Eutrophication << `yoo` truh fuh KAY shuhn >> is a process that results in low oxygen levels in bodies of water. Eutrophication can occur in rivers, lakes, and oceans. Eutrophication can cause the quality of the affected water to decline until the water can no longer support most animal life. Areas where such conditions develop are often called dead zones.

Eutrophication can occur naturally. For example, it often occurs when flooding carries abundant nutrients (nourishing substances) into rivers. But much eutrophication today is caused by human activities. Eutrophication caused by human activities is called cultural eutrophication.
How eutrophication occurs.
Bodies of water support a natural cycle of life processes. Bacteria break down the wastes of fish and other organisms (living things), releasing such nutrients as carbon dioxide , nitrate , and phosphate . Plantlike organisms called algae feed on these nutrients. Microscopic animals called zooplankton eat the algae, and fish eat the zooplankton. When this cycle is in balance, each member of the cycle supports the others. Fish obtain food and oxygen from algae. Bacteria use organic matter from fish and oxygen from algae, and algae use the nutrients released by bacteria.
People upset the balance when they pollute the water with wastes, which provide many nutrients. Algae consume the excess nutrients. They become so well nourished that they grow faster than fish can eat them. Thick layers of algae, called algal blooms, spread over the water. Algae in lower layers of the bloom cannot get the light they need for photosynthesis . These algae soon die and decay, using up huge quantities of oxygen in the water.
Water with low levels of oxygen is said to be hypoxic. When oxygen is completely absent, the water is said to be anoxic.
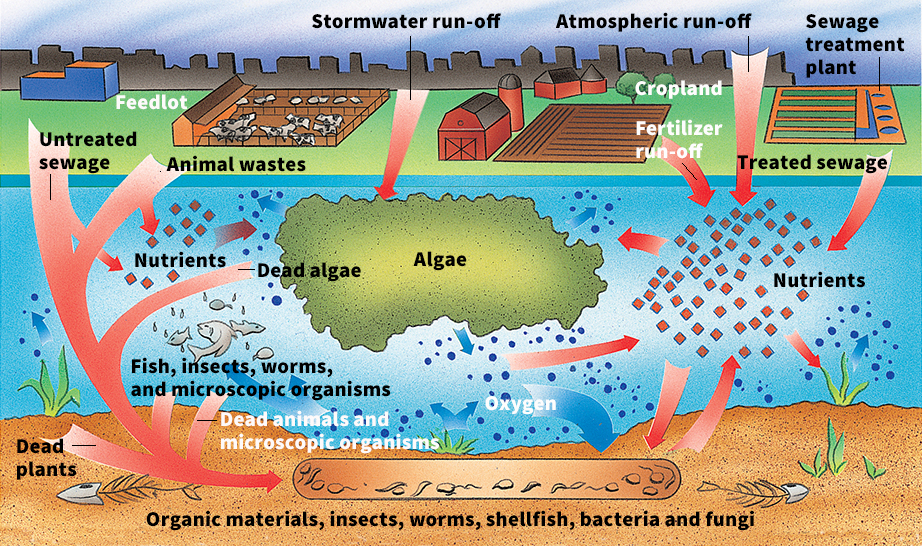
Fish and other animals die when the oxygen supply in the water becomes too low to sustain them. As the bodies of the animals decay, they consume still more oxygen. Without oxygen, the bacteria can no longer break down organic matter, and foul-smelling wastes accumulate.
Eutrophication and water pollution.
Eutrophication is a major pollution problem. Many of the excess nutrients that enter bodies of water come from the nitrate and other fertilizers used in agriculture. Sewage is another major source. In particular, the use of detergents that contain phosphate greatly increases the quantity of phosphate in sewage. Nitrates from automobile exhaust enter the water in rain and snow, and industrial plants discharge nutrients in wastewater.
