Guam << gwahm >> is a territory of the United States in the Mariana Islands. It serves as a vital U.S. air and naval base in the Pacific Ocean. Hagåtña is the capital of Guam.
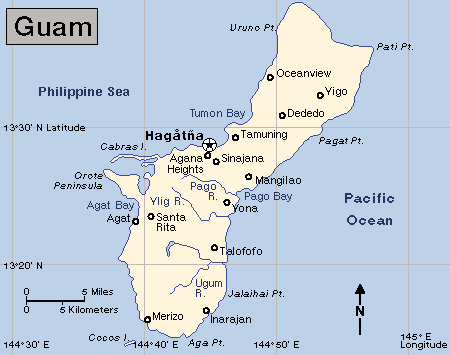
Guam lies at the south end of the Marianas, about 1,300 miles (2,100 kilometers) east of the Philippines. About 30 miles (48 kilometers) long and 4 to 10 miles (6.4 to 16 kilometers) wide, Guam covers 210 square miles (544 square kilometers). It has a population of about 172,000.

Land and climate.
Coral reefs lie off the coast of Guam. A limestone plateau rises on the northern part of the island. Many forests in the north have been cleared for farms and airfields. The southern half of Guam has a range of mountains of volcanic origin. Several rivers originate in the mountains and run to the coast. Earthquakes occasionally strike the island. The War in the Pacific National Historical Park is on Guam. It honors the U.S. troops who fought in the Pacific in World War II (1939-1945).

Guam has warm weather most of the year. Average temperatures range from 68 to 90 °F (20 to 32 °C). But typhoons frequently hit the island, and rainfall averages 90 inches (230 centimeters) a year. The rainy season generally lasts from May to November.
People.
About 40 percent of the Guamanian people are Chamorros. Chamorros are descendants of the island’s original inhabitants and other Micronesian islanders, and of Filipinos and Spaniards. Other Guamanians are descended from American, Italian, French, British, Japanese, Chinese, and Mexican settlers. About one-sixth of the people on Guam are U.S. military personnel and their dependents. English and Chamorro are the official languages of Guam. English is the most widely used language. The University of Guam, in Mangilao, is the largest university in Guam.
Economy.
Tourism and related industries produce the largest part of Guam’s income. Each year, hundreds of thousands of tourists, mostly Japanese, visit Guam. The U.S. military is the second largest source of income. It maintains Andersen Air Force Base and a number of naval facilities on the island. Military facilities provide many jobs for Guamanians. Agriculture and fishing are minor economic activities. Farmers grow coconuts, sweet potatoes, and taro. Tuna is the most important fish. Apra Harbor is Guam’s chief port.

History and government.
Chamorros were the first inhabitants of Guam. They came from Southeast Asia, perhaps as early as 3000 B.C. Through the years, many Chamorros and other settlers in Guam intermarried. The descendants of these people are still called Chamorros.
The Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan led the first European expedition to Guam. His group arrived there in 1521. Spain made the island a possession in 1565. But the Spanish did not take actual control over Guam until 1668. Spain ceded Guam to the United States in 1898 after the Spanish-American War. Guam was placed under the administration of the United States Navy. Japan attacked Guam on Dec. 8, 1941, during World War II. It captured the island on December 10. United States forces landed on Guam on July 21, 1944, but they did not completely recapture the island until Aug. 10, 1944.
After World War II ended in 1945, the U.S. military took over about one-third of Guam’s land. In 1954, the U.S. Air Force established Andersen Air Force Base in Guam.
The United States made Guam a territory on Aug. 1, 1950, and transferred its supervision from the Navy to the Department of the Interior. The people became United States citizens. Guam voters elect a one-house Legislature. They elect a governor and lieutenant governor for four-year terms. Before 1970, governors were appointed by the U.S. President. Since 1972, Guam voters have elected a delegate to the U.S. House of Representatives. The delegate may vote in House committees, but not on the House floor.
