Soapberry is the name of 13 species of trees or shrubs found in tropical and subtropical areas of Asia and North and South America, and on islands in the Pacific Ocean. These plants bear fruits that are most commonly yellowish-brown with a leathery covering. Each fruit is made up of two or three round lobes. The fruits and leaves contain a soapy substance called saponin. They produce a lather when rubbed in water and can be used as a substitute for soap. Soapberry plants are cultivated from seeds or from cuttings planted in the early spring. They grow well in dry, sandy soil.
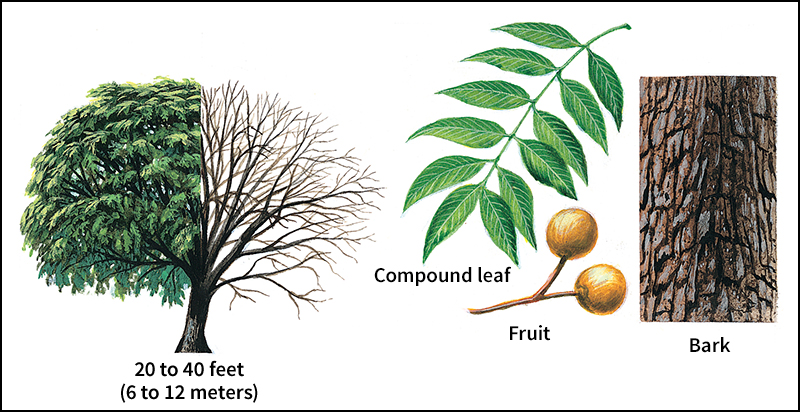
The Chinese soapberry is the most common Asian species. It is found from India to China and Japan. A species that is called soapberry or false dogwood is found in the Americas. It ranges from the southern United States to Argentina. One variety of this species is evergreen. Another variety is deciduous—that is, it loses its leaves every fall. It is found from Mexico to Kansas, Missouri, Louisiana, and northern Florida.

