Chemical reaction is a process by which one or more substances are converted into one or more different substances. The original substances are called reactants. The resulting substances are called products. In a simple chemical reaction, the reactants may be two atoms that bond together to form a product molecule. Another simple reaction might involve a reactant molecule breaking apart into two or more product atoms. In more complex reactions, some or all of the bonds of reactant molecules break and the new bonds of product molecules form. Many enduring substances, such as rock and water, are highly stable (resistant to chemical reaction). However, all substances can react chemically under certain conditions.
Chemists summarize chemical reactions using formulas called chemical equations. One of the most familiar reactions is combustion. Combustion is the process by which a material burns in air, giving off light and heat. The following chemical equation describes the combustion of methane, the main ingredient in natural gas:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O (That is, one molecule of methane and two molecules of oxygen yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water.)
The reactants appear on the left side of the equation. The products appear on the right. The arrow indicates that a chemical reaction has occurred.
Chemists balance chemical equations according to a fundamental principle of chemistry known as the law of conservation of mass. To satisfy the law, a chemical equation must have the same number and types of atoms in both the reactants and the products. In the equation for the combustion of methane, for example, both the products and reactants include one carbon atom, four hydrogen atoms, and four oxygen atoms.
Chemical equations generally show the products formed when the reaction has continued to completion. Often, however, the transformation from reactants to products involves many individual steps. Short-lived substances called intermediates may form and then react further to give final products.
The chemical bonds that hold molecules together contain energy. During a chemical reaction, old bonds can break and new bonds can form, producing changes in energy. Chemists sometimes describe these changes using an energy diagram. This energy diagram shows the combustion of methane:
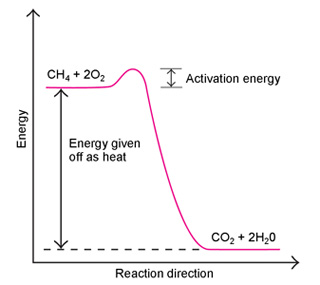
As the diagram shows, the reactants have more energy than the products. As the reaction proceeds, it releases the excess energy as heat. Combustion and other reactions that give off heat are known as exothermic reactions. In the opposite type of reaction, the reactants have less energy than the products. These reactions, called endothermic reactions, absorb heat.
The energy diagram also shows that the energy of the reactants must rise slightly before falling off to the energy level of the products. The difference in energy between the reactants and the top of the curve is called the activation energy of the reaction. For the reaction to occur, an outside energy source, such as heat or a spark, must provide the activation energy.
