Testicle is either of a pair of small oval glands in the male reproductive system. The testicles, also called testes (singular, testis), hang behind the penis in a sack called the scrotum. They have two main functions. (1) They produce sperm, and (2) they secrete male sex hormones, particularly testosterone.
In an adult man, each testicle measures about 11/2 inches (4 centimeters) long and about 11/4 inches (3 centimeters) wide, and each weighs about 2/3 ounce (20 grams). The testicle is covered by a dense fibrous material. This material enters the rear of the gland and separates into sheets that divide the testicle into about 250 sections. Each section contains one to four twisting tubes called seminiferous tubules, in which sperm are produced. All of the tubules combine to form 12 to 15 larger tubes called efferent ducts, which transport the sperm to the epididymis, a highly coiled tube at the rear of each testicle. In the epididymis, the sperm develop further before being released from the body during sexual arousal.
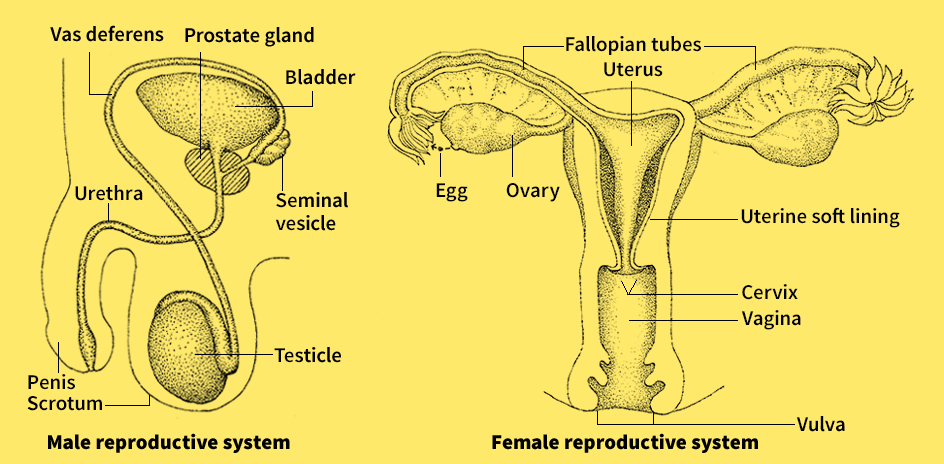
Testosterone is produced in the tissue between the seminiferous tubules by specialized cells called Leydig cells. Testosterone controls the development during puberty of such male characteristics as a beard, enlarged muscle mass, a deep voice, and increased size of the sex organs. This hormone also stimulates male sexual behavior.
