Bug is a common name of all insects, but true bugs belong to an order (large group) of insects called Hemiptera. Hemiptera vary in appearance. Some kinds have wings, and others do not. Bugs may live in water, but most live on land. No Hemiptera has teeth or chewing parts. They suck blood or juice from animals or plants through horny, jointed beaks which are attached to their heads.
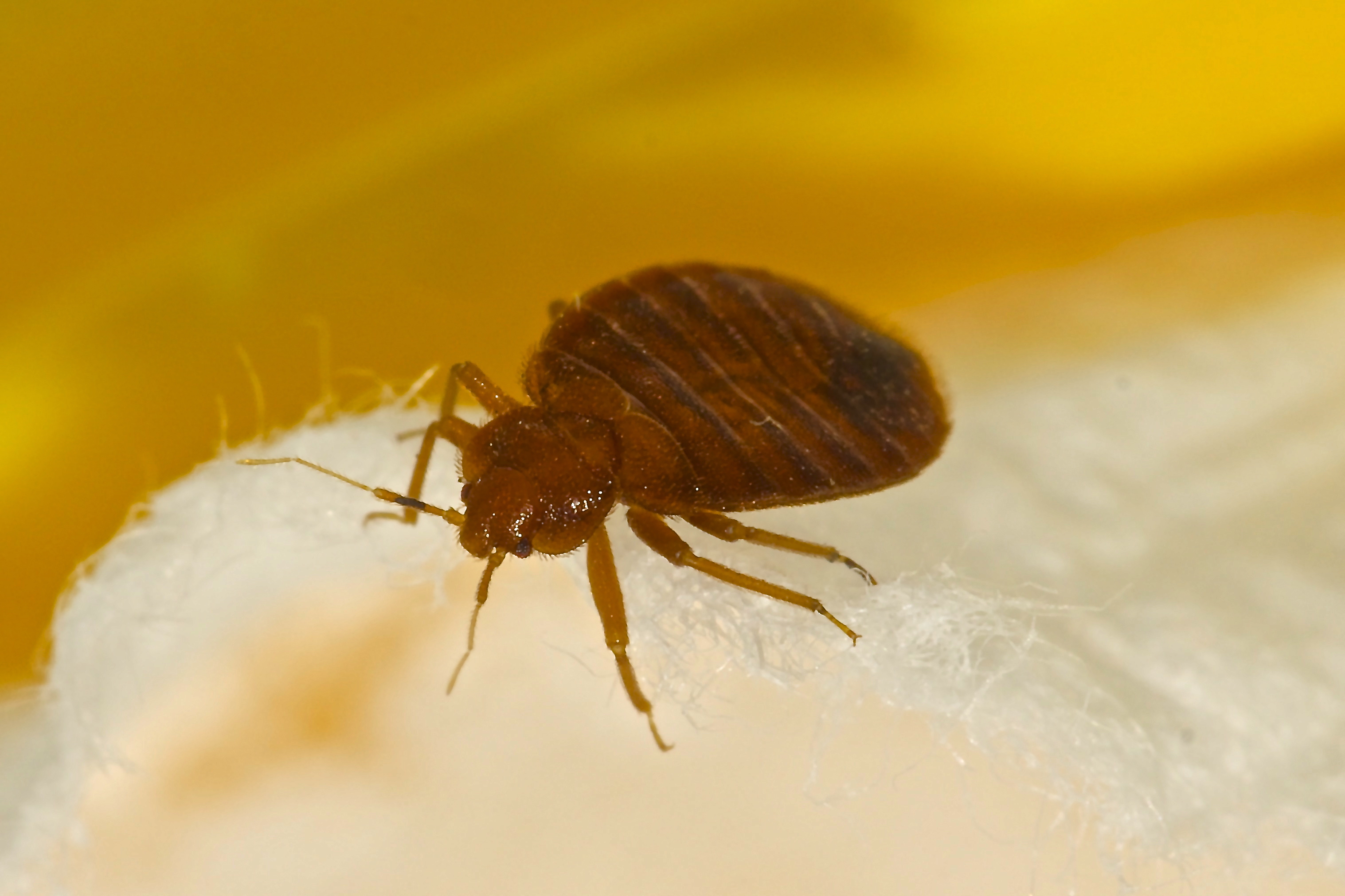
Some bugs give off an unpleasant odor for protection. These bugs are called stink bugs. Some bugs have “bug” as part of their name. Examples include bed bugs, chinch bugs, and water bugs. Junebugs, ladybugs, and tumblebugs belong to the beetle family. They are not true bugs.

The two pairs of wings on bugs are not the same. The back wings consist entirely of membrane, and the front wings have membrane tips on a hard base. When the insect is at rest, the tips of the front wings cross and often appear to form an “X” on the insect’s back.
Bugs lay their eggs in a variety of places, such as inside plant tissues, on plants, or glued to hairs. The eggs are oddly shaped, and some have attractive colors. Some bugs injure crops or attack people or other animals, but most are harmless. Bugs usually are controlled with chemicals called insecticides, though other insects may provide the best control.
