Xenon, << ZEE non or ZEHN on, >> is a chemical element that makes up about 1 part in 20 million of Earth’s atmosphere. The British chemists Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers discovered xenon in 1898 (see Ramsay, Sir William ). Industry uses xenon in filling flash lamps and other powerful lamps. Xenon is also used to make bubble chambers, which are instruments used by physicists to study nuclear particles.
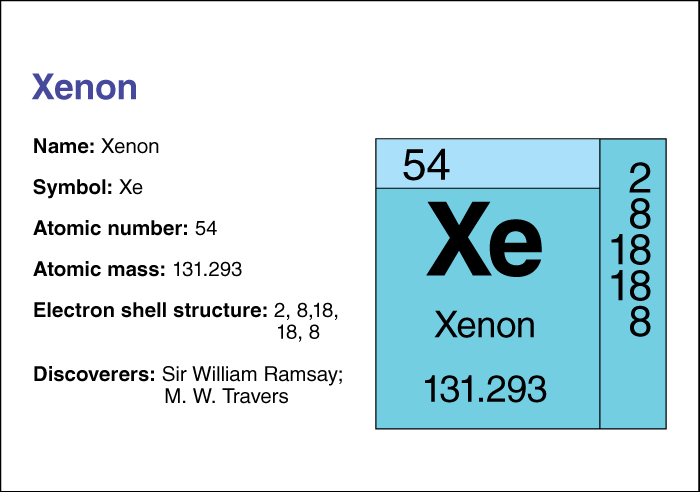
Xenon is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas. It is obtained from liquid air. It does not react readily with other substances. The chemical symbol for xenon is Xe. Xenon has an atomic number (number of protons in its nucleus) of 54. Its relative atomic mass is 131.293. An element’s relative atomic mass equals its mass (amount of matter) divided by 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon 12, the most abundant form of carbon. Xenon may be condensed to a liquid that boils at –107.1 °C and freezes at –111.9 °C. It forms compounds with two chemical elements, fluorine and oxygen. Chemists classify xenon as a noble gas . For information on the position of xenon on the periodic table, see the article Periodic table .
