Himachal Pradesh (pop. 6,864,602) is a wholly mountainous state in the Himalaya in the far north of India. Its name means Province in the lap of snow. The territory was formed in 1948 by bringing together 30 small princely states. The neighboring state of Bilaspur merged with the Himachal Pradesh territory in 1954. In 1971, Himachal Pradesh became a state. Himachal Pradesh is a popular trekking region and has a flourishing orchard.
People and government.
The population comprises a mixture of hill peoples, including the Gaddis, Gujars, and Lahaulis. About 95 percent of the population is Hindu. Pahari, a Hindi dialect, is the local language. Hindi is widely spoken and is used for instruction in schools. The state is the least urbanized in India, with about 10 percent of the population living in towns. Only the state capital, Shimla (also spelled Simla), has more than 100,000 inhabitants.
The governor, who is appointed by the president, is head of state. The chief minister and council of ministers are elected from the state’s legislature, which has 68 members. Himachal Pradesh has four elected members in the Lok Sabha (lower house) and three nominated representatives in the Rajya Sabha (upper house) in the Indian national Parliament.
Economy.
The economy depends almost entirely on agriculture. Farmers grow crops on terraces wherever possible, and at higher altitudes they also raise livestock.
Barley, corn, potatoes, rice, and wheat are the main food crops. Apples are an important cash crop. Other fruit include peaches, plums, and pomegranates. Ginger and mushrooms are also grown. Sheep and goat rearing is common. The high quality goat’s wool produced in the region is known as pashmina or cashmere wool.Cashmere
Forests cover one-third of the state. Timber, fuel wood, gum, and resin are important sources of revenue from the forests. Mines in the state produce small amounts of baryte, dolomite, gypsum, limestone, pyrite, salt, and slate. Himachal Pradesh has little industry. There are resin and turpentine factories, and an iron foundry. Fertilizer production is of growing importance. There are cement plants and an electronics complex near Shimla. Village industries include bamboo crafts, leather tanning, pottery, woodcarving, and wool spinning.
Shimla has an airport at Jabbarhatti. There are also airports at Bhuntar and Gagal. Narrow gauge railroads link Himachel Pradesh with Haryana and Punjab. There is a broad gauge railroad from Nangal in Punjab to Una. The main means of transport are by motor vehicle and on foot. After the 1962 border war between China and India, the Indian government built roads up to the border. Shimla, Kulu, and Manali are popular tourist destinations.
Land and climate.
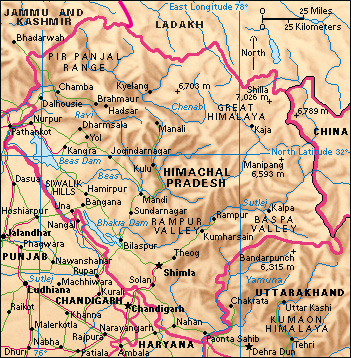
Himachal Pradesh is bordered by Jammu and Kashmir and by Ladakh in the north, Punjab in the west, Haryana and Uttarakhand in the south, and the Tibet region of China in the east.
The mountainous landscape of the state contains peaks of more than 21,980 feet (6,700 meters). The two main ranges are the Dhaula Dhar range and the more northerly Pir Panjal, which run parallel to one another. Further north are the sparsely populated regions of Lahul and Spiti. The higher mountains are permanently under snow.
The average daily minimum temperature is 36 °F (2 °C) in January and 61 °F (16 °C) in June. The maximum is 48 °F (9 °C) in January and 75 °F (24 °C) in June. Shimla receives 59 inches (150 centimeters) of rain a year, of which nearly 80 percent falls between June and September. The monsoon arrives in the middle of June and lasts until the middle of September. Snow is common in winter.
The major rivers are the Chenab, the Ravi, and the Beas in the west, and the Sutlej and the Yamuna in the east. The Bhakra Dam across the Sutlej created the largest lake in the state in 1971.
History.
The early inhabitants of Himachal Pradesh were nomadic tribes, including the Dahsas, Kinners, Kirates, and Kharasas. The Maurya, Kushana, and Gupta rulers, in turn, forced the region to accept their rule. After the decline of the Gupta Empire, 31 independent kingdoms reemerged. The state of Chamba was the most important. They eventually became tributaries of the Mughal Empire under Akbar. During the 1600’s and 1700’s, Basohli, Kangra, and Guler developed as major centers of painting. Afghans, Sikhs, and Gurkhas invaded Himachal Pradesh after the fall of the Mughal Empire. Maharajah Ranjit Singh brought the area under his control in the 1800’s. The British took over the princely states following the Anglo-Nepalese War of 1814-1816.
The British founded Shimla in 1819 as their summer headquarters. After India became independent in 1947, Shimla served as the temporary capital of East Punjab. Since 1971, it has been the state capital of Himachal Pradesh. Dharamsala has been the home of the Dalai Lama since the Chinese takeover of Tibet in 1956.
