Density is the amount of matter in a particular volume of a substance. Density is generally expressed in terms of mass (amount of matter) per unit of volume. Our everyday experience of density is closely related to weight. For two objects with the same volume or bulk, the denser object will be heavier. For this reason, weight is often used in place of mass in describing density. Density is generally given in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3), grams per milliliter (g/ml), or pounds per cubic foot (lbs/ft3). Densities vary with temperature and pressure. Thus, it is important to know the temperatures and pressures under which densities are measured.
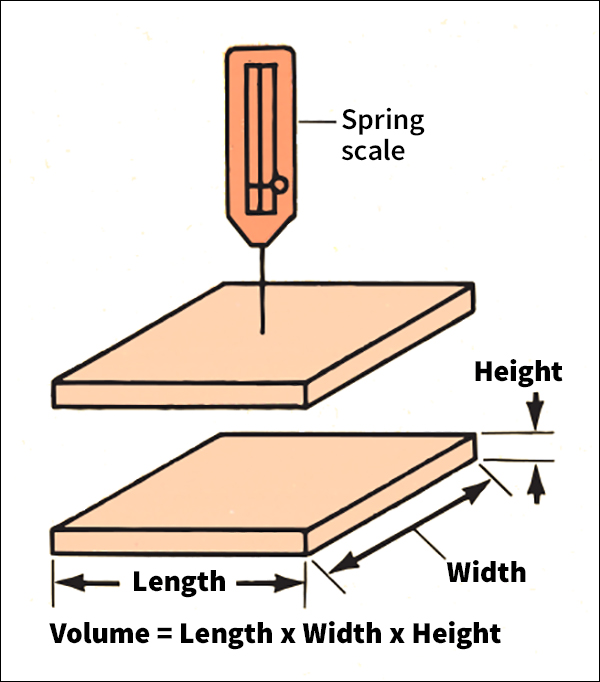
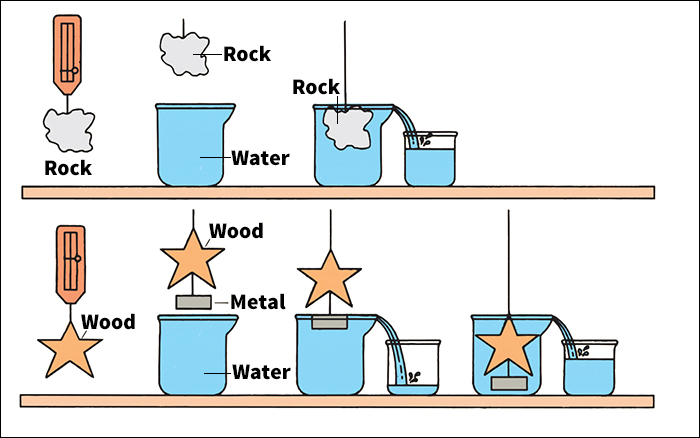
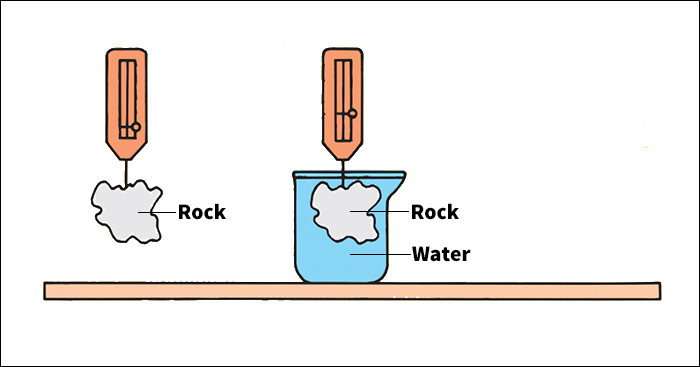
The density of a substance that is uniform (identical throughout) equals the substance’s mass or weight divided by its volume. Mass or weight can be measured on a scale or balance. The volume of a regularly shaped solid can be calculated by measuring its dimensions and applying a mathematical formula (see Volume). It is harder to determine the volume of an irregularly shaped solid. Two methods call for submerging the object in water. To use the first method, submerge the object. Then measure the volume of the water displaced. This volume equals the volume of the object. To use the second method, weigh the object in air. Then suspend it in water and weigh it again. The volume equals the apparent decrease in weight divided by the density of water.
The density of a gas depends greatly on its temperature and pressure. To determine the density of a gas at a given temperature and pressure, first weigh an empty container. Next, fill the container with the gas at the designated temperature and pressure and weigh it again. Then subtract the first measurement from the second. To determine the volume of the container, measure the amount of water that the container holds.
Specific gravity is a measure that compares a substance’s density to that of water. It equals the density of the substance divided by the density of water.
Density has many uses in science and engineering. Earth scientists can identify minerals and other solids by measuring their density. Chemists can measure the density of a solution to determine the concentration of a particular substance.
