Black mamba is among the world’s deadliest snakes. It is known for its extremely deadly venom. The black mamba is also known for its speed. It can move up to 12.5 miles (20 kilometers) per hour. The black mamba belongs to the mambas, a group of deadly venomous snakes of central and southern Africa.
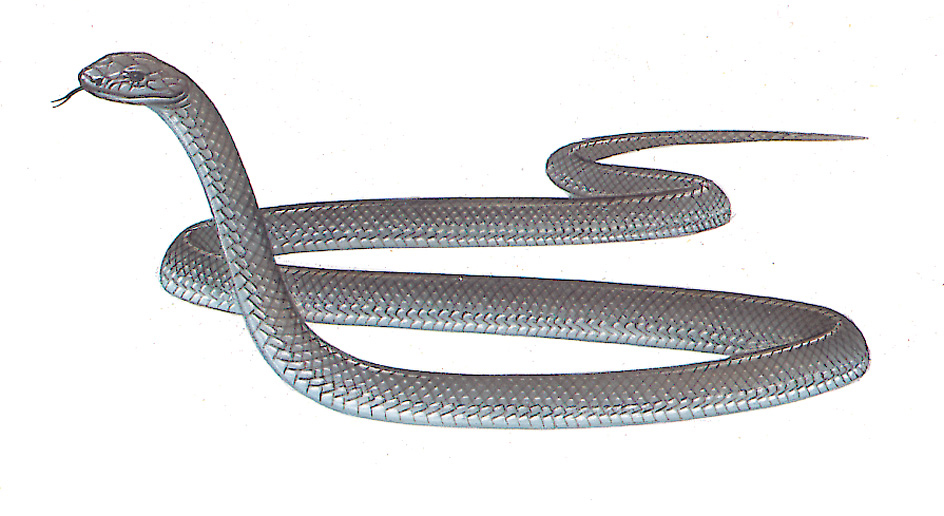
The black mamba gets its name from its black mouth. When threatened, it opens its mouth wide, revealing a dark color. Black mambas are brownish in color, ranging from olive to gray in tone. The average length of a black mamba is 8 feet (2.4 meters). Some black mambas can grow to 14 feet (4.3 meters) in length. Black mambas weigh up to 3.5 pounds (1.6 kilograms). Black mambas can live about 11 years in the wild.
Black mambas are found in southern and eastern Africa. They live in such places as savannas, rocky hills, and woodlands. They prefer to live in hollow trees or rock crevices (cracks). Black mambas hunt during the day. They eat small mammals and birds. A black mamba hunts an animal by biting it, releasing its venom. The snake then lets the animal go. The black mamba follows the prey until the prey becomes paralyzed (unable to move) or dies. The black mamba then eats the animal. The black mamba returns to the same place to sleep each night.
Black mambas mate during the spring and summer. The female lays from 6 to 25 eggs. She lays the eggs in a damp, warm burrow and then leaves, providing no additional care. Two to three months later, the young hatch.
Black mambas are shy unless confronted. When threatened, they raise their heads. As much as one-third of their bodies can raise off the ground while moving. They then open their black mouths and hiss.
