Francium, << FRAN see uhm, >> is a radioactive element produced in certain nuclear reactions. It is the heaviest member of the group of elements called the alkali metals . The group also includes lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, and cesium. The chemical properties of francium closely resemble those of Cesium . For information on the position of francium on the periodic table, see the article Periodic table .
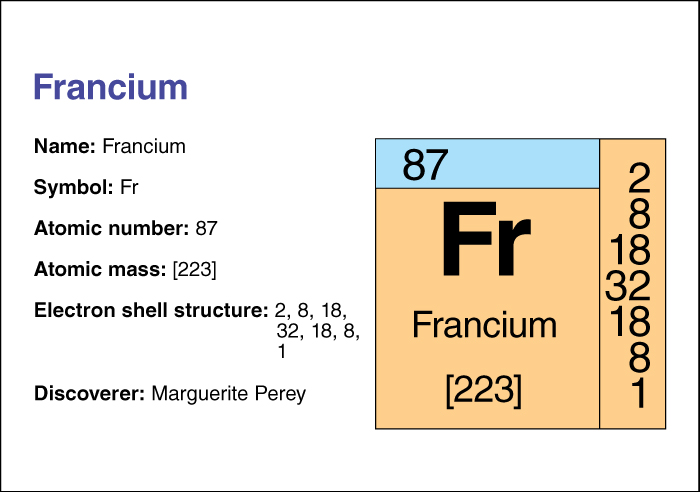
The chemical symbol of francium is Fr, and its atomic number (number of protons in its nucleus) is 87. Francium has many isotopes, forms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. The most stable isotope has an atomic mass number (total number of protons and neutrons) of 223. This isotope has a half-life of 22 minutes—that is, due to radioactive decay, only half the atoms in a sample of isotope 223 would still be atoms of that isotope after 22 minutes.
The French scientist Marguerite Perey discovered francium in 1939 as a product of the radioactive decay of actinium.
