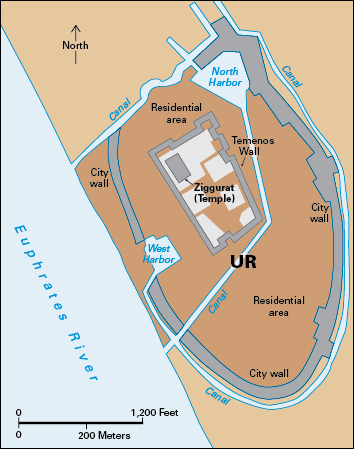
Ur, << ehr or oor, >> a city in the ancient region of Sumer (now southeastern Iraq), was one of the world’s first cities. It stood on the Euphrates River near the Persian Gulf and thrived as a commercial port as early as 3500 B.C. By about 2800 B.C, Ur had become a strong city-state, an independent unit consisting of the city and its surrounding villages and farmland. It had a major temple to the Sumerian moon god Nanna.
From 2400 to 2100 B.C., rival states and empires outshone Ur in political importance. About 2100 B.C., King Ur-Nammu founded Ur’s third major dynasty (family of rulers). Under this dynasty, Ur controlled a large, well-regulated empire that extended from Assyria in the north to Elam in the east. This dynasty ended about 2000 B.C. Ur, though no longer the center of political power, remained a commercial and cultural center. Ur was abandoned by about 500 B.C.
See also Woolley, Sir Leonard.
