Tennis is a game in which opposing players—one or two on each side—use rackets to hit a ball back and forth over a net. The game is played on a flat surface called a court. Each player tries to score points by hitting the ball so that the opposing player or players cannot return it over the net and inside the court.

Tennis may be played indoors or outdoors. If two people play, the game is called singles. If four people play, it is called doubles. In most singles and doubles matches, men play men and women play women. In mixed doubles, a man and a woman play on each side.

Millions of people throughout the world play tennis for exercise and recreation. They play on courts in public parks and in private tennis clubs. Players of almost any age can enjoy the sport. The United States Tennis Association (USTA), which governs American tennis, sponsors national tournaments for players as young as 12 and as old as 75.
Professional tennis players travel throughout the world to compete in tournaments that offer millions of dollars in prize money. Many countries enter men’s and women’s teams that compete for international trophies. The most famous trophy is the Davis Cup, which represents the world’s men’s team championship.
Tennis ranks as one of the world’s most popular spectator sports as well as a favorite participant sport. Thousands of fans attend the many tournaments held each year. Millions more watch important matches on TV.
Tennis as it is played today developed in the United Kingdom during the late 1800’s. The game quickly spread to the United States and other countries. By 1900, tennis had become a major international sport.
The court and equipment
The court
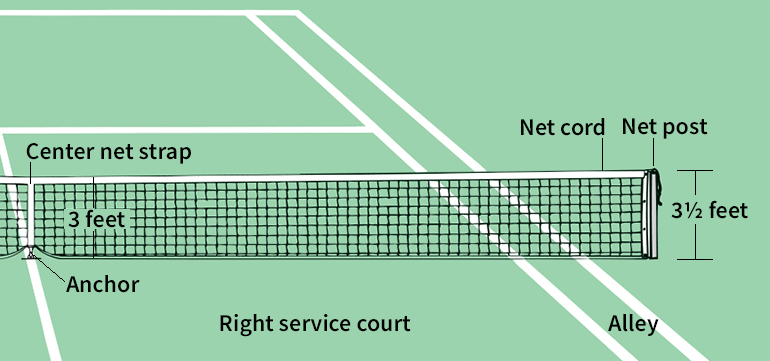
is a rectangle divided into halves by a net stretched across the middle. The net measures 3 feet (91 centimeters) high at the center and 31/2 feet (107 centimeters) high at the side posts that support it. The court is 78 feet (23.7 meters) long. Almost all courts are marked off so that both singles and doubles games can be played on them. The singles court measures 27 feet (8.2 meters) wide. The doubles court is 41/2 feet (1.37 meters) wider on each side. Various lines divide the singles and doubles court into sections. 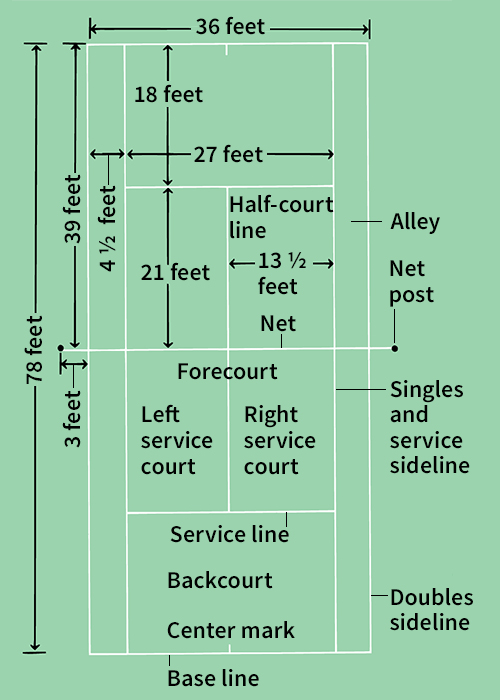
For many years, major tennis tournaments were played on grass courts. In fact, the early name for the sport was lawn tennis.. Grass courts are the most comfortable for players, but require daily maintenance and a rest period after heavy play. Therefore, they are limited to private clubs and residences that can afford the expense.
The most popular court surfaces for outdoor courts are hard courts. These courts can have an asphalt or concrete base and an acrylic color surface or a cushioned surface. Clay courts are more comfortable for playing than hard courts but require daily maintenance. Indoor tennis can be played on either hard surfaces or clay courts.
Tennis balls
are hollow. They are made of rubber and covered with a felt fabric woven of Dacron, nylon, and wool. A tennis ball must have a diameter of more than 21/2 inches (6.35 centimeters) but less than 25/8 inches (6.67 centimeters). It must weigh more than 2 ounces (56.7 grams) but less than 21/16 ounces (58.6 grams). Balls used in tournaments may be either white or yellow. Manufacturers also make balls in other colors.
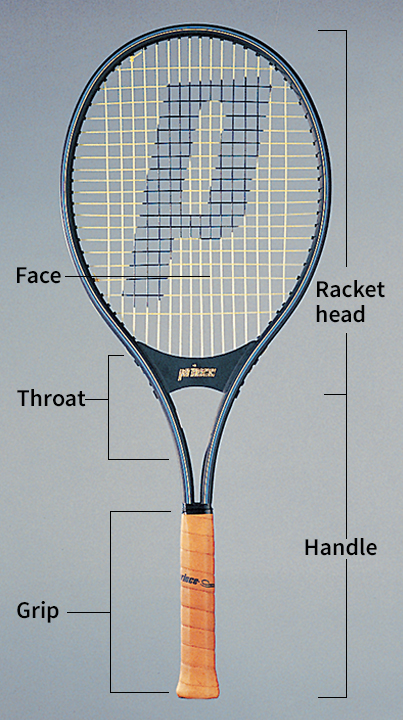
Tennis rackets.
Rules allow the use of tennis rackets that are up to 29 inches (74 centimeters) long and up to 12 1/2 inches (32 centimeters) wide. No rules govern racket weight. Most men and women players use a racket that weighs 10 to 11 ounces (283 to 312 grams). In general, young players use a racket that weighs about 9 ounces (255 grams). A typical racket frame is made of fiberglass and graphite. The most common striking surface is a web of tightly strung strings made of nylon or other synthetic material.

Tennis clothes
should fit comfortably so that a player can move freely. During the late 1800’s and early 1900’s, men players wore long-sleeved shirts and trousers, and women wore ankle-length dresses. Such bulky clothing limited a player’s movements. Today, men wear short-sleeved shirts and shorts. Women wear minidresses or blouses and short skirts.
Shoes are perhaps the most important item in a player’s wardrobe. Tennis shoes are designed specially for the sport. They are made of cloth and have rubber soles and no heels. The shoes help keep players from slipping and do not damage the court.
How tennis is played
Before they begin to play tennis, the players must decide who serves first and which end of the court each player or team will defend. Most players make these decisions by means of a racket “toss.” For example, they may use the manufacturer’s markings on one side of a racket handle as “heads” and on the other side as “tails.” One player stands the racket upright on the frame and spins it. The opposing player or team calls which side will land face up. If the call is correct, the player or team may either (1) choose to serve or receive first or (2) decide which end of the court to defend.
The court diagram in this article locates the various lines and playing areas discussed in this section.
Scoring.
Tennis is scored in terms of points, games, and sets. A player or doubles team scores a point when the opposing side fails to return the ball properly or commits an error. To win a game, one side must score four points and lead by at least two points. The first point is called 15; the second, 30; the third, 40; and the fourth, game point. A score of zero is called love. Historians are not certain how this scoring system began.

The server’s score is always given first. For example, if the serving side leads three points to one, the score is 40-15. If the receiving side wins the first two points, the score is love-30. If both sides win three points, the score is 40-40, which is called deuce. To win a deuce game, one side must lead by two points. The first point scored after deuce is called the advantage or ad. If the server wins the first point after deuce, the point is often announced as ad in. If the receiving side wins the point, it may be announced as ad out. If the side with the advantage loses the next point, the game returns to deuce.
To win a set, one side must win six games and lead by at least two games. If the score is tied at 5-5, play continues until one side has a two-game margin. In some tournaments, if the score reaches 6-6, a tie breaker is played. The first player or team to win at least seven points and lead by two points wins the set by a score of 7-6.
In most competitions, the first side to win two sets wins the tennis match. In some tournaments, the first side to win three sets takes the match.
The serve,
or service, puts the ball into play at the start of each game and after each point is scored. The server must toss the ball into the air and hit it before it strikes the ground. The ball must then travel into the service court diagonally opposite. The server begins each game by serving from the right side of the court. The serve then alternates between the left and right sides following each point. The server must serve from behind the base line and within the imaginary continuation of the center mark and the singles sideline.

In a singles match, a player serves until a game is completed. Then the receiver becomes the server. The players continue to alternate serves after each game. In a doubles match, the serve also changes sides after each game. But in addition, the members of each team alternate serves. If a team serves odd-numbered games, for example, one member would serve the first game, the other the third game, and so on. In both singles and doubles matches, the opposing players change ends of the court after the first, third, and all following odd-numbered games.
If a serve lands in the net or outside the receiver’s service court, the server has committed a fault. A server commits a foot fault by stepping on or over the base line or changing position by running or walking before hitting the ball. A player who commits a fault or foot fault gets a second serve. But if this serve fails through a fault or foot fault, the player has committed a double fault and loses the point. If the ball hits the top of the net and drops into the proper service court, the serve is called a let and is replayed. A let is also called if a player serves before the receiver is ready.
A powerful, accurate serve can help a player win easy points. A player can serve an ace, which is a legal serve that the receiver is unable to touch. Even if the receiver manages to return a serve, the return may be so weak the server can easily hit a winning shot.
Receivers may stand anywhere on their end of the court during the service. A receiver often takes a position based on knowledge of an opponent’s serve. If the server has a very fast serve, for example, the receiver will stand far back to allow enough time to sight the ball for the return shot.
The ball in play.
After the serve, the receiver must hit the ball on the first bounce and return it over the net. The ball must land in the area bounded by the base line and the singles sidelines or, in team play, the doubles sidelines. A shot that lands on a sideline or base line is in play. A shot that hits the net and drops into the opposing court is also in play. After the ball has been served and returned, it may be hit either on the fly, which is called a volley, or after the first bounce, which is called a ground stroke. The players continue to rally (hit the ball back and forth) until one side scores a point. During play, a player or team wins a point if the opposing side (1) hits the ball into the net, (2) hits the ball outside the court, (3) allows a ball to bounce twice, or (4) touches the ball.
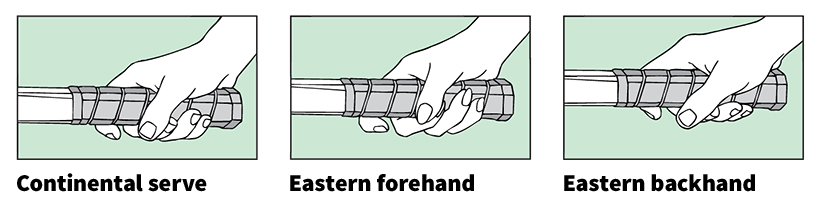
Players may use a variety of ground strokes and volleys. The basic shots are the forehand and the backhand. Right-handed players hit a forehand on the right, or racket, side of the body. They hit a backhand by reaching across the body to the left side. Left-handed players hit a forehand on the left side and a backhand on the right.
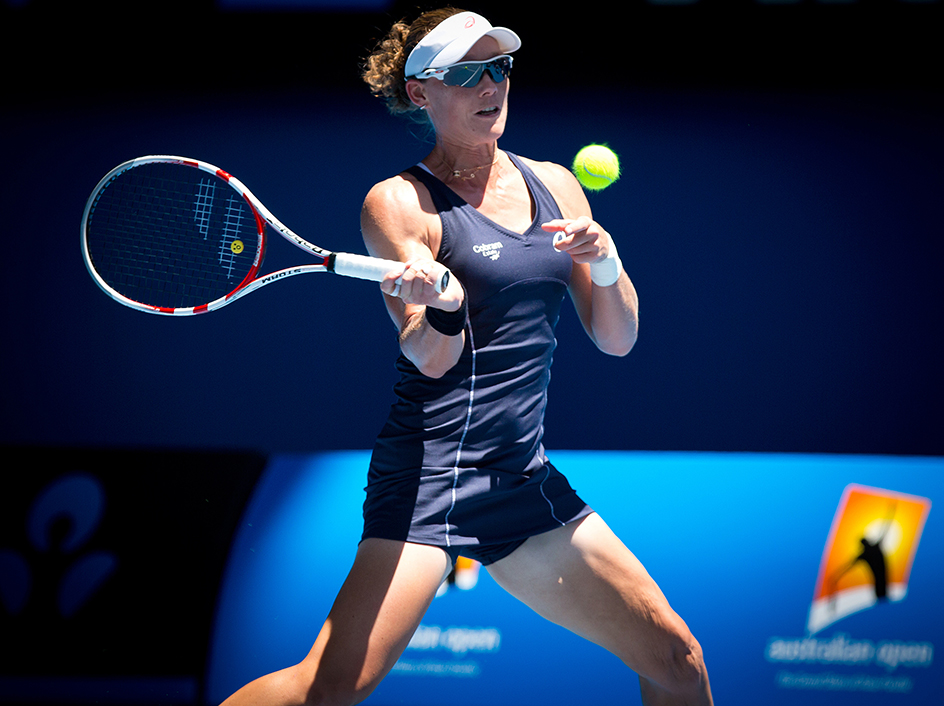

To force an opponent away from the net, a player may hit a lob—a high shot deep into the opponent’s court. The opponent must retreat from the net to reach the ball. If the lob is not hit deep enough, however, the opponent may reply with an overhead smash. This shot is made by hitting the ball from above the head. A smash often is so powerful that it cannot be returned.
By hitting the ball in a certain way, a player can give a shot topspin or underspin. Spin causes the ball to react in such a way that it is difficult to return. A lob hit with topspin accelerates. A shot hit with underspin decelerates.

Officials.
In most tennis matches, the players themselves act as officials and keep their own score. But in most tournaments, many officials may be used. The chief official is the tournament referee, who has charge of the entire tournament. On the court, the top official is the chair umpire. The chair umpire sits on a high chair alongside center court and announces the score to the crowd. The chair umpire also supervises as many as 13 linespersons. These officials are positioned along the lines around the court. They determine whether a ball has been served legally and whether shots are good (inside the court) or out (outside the court).
Organized tennis
Amateur tennis.
Most of the world’s tennis players are amateurs. They play for enjoyment and exercise and receive no pay. Many of them play in small organized interclub competitions, chiefly on weekends. High schools and colleges also sponsor tennis teams as part of their athletics programs.
The International Tennis Federation (ITF) governs tennis throughout the world. The ITF consists of the national tennis associations of about 100 countries. These associations include the U.S. Tennis Association, the Canadian Lawn Tennis Association, the Lawn Tennis Association of Australia, and the United Kingdom’s Lawn Tennis Association.
Professional tennis.
For many years, nearly all the world’s leading tournament players were amateurs. Professional tennis first became widely accepted in the late 1960’s, and today all the top players are professionals. Professionals play tennis for money, or they are paid for coaching or teaching the game.

Both men and women professionals have formed organizations to represent them and supervise their tournaments. Men professionals established the Association of Tennis Professionals in 1972. The same year, women professionals formed the Women’s Tennis Association.
Tennis tournaments.
Only amateurs could play in major tournaments before 1968. That year, the member countries of the ITF voted to allow amateurs and professionals to compete in the same tournaments. These events became known as open tournaments. Today, almost all major tournaments are open.
The most important tournaments for individual players are the national championships of Australia, France, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The United Kingdom’s championship is commonly known as Wimbledon. Together, the four championships make up the grand slam. Only two men have won all four in the same year. Don Budge of the United States won the grand slam in 1938. Rod Laver of Australia is the only player to win it twice, in 1962 and 1969. Three women have won the grand slam—Maureen Connolly of the United States in 1953, Margaret Smith Court of Australia in 1970, and Steffi Graf of West Germany in 1988.
Three organizations are in charge of tournaments for professional players. The ITF supervises the major international events, including the grand slam tournaments. The ITF also organizes international junior tournaments in which young players compete for international rankings. The Association of Tennis Professionals (ATP) organizes the men’s professional tennis tour. The Women’s Tennis Association (WTA) supervises the women’s professional tour. Both the ATP and WTA set schedules for the tours and award dates to the sponsors.
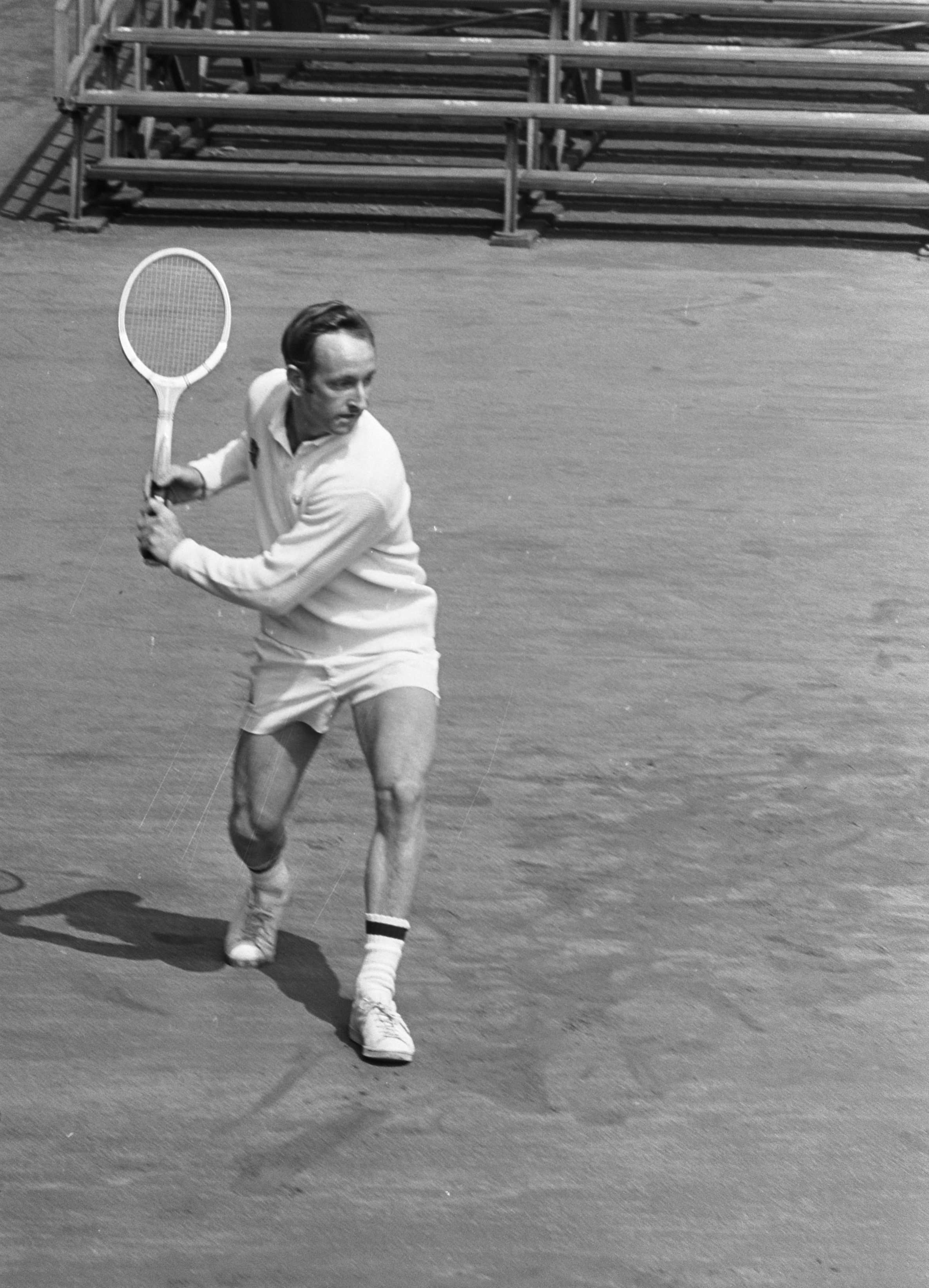

Most amateur and professional tournaments use a system called seeding to prevent the top players from meeting each other in an early round. The best player would be seeded number one; the next best, number two; and so on. Players are seeded according to their records and reputations. One player is normally seeded for every four in the tournament. The matches are arranged so that seeded players do not face each other until the quarterfinal round, unless unseeded players defeat them.
Several tournaments are held for international team trophies. The best-known trophy is the Davis Cup, donated in 1900 by Dwight Davis, an American player. Competition for the cup takes place every year for teams of male players from 16 qualifying nations. The 16 teams first compete in a group stage. The top 8 teams from the group stage meet in the Finals, a single-elimination tournament. The ITF supervises the Davis Cup. For the annual results of the final round of cup competition, see Davis Cup.
In 1963, the ITF established the Federation Cup (now called the Billie Jean King Cup) for teams of women representing member nations. Each year, 12 qualifying nations compete in the Finals.
History
Beginnings.
Most historians agree that the French originated tennis during the 1100’s or 1200’s. The French called it jeu de paume, meaning game of the palm. The players batted the ball back and forth over a net with the palm of their hand.
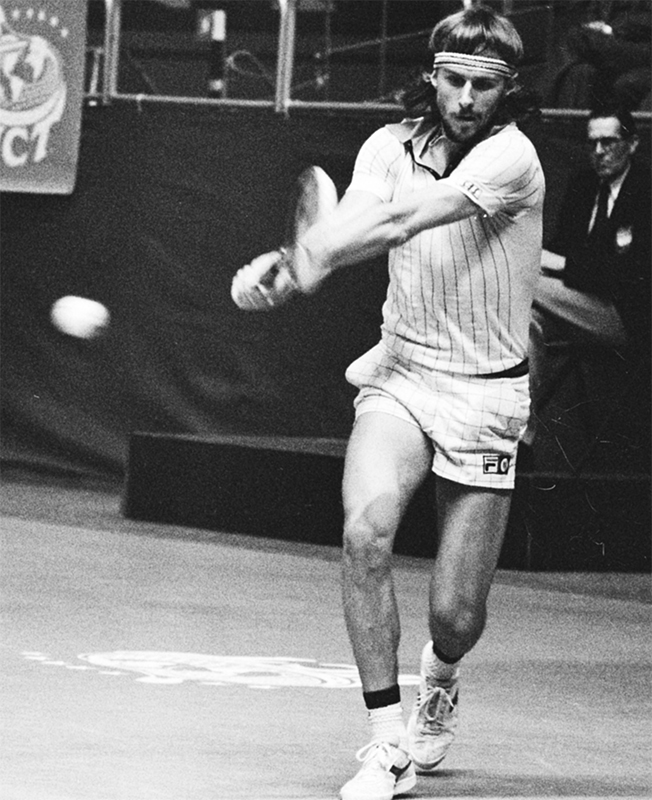

Major Walter Clopton Wingfield of England is generally considered the father of modern tennis. In 1873, he introduced a version of the game closely resembling the modern sport. In 1874, he patented tennis equipment and rules for playing on grass courts. Wingfield called the game sphairistike, the Greek word for playing ball. But the name was soon replaced by lawn tennis. Some historians feel that Major Harry Gem of England should share credit as the sport’s founder. Gem played a form of tennis in the 1860’s.
Tennis soon replaced croquet as England’s most popular outdoor sport. In 1877, the All England Croquet Club changed its name to the All England Lawn Tennis and Croquet Club. Also in 1877, the club sponsored the first major tennis tournament at its headquarters in Wimbledon, a suburb of London. This tournament has become the unofficial world championship for men’s and women’s singles and doubles.
The spread of tennis.
Mary Ewing Outerbridge, an American sportswoman, introduced tennis into the United States. In 1874, she purchased tennis equipment from British army officers in Bermuda. Outerbridge used the equipment to set up the first U.S. tennis court. The court was on the grounds of the Staten Island Cricket and Baseball Club in New York City.
The United States National Lawn Tennis Association (now the United States Tennis Association) was established in 1881. That same year, the association sponsored the first U.S. men’s championship tournament in Newport, R.I.
In 1900, the American player Dwight Davis donated the Davis Cup to be awarded annually to the country that wins the world’s men’s championship. The trophy became recognized as the top prize in team tennis.

Many of the greatest stars in tennis history played during the 1920’s. But the period was dominated by Bill Tilden, an American. Tilden won the United States singles title every year from 1920 through 1925 and again in 1929. He also won the Wimbledon championship three times.
The top women players in the 1920’s were Suzanne Lenglen of France and Helen Wills (later Helen Wills Moody) of the United States. Lenglen won six Wimbledon and six French championships. Moody won eight Wimbledon and seven U.S. championships.
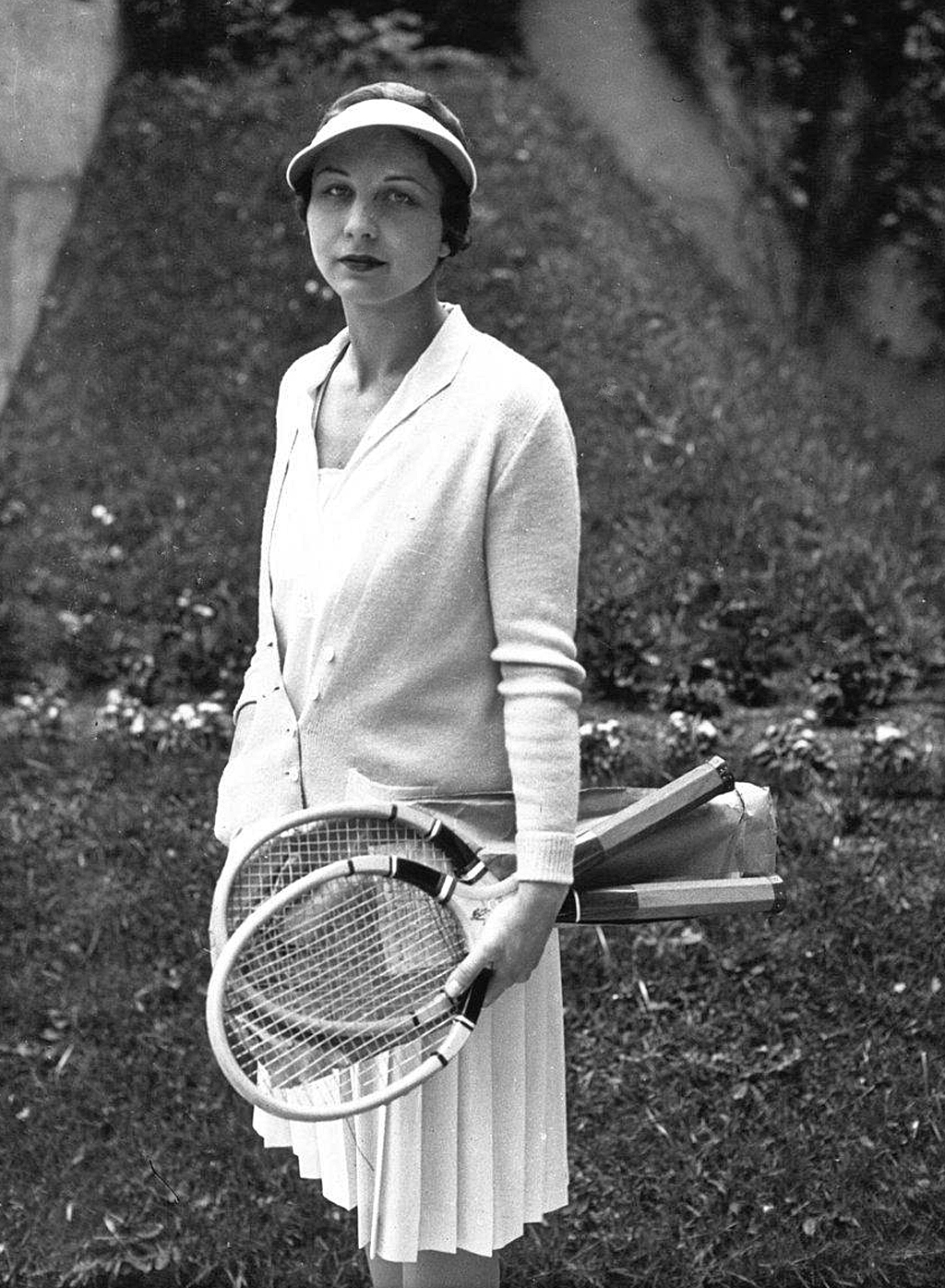

Perhaps the outstanding individual player of the 1930’s was Don Budge of the United States. In 1938, Budge became the first player to win the grand slam.
The mid-1900’s.
Until the 1950’s, France, the United Kingdom, and the United States produced almost all of the world’s major players. Then Australia became the leader in men’s competition. From 1950 through 1967, Australian teams won the Davis Cup 15 times. Such players as Roy Emerson, Lew Hoad, Rod Laver, John Newcombe, Ken Rosewall, Frank Sedgman, and Fred Stolle helped Australia maintain its top international position.
During the 1940’s and 1950’s, several American players achieved worldwide success. The most notable included Pancho Gonzalez, Jack Kramer, Art Larsen, Frank Parker, Ted Schroeder, Vic Seixas, and Tony Trabert.
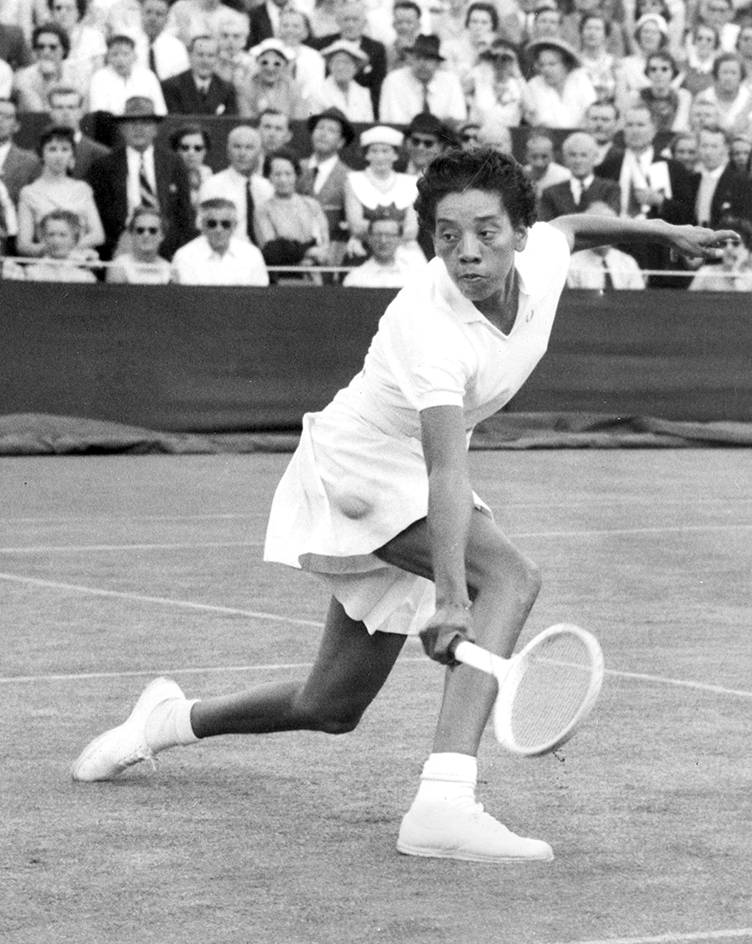

The United States provided most of the top women stars from the mid-1940’s through the mid-1960’s. These outstanding players included Louise Brough, Maureen Connolly, Margaret Osborne duPont, and Doris Hart. Connolly was probably the greatest woman player of this period. In 1953, she became the first woman to win the grand slam.
Althea Gibson of the United States became the first important Black tennis player. She won the U.S. and Wimbledon titles in 1957 and 1958. In the late 1960’s, Arthur Ashe of the United States became the first Black male tennis star. In 1968, he won the U.S. singles championship.
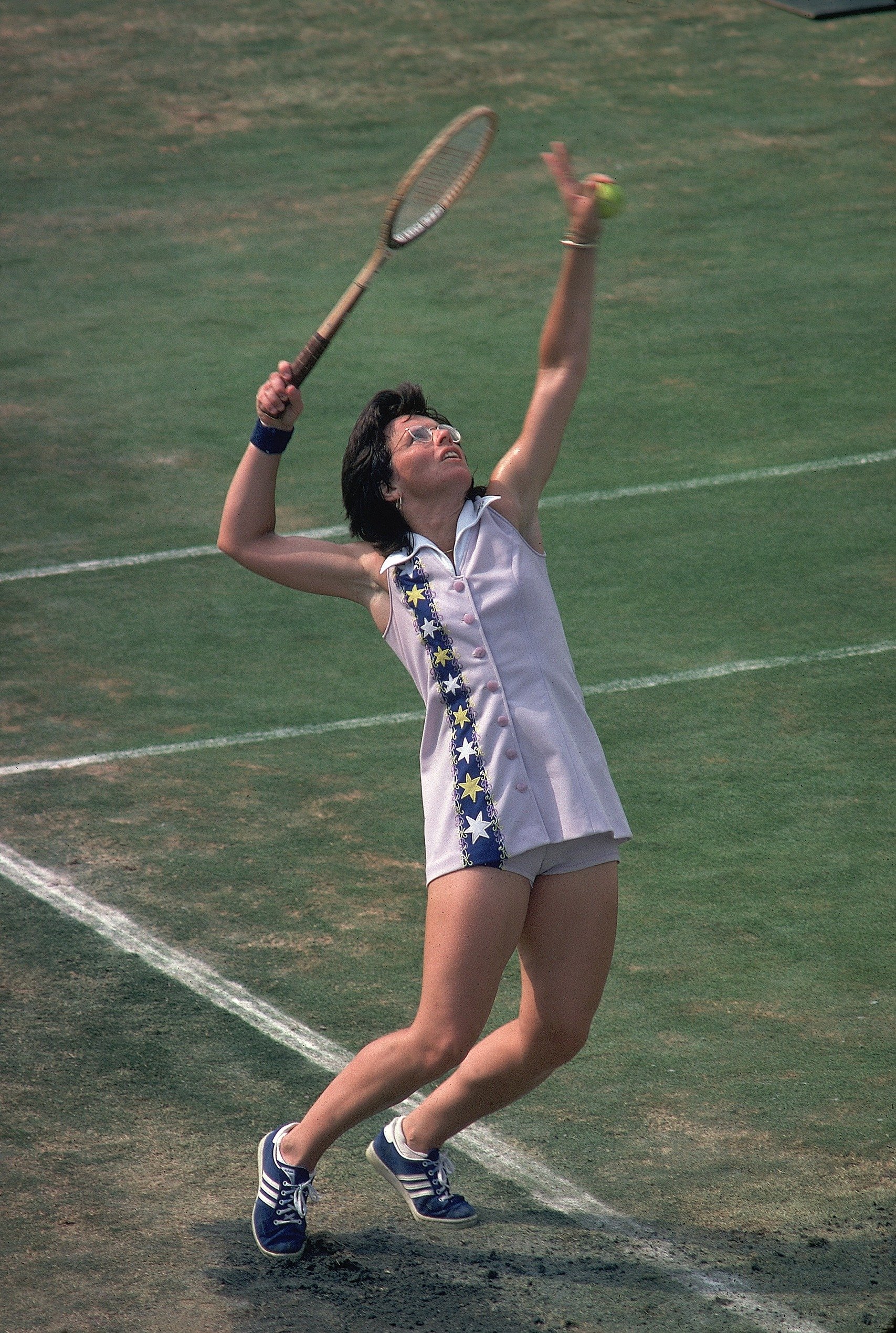

Laver ranked as the top male star of the 1960’s. The Australian became the only player to win the grand slam twice, in 1962 as an amateur and in 1969 as a professional. Other leading male players of the 1960’s included Manuel Santana of Spain and Stan Smith of the United States. In the 1960’s, Margaret Smith (later Margaret Smith Court) became the first Australian woman to win the U.S. and Wimbledon singles titles. She won the grand slam in 1970. Maria Bueno of Brazil and Billie Jean King of the United States also ranked as important players of the period.
The rise of international tennis.
International tennis has largely been a professional sport since 1968. Professionals compete for millions of dollars in prize money annually. Television played an important role in increasing the popularity of tennis during the 1970’s and 1980’s. Major tournaments are televised to many countries.
Several highly publicized matches were arranged largely for television audiences. In 1973, Bobby Riggs, a top-ranked American player of the late 1930’s and 1940’s, defeated Margaret Smith Court in a televised “battle of the sexes.” Later that year, Riggs played Billie Jean King in the Houston Astrodome before 30,472 spectators, the largest crowd ever to watch a tennis match. Millions more people watched on television as King defeated Riggs.
The Davis Cup became a center of political dispute in the 1970’s. In 1974, South Africa won the cup by forfeit from India. The Indian government refused to allow its team to play because of South Africa’s apartheid (racial separation) policies. The Davis Cup had already lost some of its importance because many professionals refused to play for their countries. These players claimed that the many weeks of cup play-offs would force them to miss too many tournaments. In 1981, Davis Cup competition was compressed into a shorter period of time and the prize money was increased.
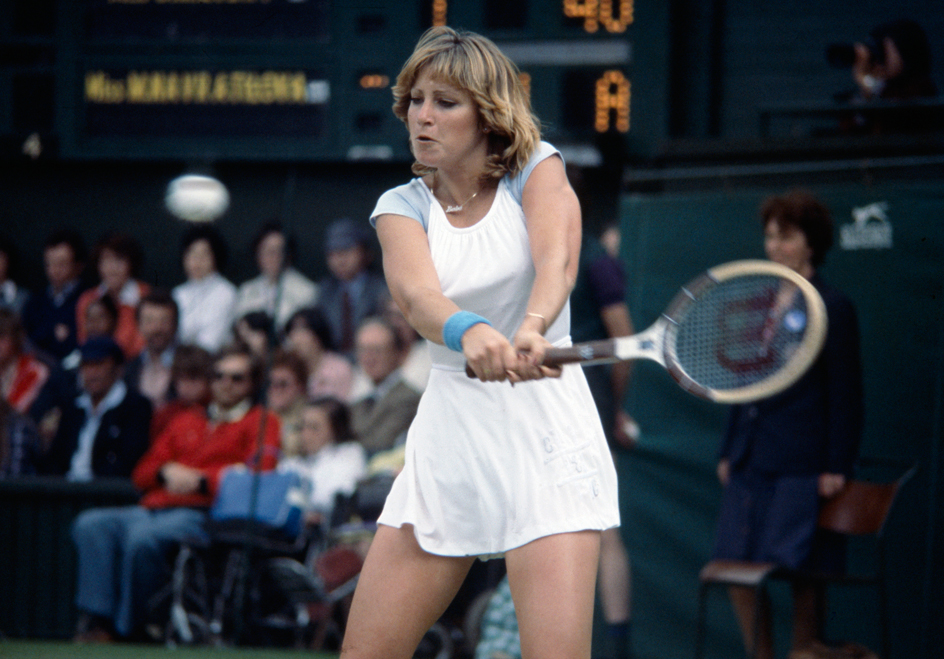

By the mid-1970’s, a new generation of players had begun to dominate tennis. The most successful men players of the 1970’s and early 1980’s included Jimmy Connors, Arthur Ashe, and John McEnroe of the United States; Bjorn Borg of Sweden; Guillermo Vilas of Argentina; and John Newcombe of Australia. Leading women players included Tracy Austin, Chris Evert, Andrea Jaeger, and Martina Navratilova of the United States; and Evonne Goolagong of Australia.

From the 1990’s to today.
In 1990, Navratilova won the women’s singles championship at Wimbledon for the ninth time. No woman had ever won a singles title at Wimbledon more than eight times in the history of modern tennis. In 1992, Navratilova set a career record by winning her 158th singles championship.

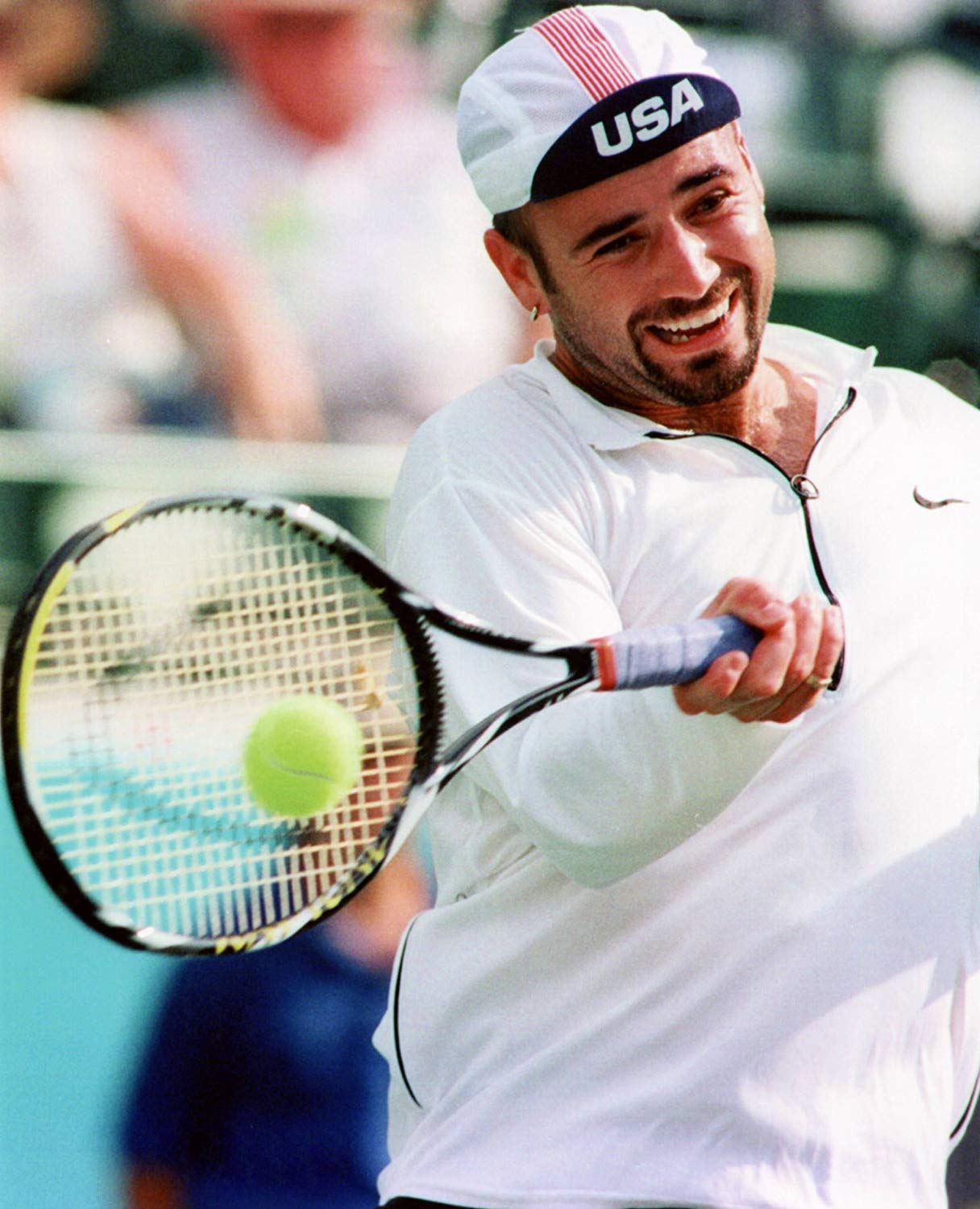
By the mid-1990’s, a new group of young players began to dominate the sport. The leading men players included Marcelo Rios of Chile; Boris Becker of Germany; Thomas Muster of Austria; and Andre Agassi, Michael Chang, Jim Courier, and Pete Sampras of the United States. Top women players included Conchita Martinez and Arantxa Sanchez Vicario of Spain; Steffi Graf of Germany; and Lindsay Davenport and Monica Seles of the United States.
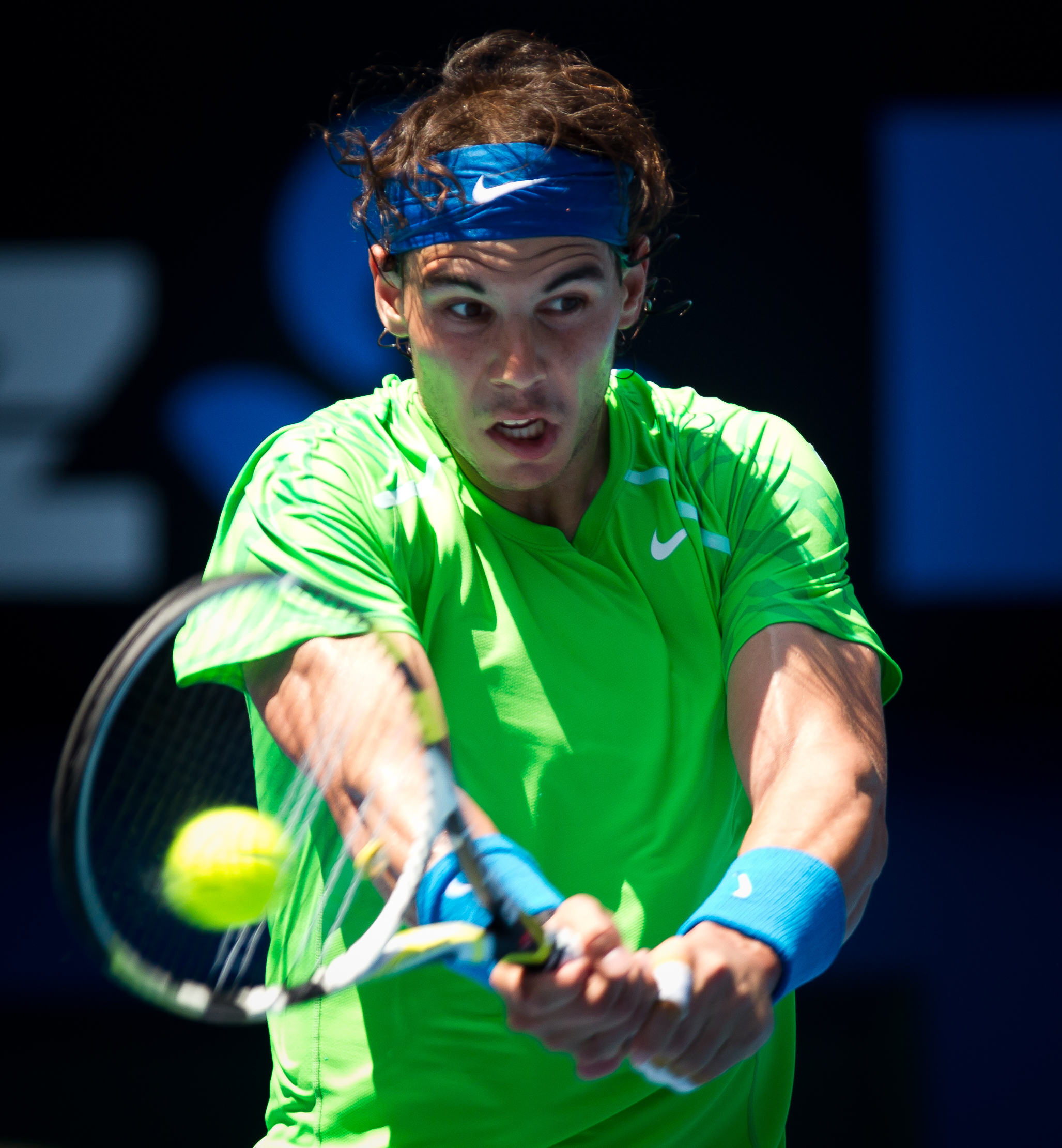
During the early 2000’s, the sisters Serena and Venus Williams of the United States dominated women’s tennis. Men stars of the early 2000’s included Novak Djokovic of Serbia, Roger Federer of Switzerland, Andy Murray of the United Kingdom, and Rafael Nadal of Spain.
