Aegean << ih JEE uhn >> Sea is a gulf or arm of the Mediterranean Sea. It lies between Greece on the west and north, Turkey on the east, and the island of Crete to the south. The Aegean covers about 69,000 square miles (179,000 square kilometers). It is about 400 miles (640 kilometers) long and more than 200 miles (320 kilometers) wide at its widest point. The Dardanelles, a strait on the northeast shore, links the Aegean to the Sea of Marmara.
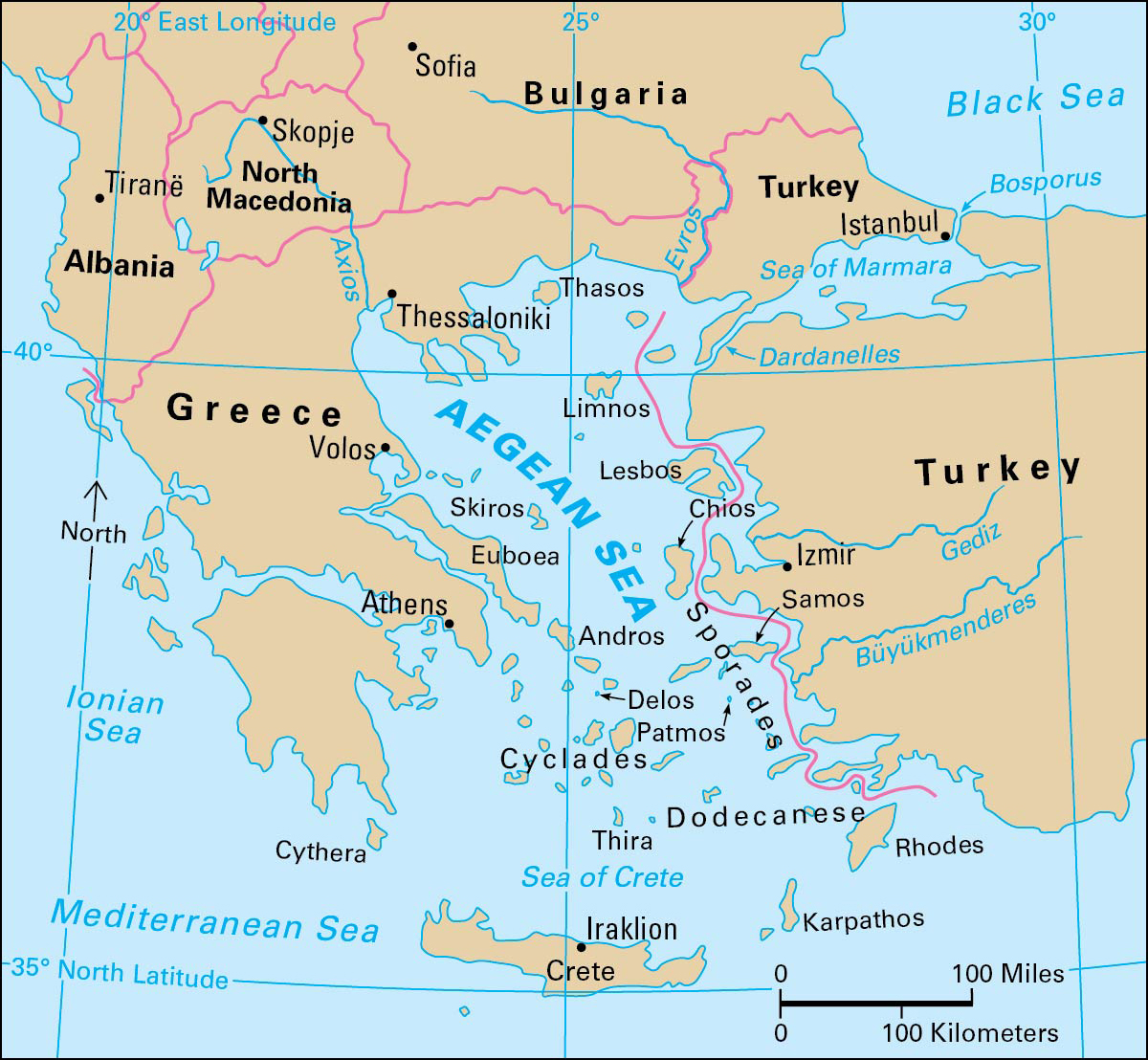
Around a thousand islands, known as the Grecian Archipelago, lie throughout the clear blue waters of the Aegean Sea. Some have fertile plains, while others are rocky and barren volcanic islands. Some islands have large deposits of pure white marble or black obsidian. Wheat, wine, olive oil, and figs are all produced on the Aegean islands. Fishing and tourism are the two biggest industries.
The Aegean islands and shores are famous in Greek history and legend, having given birth to the Minoan and Mycenean civilizations. Three major island groups—the Cyclades, the Dodecanese, and the Sporades—contain such historically important islands as Delos, Samos, and Rhodes.
See also Aegean civilization; Dardanelles; Lesbos; Rhodes.
