Cretaceous << krih TAY shuhs >> Period was a time in Earth’s history from about 145 million years ago to 66 million years ago. The period’s name comes from a Latin word meaning chalk. Rocks of this age in northern Europe contain numerous layers of chalk. The Cretaceous Period was the last of the three periods that make up the Mesozoic Era. The Mesozoic was the time when the dinosaurs lived.
Many of the best-known dinosaurs lived during the Cretaceous Period. These include the huge Brachiosaurus, the three-horned Triceratops, and the large meat-eater Tyrannosaurus. Many duckbilled, plant-eating dinosaurs also thrived. The flying reptile Pteranodon also lived during the Cretaceous Period. Pteranodon had a wingspan of up to 25 feet (7.6 meters). In the seas, dolphinlike reptiles called ichthyosaurs declined. However, four-flippered, long-necked reptiles called plesiosaurs swam the seas. Plesiosaurs reached their greatest lengths, up to 46 feet (14 meters) long. In addition, the oceans held sea turtles up to 12 feet (3.7 meters) long. They also held mosasaurs, serpentlike reptiles. They grew more than 40 feet (12 meters) long.
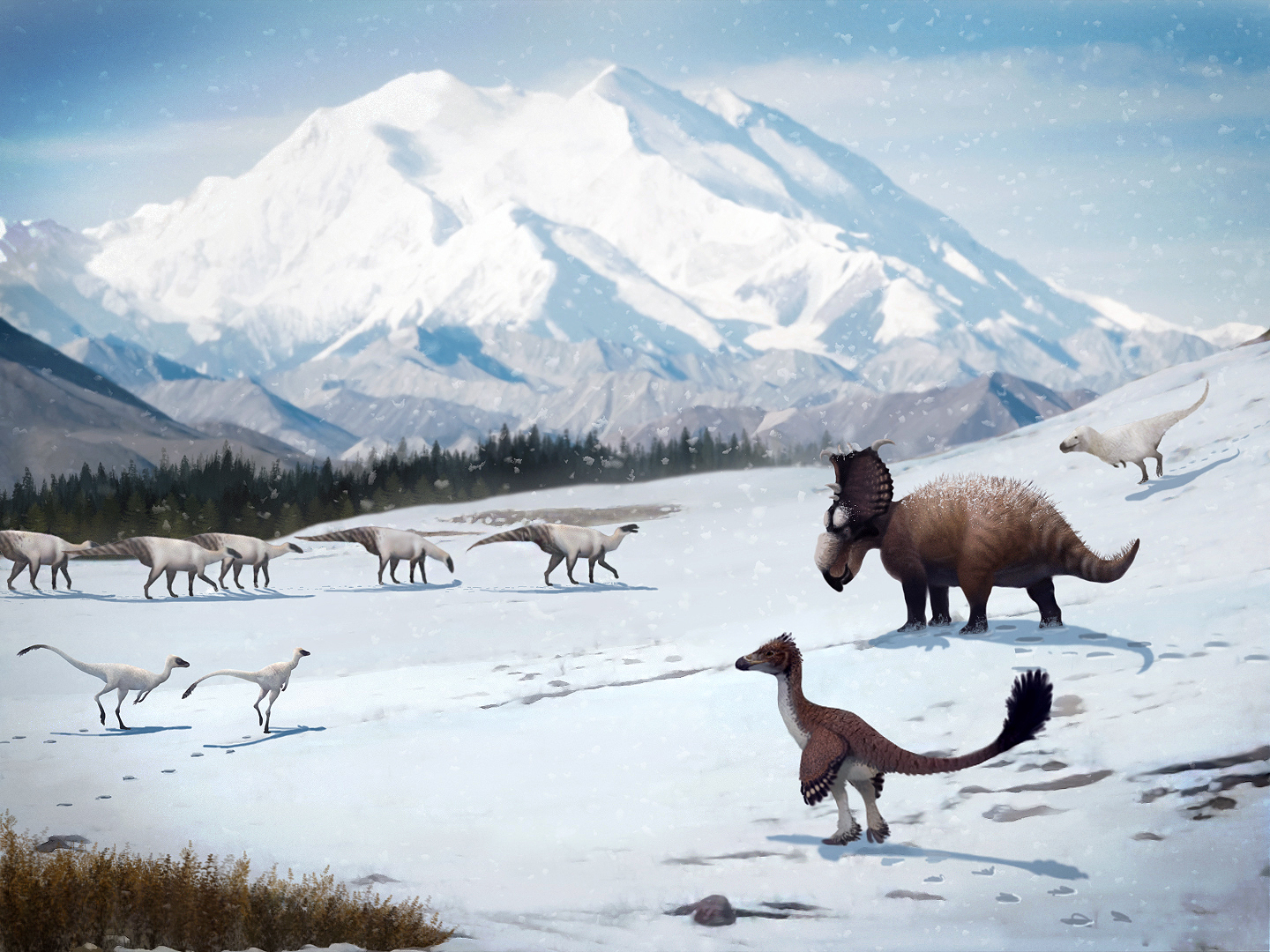

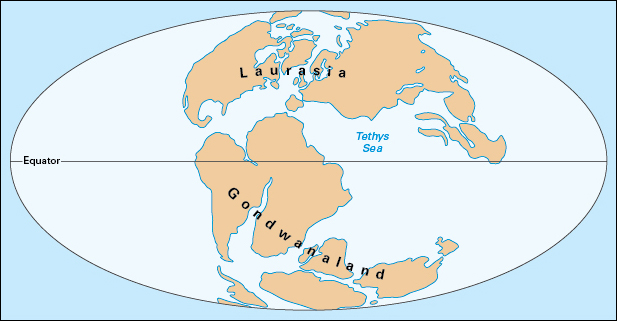
At the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, most of Earth’s land was arranged in two huge land masses. These masses are now called Laurasia and Gondwanaland. During the Cretaceous Period, they broke apart into what would become the present continents. First, Gondwanaland split to form South America and another land mass. Then, that mass broke up to form Africa, India, and another land mass. This mass consisted of what are now Australia and Antarctica. Toward the end of the Cretaceous Period, Laurasia split into North America and Eurasia. After a few million years, Greenland broke from Eurasia.
Sea levels around the world rose during the Cretaceous Period. At their highest, a band of water stretched across the entire length of North America from what is now the Gulf of Mexico to the Arctic Ocean. In western North America, the uplift of the Rocky Mountains began.
The Cretaceous Period ended with the sudden extinction of the dinosaurs and many other living things. One widely accepted explanation holds that a large meteor impact caused this mass extinction. Dust from the impact would have reduced the amount of sunlight reaching Earth’s surface. The reduced light killed off plants and the animals that depended on them. Reduced sunlight may also have cooled the planet. Such cooling may have led to the extinction of some plants and animals.
