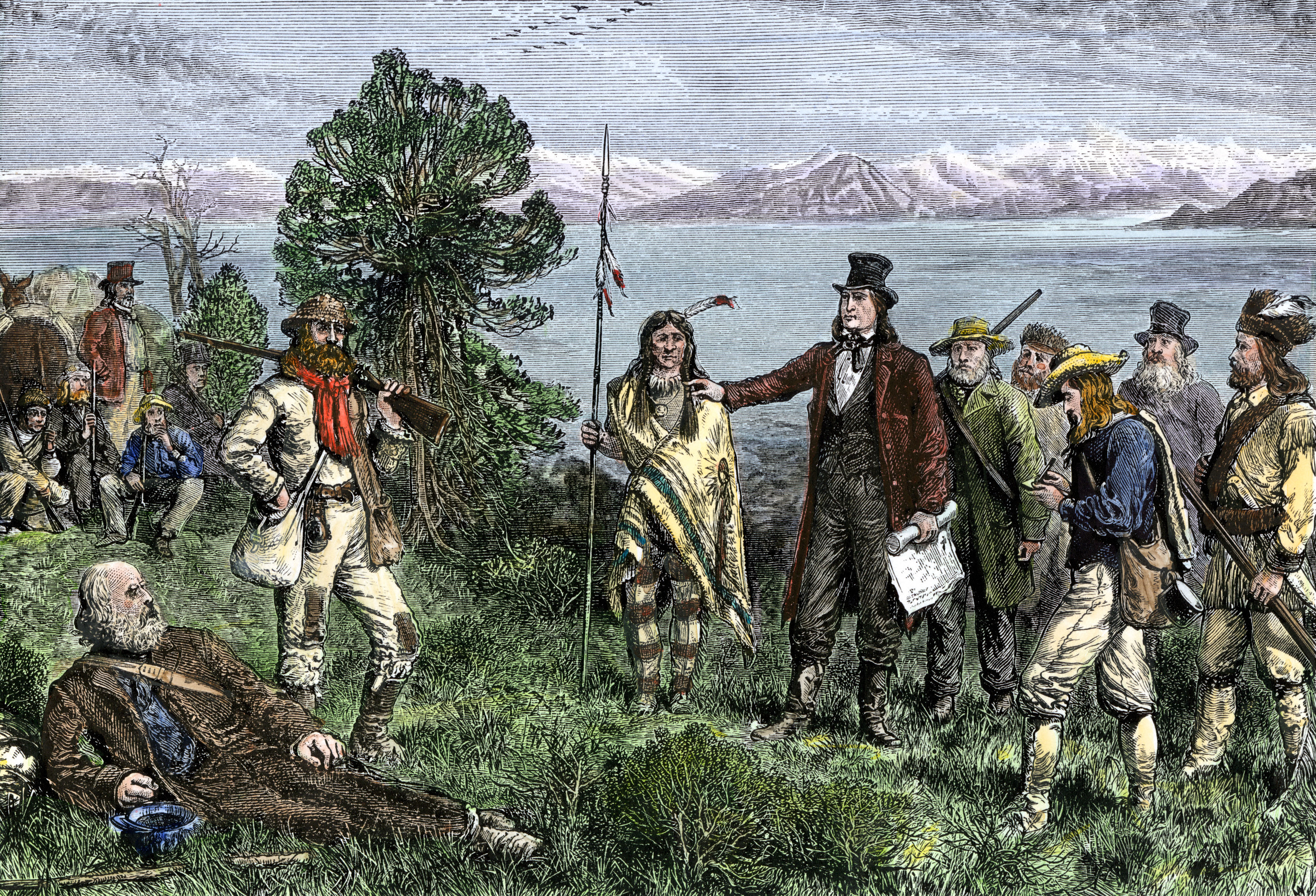 
The city
occupies 111 square miles (287 square kilometers). It is the county seat of Salt Lake County. The Salt Lake City-Murray metropolitan area covers 7,684 square miles (19,901 square kilometers) of land. It consists of Salt Lake and Tooele counties. About 40 percent of Utah’s people live in this area. 
Temple Square is at the heart of downtown Salt Lake City. In and near the square are a number of buildings of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Salt Lake Temple, with its majestic six spires, stands there. Next to it is the Mormon Tabernacle (officially Salt Lake Tabernacle). The tabernacle is famous for its choir and its huge organ with 11,000 pipes. Temple Square also includes the Seagull Monument. The monument is a tribute to the gulls that ate crop-destroying grasshoppers, known as Mormon crickets, during the summer of 1848. Across the street from the square stands the 21,000-seat Conference Center. Nearby is the 28-story Church Office Building. Also downtown is the Salt Palace, the city’s convention and civic center.
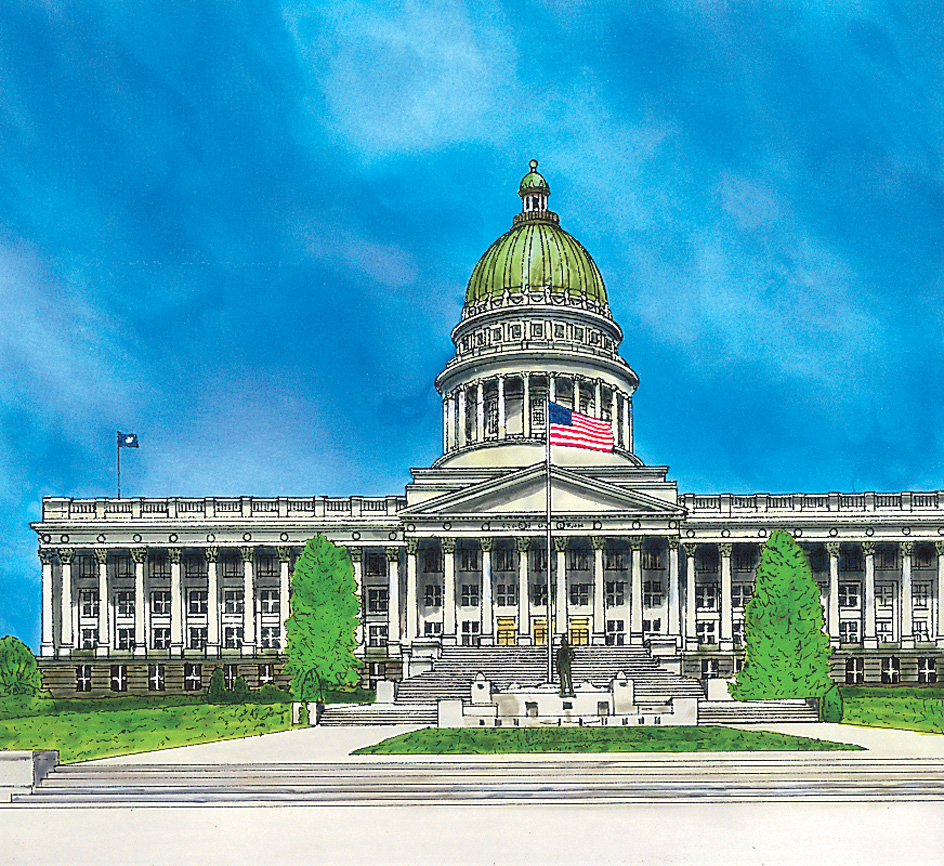
The Utah State Capitol overlooks the city from the north. Its rotunda (room under its dome) measures 165 feet (50 meters) from floor to ceiling. A monument stands in This Is the Place Heritage Park in eastern Salt Lake City, near the spot where the Mormons entered the valley. The monument commemorates Utah’s explorers, Indians, and pioneers.
About 80 percent of the city’s people were born in the United States. People of English, German, and Mexican ancestry form the largest groups in the city.
Economy.
The metropolitan area’s leading industries make aircraft parts, chemicals, computer software, electronics, food products, and metal products. A number of petroleum refineries are also in the area. 
The city owes much of its industrial importance to the rich natural resources in the area. The largest open-pit copper mine in North America operates in nearby Bingham Canyon. Chemical plants take large amounts of chlorides, magnesium, and potash from Great Salt Lake. Many ski resorts and camping areas in the Wasatch Range help make tourism an important industry in Salt Lake City. State and federal government agencies rank among the chief employers in the city. Salt Lake City also ranks as an important banking center.
Passenger trains and rail freight lines serve the city. Airlines use Salt Lake City International Airport. The city has two daily newspapers, the Deseret News and The Salt Lake Tribune.
Education.
An elected Board of Education oversees public schools in the Salt Lake City School District. The city also has several private schools and church-supported schools. The University of Utah and Westminster University are in the city.
Cultural life and recreation.
The city is the home of Ballet West, a dance company. The city also has the Pioneer Theatre Company, a professional acting company. The Mormon Tabernacle Choir; the Utah Symphony; and the Utah Opera provide musical performances. The Natural History Museum of Utah, in the Rio Tinto Center, focuses on geology and archaeology. The Leonardo is a museum that blends art, science, and technology. Other cultural attractions include Clark Planetarium, Hogle Zoo, Utah Museum of Contemporary Art, and Utah Museum of Fine Arts. The International Peace Gardens feature flowers and displays representing more than 25 countries. The city is also the home of the Utah Jazz of the National Basketball Association and the Utah Hockey Club of the National Hockey League.
Government.
Salt Lake City has a mayor-council form of government. The voters elect a mayor and seven council members to four-year terms. Property taxes and sales taxes provide most of Salt Lake City’s revenue.
History.
Gosiute (also spelled Goshute), Shoshone, and Ute Indians were living in the Salt Lake Valley when Spanish explorers visited the region in 1776. The American frontiersman Jim Bridger saw the Great Salt Lake in 1824. The American explorer Jedediah Smith traveled the area in the 1820’s. He called it his home in the wilderness. Mormon pioneers established Great Salt Lake City in 1847. By 1850, the city had about 5,000 settlers. It served as an important way station on the Oregon and California trails. Congress created the Utah Territory that year. The Mormon leader Brigham Young was appointed the first territorial governor. Salt Lake City was incorporated in 1851. It officially became the capital of the Utah Territory in 1856.
The discovery of lead and silver in Bingham Canyon in 1863 led to the development of mining in the region. In 1861, telegraph lines met at Salt Lake City, providing the first transcontinental telegraph service. In 1869, at nearby Promontory, workers laid the tracks that completed the nation’s first transcontinental railroad system. The rail service boosted the economy of the Salt Lake City area by opening new markets for its farm and mining products. Utah became a state in 1896, with Salt Lake City as the capital.
Copper, lead, and silver mining boomed in Bingham Canyon during the late 1800’s and early 1900’s. Mining companies built large smelters to refine the rich ores. Salt Lake City prospered and grew rapidly. Between 1900 and 1930, the population increased from 53,531 to 140,267. Demand for metals in World War II (1939-1945) brought new prosperity to Salt Lake City’s mining industry. Industrial expansion continued after the war. The city’s population reached 189,454 by 1960.
The population of Salt Lake City dropped in the 1960’s, chiefly because of a trend toward suburban living. In the 1970’s, commercial development helped revitalize the city’s downtown. During the next 20 years, the city became a center for medical research, technology, and tourism. In the 1990’s, the rebuilding of interstate highways and the completion of a light rail system improved the transportation in the area. In 2002, Salt Lake City hosted the Winter Olympic Games. City Creek Center, a sprawling shopping and entertainment complex, opened in downtown Salt Lake City in 2012.
For the monthly weather in Salt Lake City, see Utah (Climate).
