Bottle is a container for holding liquids. Most bottles are made of glass or plastic. Other materials used to make bottles include earthenware and such metals as steel and aluminum. Bottles have either narrow or wide mouths that are closed with corks, glass stoppers, or plastic or metal covers.
The United States leads the world in the manufacture of glass and plastic containers. It produces about 46 billion glass containers and about 11 billion plastic containers each year for use with beverages, cosmetics, foods, and pharmaceuticals.

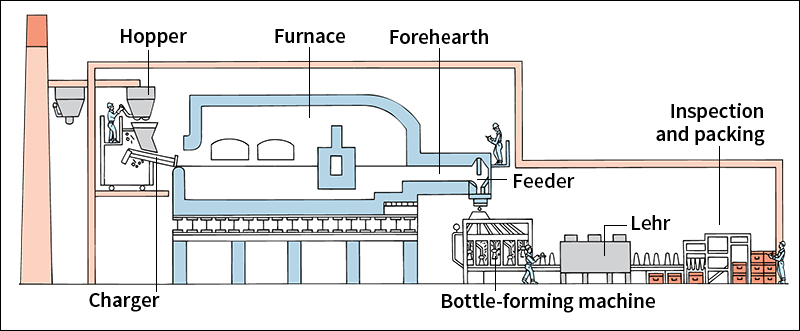
Almost all bottles are made by automatic machinery. In glass-bottle making, an automatic feeder separates a stream of molten (melted) glass into individual gobs. Each red-hot gob is sent to a mold and shaped into a parison. The parison looks like a short bottle with thick sides. The machine transfers the parison to the final mold. There air is pumped into the parison, expanding the hot glass into the exact shape of the mold. This expanding procedure is called blowing.
Materials used to make plastic bottles include polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride. There are three different processes used for producing plastic bottles: (1) extrusion blow molding, (2) injection blow molding, and (3) injection-stretch blow molding. These processes resemble the glass-bottle making process. In extrusion blow molding, however, the parisons are tube-shaped. In injection blow molding, the molten plastic is injected through a small hole to form the parisons. In injection-stretch blow molding, the plastic is stretched–in most cases, by a metal rod–as it is blown into a mold. Large soft drink containers made of polyethylene terephalate (PET) are made by injection-stretch blow molding. This process changes the chemistry of the plastic so the PET containers will keep the gases used in the carbonation of soft drinks from escaping.
People discovered how to form glass containers about 2,000 years ago. They gathered molten glass on the ends of hollow iron pipes and expanded the glass by blowing through the pipes. Later, people found that molten glass could be blown into molds. In the 1930’s, Independent Section (I.S.) glass-bottle making machines were introduced. Today, improved models of the I.S. machines produce almost all the glass bottles made in the United States.
The first plastics blow molding machines were patented in the early 1940’s. Polyethylene squeeze bottles soon became the first plastic bottle products.
In the early 1970’s, some people argued that glass bottles added to environmental pollution. Recycling centers were set up so people could return bottles for reuse in other bottles. Most recycled plastic bottles are used to manufacture lower quality plastics than those used to make bottles.
