Ecosystem is the most complex level of organization in nature. An ecosystem is made up of all the living and nonliving things in a particular environment , including climate, soil, water, air, nutrients, and energy, and the interactions that occur among them. Scientists called ecologists study how ecosystems work. They recognize and study ecosystems at different scales, from a small pond to a vast desert or forest. Even the entire planet Earth can be thought of as a single ecosystem.
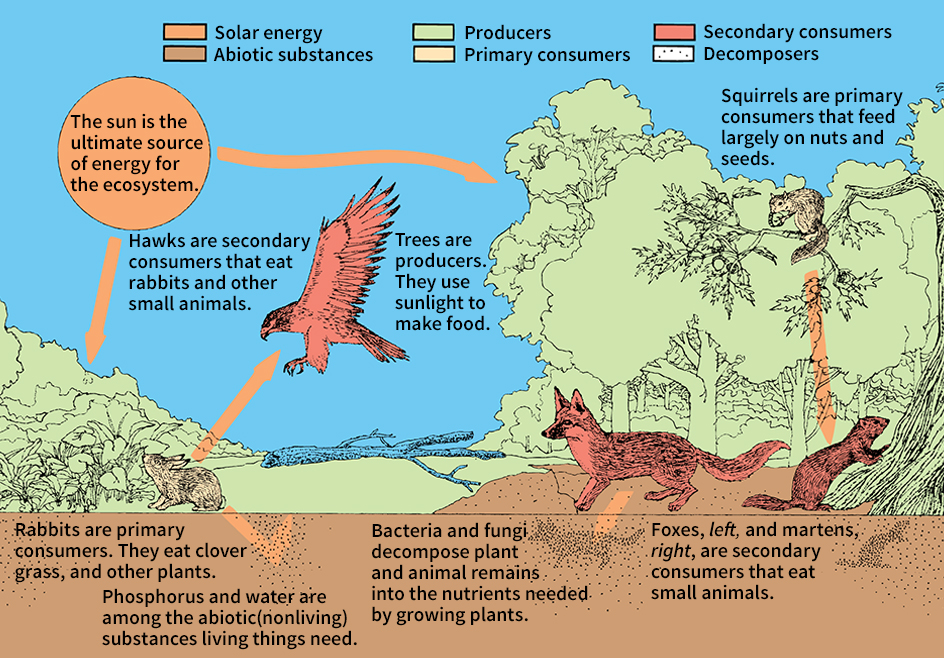
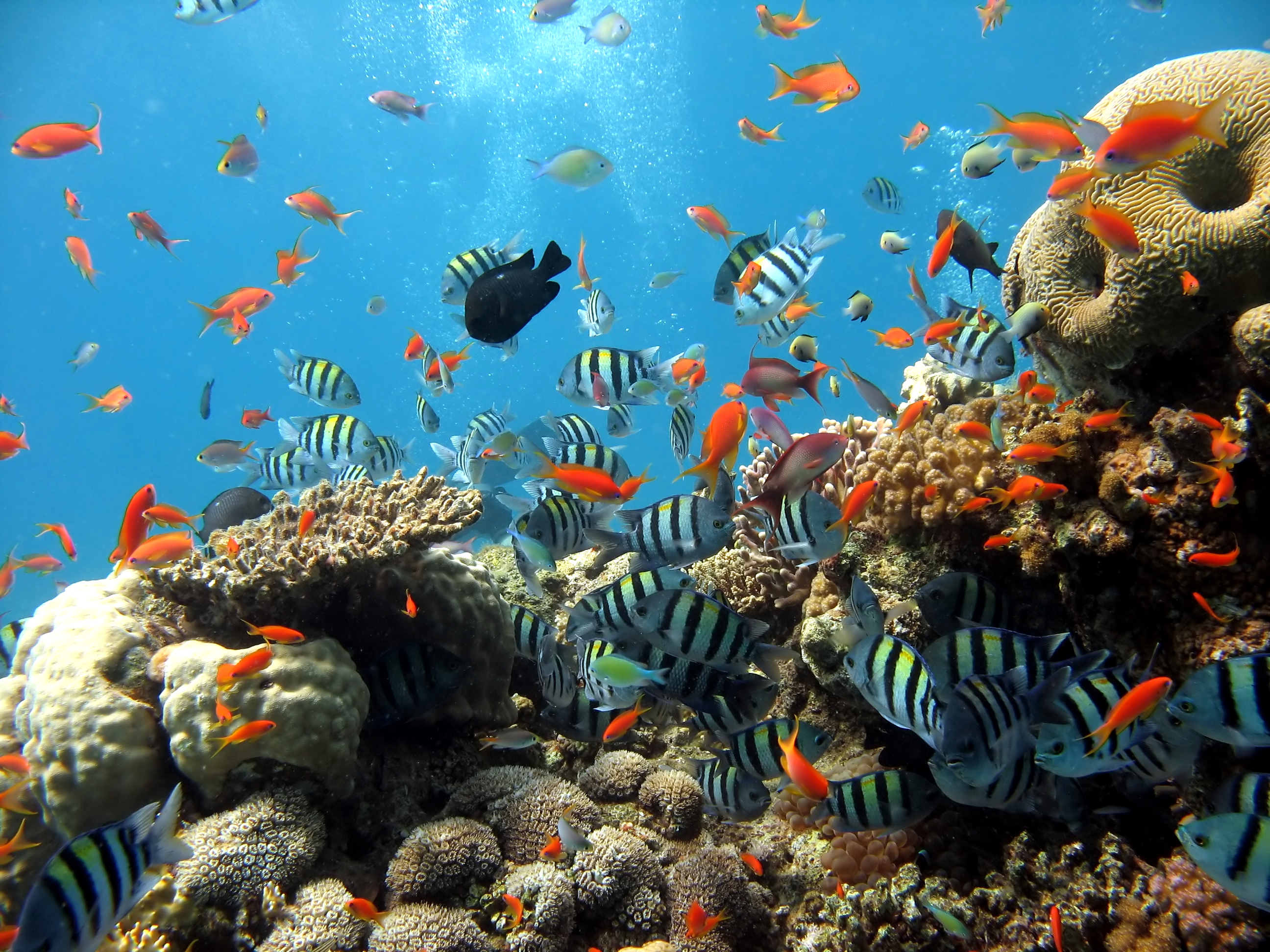
The living part of an ecosystem is known as the biotic environment. It includes organisms such as plants, animals, algae, fungi, bacteria, and their complex interactions. Populations of different organisms interacting with one another form communities. Interactions can include predation, competition, or parasitism. Predation occurs when one organism eats another—for example, a lynx eating a rabbit in a forest community. Competition occurs when two or more organisms use the same limited resources in a particular community. Two species of mice feeding on seeds in a meadow would be competing against each other. Parasitism occurs when one species relies on another. For example, ticks are parasites of deer. Ticks survive by feeding on the blood of the deer.
The abiotic environment is the physical, nonliving part of an ecosystem. It includes the atmosphere, rocks, water, and components of soil. The abiotic environment interacts with the biotic environment by providing the materials and physical conditions needed for organisms to survive. The abiotic environment may also limit where an organism can live. Temperature and the availability of water are important abiotic factors that determine which types of organisms can live in an area. For example, only certain organisms that can withstand high temperatures are able to live in hot springs. In some instances, the biotic environment can also influence the abiotic environment. For example, beavers build dams that may affect the flow of rivers and streams.

