Virgin Islands are an island group in the Caribbean region. They lie about 40 miles (64 kilometers) east of Puerto Rico. They form the western end of the Lesser Antilles island chain. The islands are divided into two political units, each with territorial status. The British Virgin Islands are a territory of the United Kingdom. The rest of the islands comprise the United States Virgin Islands. The Virgin Islands have a total land area of 192 square miles (499 square kilometers). The North Atlantic Ocean lies to the north of the islands, and the Caribbean Sea lies to the south.
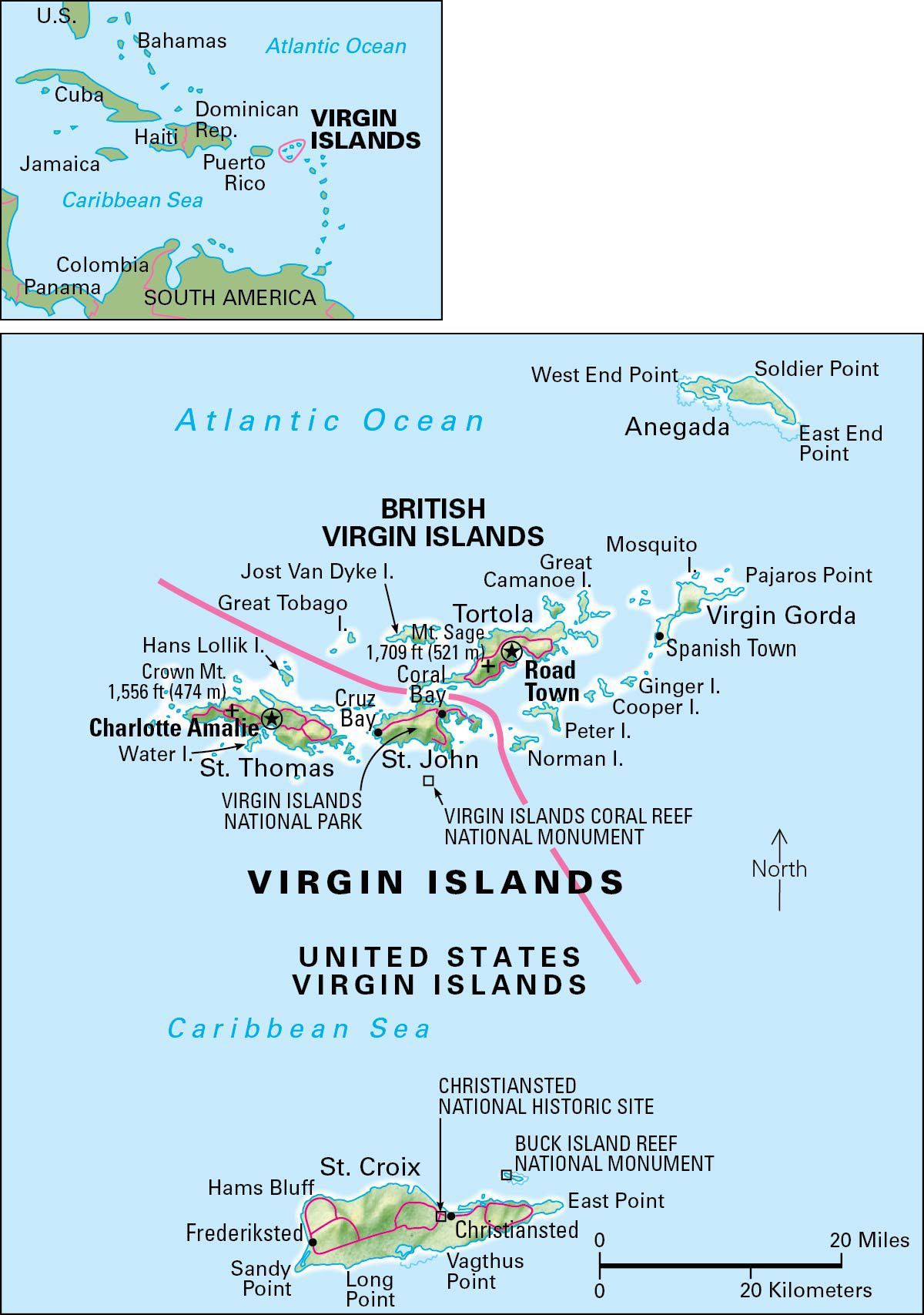
The main populated islands in the British territory are Jost Van Dyke, Tortola, and Virgin Gorda. The chief islands of the U.S. territory are St. Croix, St. John, and St. Thomas. The Virgin Islands group also has many islets and reefs, most of which are uninhabited.
About 141,000 people live on the Virgin Islands. A large majority of the population is of African descent. English and Spanish are the main languages spoken. Tourism is a major source of employment for islanders. Other important economic activities include manufacturing and financial services.
The Virgin Islands have a mild, subtropical climate. Temperatures range from about 70 to 90 °F (20 to 32 °C). The islands receive from 40 to 60 inches (100 to 150 centimeters) of rainfall annually. Many of the islands are rugged and hilly. Mount Sage, on Tortola, is the highest point, at 1,709 feet (521 meters).

Fossils show that the ocean once covered the Virgin Islands. The composition of the rocks that form much of the land is evidence that volcanoes pushed the islands up from the ocean floor.
Arawak, Carib, and Ciboney people lived on the Virgin Islands before Europeans settled there. In 1493, Christopher Columbus, an Italian navigator employed by Spain, sighted the islands and claimed them for Spain. But Spain did not settle the islands. Beginning in the 1600’s, Denmark, the Dutch Republic (now the Netherlands), England (now part of the United Kingdom), and France established settlements. England annexed the British Virgin Islands in 1672, and the United States took control of the U.S. Virgin Islands from Denmark in 1917.
See also Virgin Islands, British ; Virgin Islands, United States .
