Trap-door spider is a spider that digs a burrow in the ground and covers the entrance with a lid, or trap door. It lives in warm climates, including the southern and western United States. It is harmless to human beings. Some trap-door spiders grow over 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) long.
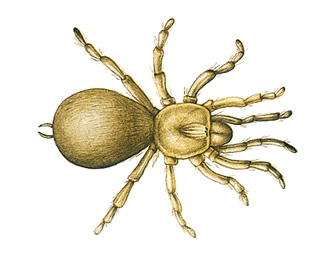
Trap-door spiders use their burrows for protection and as nests in which to raise young. The burrows are lined with silk. Some burrows are more than 10 inches (25 centimeters) deep and over 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) wide. Some trap-door spiders dig simple, tubelike burrows. Others dig burrows that have a branch tunnel. The branch tunnel, sometimes hidden by a second trap door, serves as an extra hiding place.
The trap doors are made of silk and mud, and are attached to the lining of the burrows by silk hinges. Some trap-door spiders build thin, waferlike doors that cover the burrow entrance loosely. Others construct thick doors, like corks, that fit so snugly into the tunnel entrance they are watertight. Still others build circular folding doors that open in the middle.
Trap-door spiders eat insects, including many kinds that damage valuable plants. The spider waits behind its door until its prey walks by. Then it quickly opens the door, seizes and poisons its victim, and drags it into the burrow. Trap-door spiders are timid, and the females seldom leave their nests.

