White blood cell, also called a leukocyte << LOO kuh syt, >> is a type of cell of the immune system. The immune system defends the body against illness. White blood cell is sometimes abbreviated WBC. All vertebrates (animals with backbones), including humans, have these cells in their bodies. White blood cells are one of three types of cells found in blood. The other types are red blood cells and platelets. White blood cells are also found in the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is a network of small vessels that return fluid to the bloodstream from body tissues. In the lymphatic system, white blood cells are found in bean-shaped masses called lymph nodes.
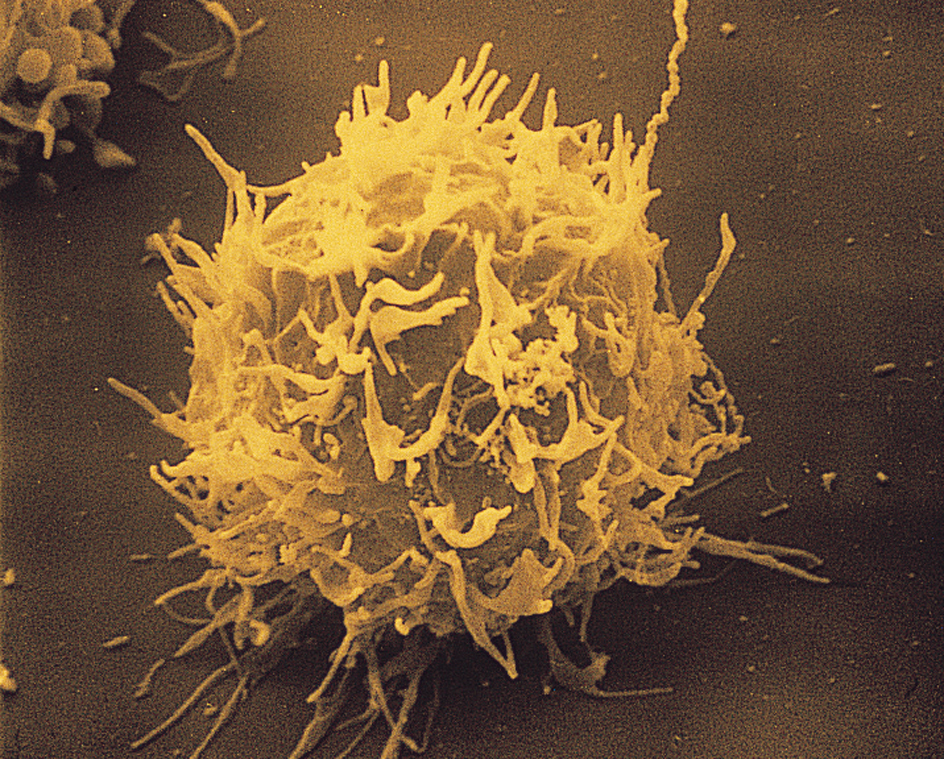
Scientists classify white blood cells into many different types. These types include B cells, T cells, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, neutrophils, basophils, mast cells, and eosinophils. All the different subtypes contribute in various ways to the work of the immune system. All of them are originally generated from a single type of cell in the bone marrow. Each cell becomes a particular subtype depending on certain signals received during the cell’s growth and development. Once a white blood cell has developed into a particular type, it cannot change into another type.
White blood cells fight pathogens (disease-causing microorganisms) and harmful substances that invade the body. They circulate throughout the body in the blood and the lymphatic system. White blood cells can also leave the blood and the lymphatic system, entering other tissues at the site of an injury or infection. Some leukocytes eventually establish themselves in tissues. For example, mast cells are usually only found within tissues, including those of the heart, lungs, and skin. 
White blood cells work together within the immune system. They can recruit other white blood cells to the site of a pathogen and remove the pathogen from the body. Some of them release proteins called cytokines. These proteins perform a variety of functions, such as helping other white blood cells to find a pathogen, or damaging pathogens themselves. Some white blood cells produce antibodies. These proteins bind to pathogens, targeting them for removal and destruction. Some white blood cells engulf pathogens and destroy them.
See also Blood; Immune system.
