Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is a spacecraft in orbit around Earth that measures and images the sun’s magnetic field. A magnetic field is the invisible region around a magnetic object where its influence can be felt. SDO takes pictures of the sun more often and at a higher resolution than previous missions. Resolution is the ability to produce images with sharp detail. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched SDO on Feb. 11, 2010.
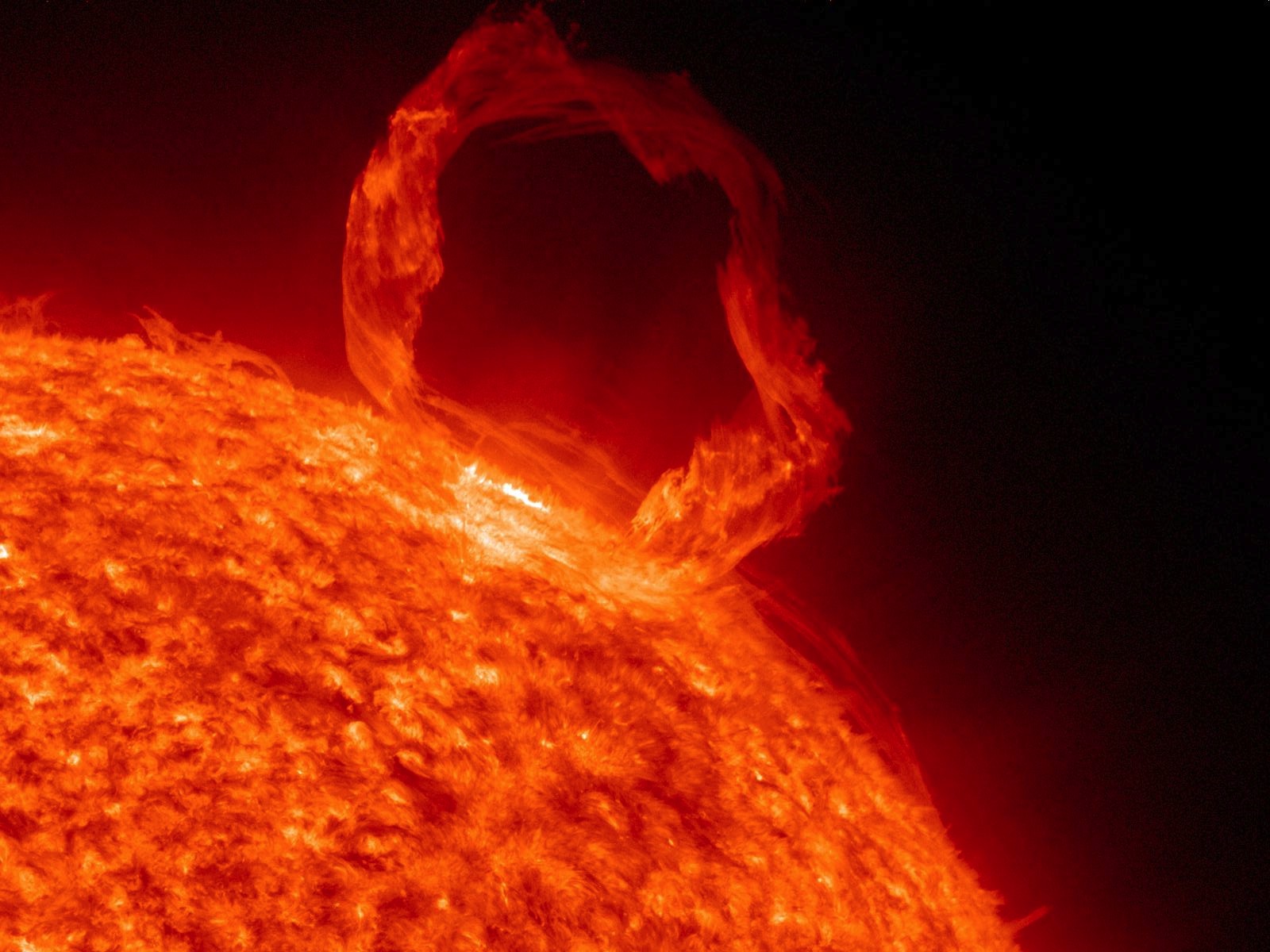

The main goal of SDO is to observe changes in the sun’s magnetic field. The craft’s instruments observe the invisible field indirectly by recording changes in the sun’s plasma, a hot gaslike material. Researchers study the changes to understand how magnetic energy is created inside the sun and released as different types of energy at the surface. One such release of energy is a sudden release of heat and light called a solar flare. Another kind is called a coronal mass ejection (CME). A CME is a large explosion of particles from the sun’s outer atmosphere out into the solar system. If a large CME were to strike Earth directly, it could cut electrical power, damage satellites, or disrupt radio transmissions.
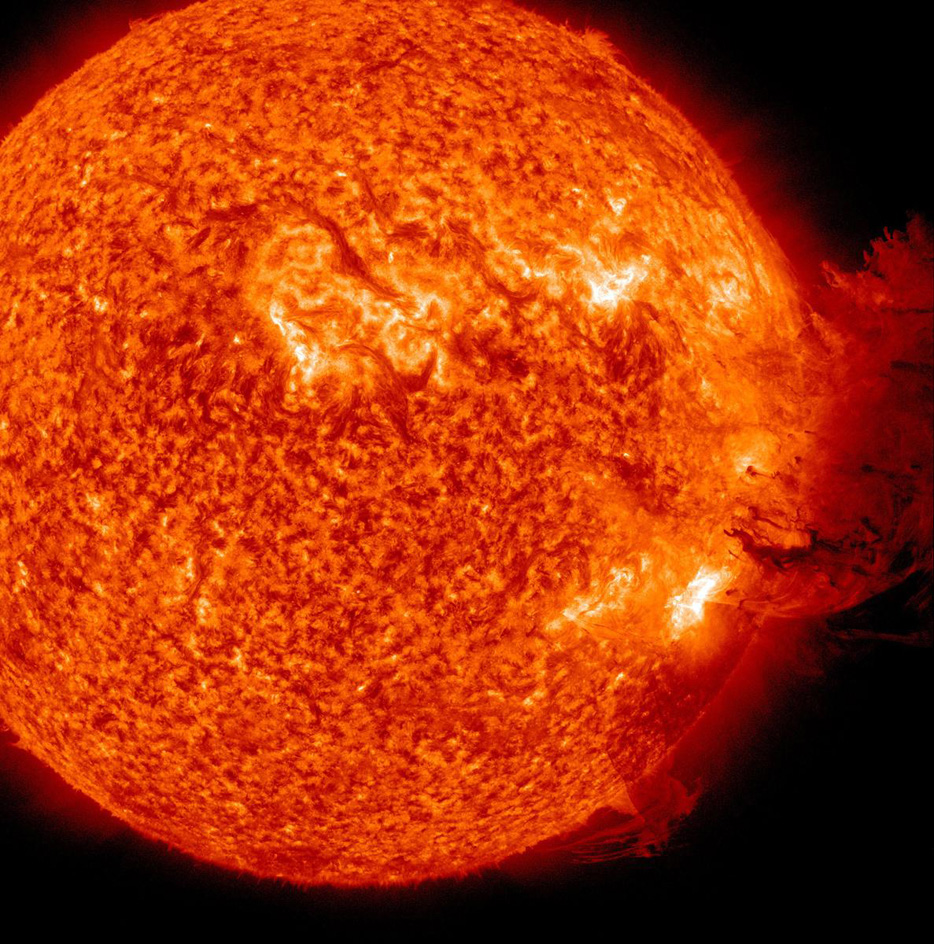
SDO uses three different instruments to observe the sun in visible, ultraviolet, and X-ray wavelengths. A visible light telescope measures waves rippling across the face of the sun and also the strength and direction of the magnetic field at the surface. Another instrument observes the corona, the outermost layer of the sun’s atmosphere, in X-ray and ultraviolet light. This same instrument also observes the region just below the corona, called the transition region. A third instrument measures extreme ultraviolet and X-ray light emitted (given off) by the entire sun.
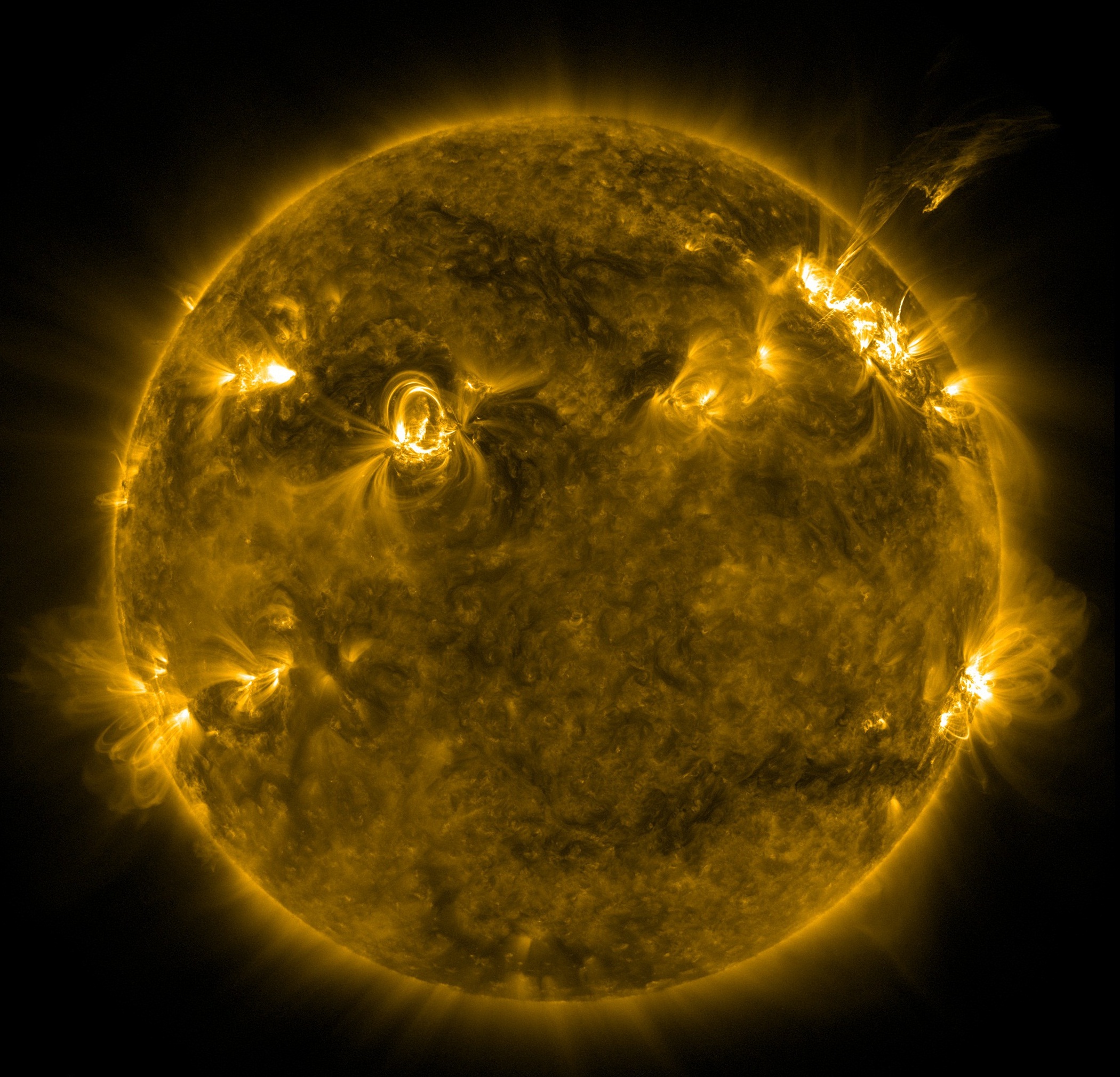

SDO circles Earth once a day in an orbit that keeps it within sight of the sun and also of a ground station in New Mexico. The station collects the data the satellite transmits back to Earth. However, the satellite loses sight of the sun whenever Earth passes between the sun and SDO.
See also Space exploration (Exploring the sun).
