Luzon (pop. 62,000,000) is the largest and most important island of the Philippines. More than half the country’s people live there. The island covers an area of 40,420 square miles (104,688 square kilometers), more than one-third of the entire land area of the Philippines.
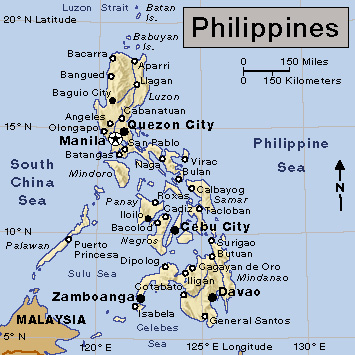
Luzon includes all or part of seven administrative regions of the Philippines. The Ilocos Region in northwestern Luzon is noted for its tobacco, rice, gold, silver, and copper. The Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) lies in north-central Luzon, and the Cagayan Valley Region lies in northeastern Luzon. The valley has spectacular rice terraces at Banawe. The Central Luzon Region lies to the south. It is the main rice-producing area of the Philippines. The National Capital Region (NCR), sometimes called Metro Manila, lies south of the Central Luzon Region. The National Capital Region is the main economic, political, and social center of the nation. It is the most densely populated region, with the national capital, Manila, and several other cities lying within its borders. Farther south is the Calabarzon Region. Rice, corn, sugar, coconuts, coffee, timber, minerals, oranges, and livestock are the major products. In southeastern Luzon lies the Bicol Region. Its varied landscape includes volcanoes, plains, and the low-lying Bicol Valley. Most of the region’s inhabitants speak the local dialect, Bicol. Typhoons frequently sweep over the region from the Pacific Ocean. The Bicol Region includes the islands of Masbate and Catanduanes. An eighth administrative region, Mimaropa, is often considered part of the Luzon island group. The Mimaropa Region includes the islands of Marinduque, Mindoro, and Palawan, which lie southwest of Luzon.

