Halogen << HAL uh juhn >> is any of the chemical elements that make up group 17 of the periodic table . The halogens are the elements fluorine (chemical symbol, F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). Tennessine does not occur in nature and has only been produced in small quantities in laboratories, so little is known about its properties. Halogen means salt producer. Many of the salts in the sea are compounds of halogens with metals. Common table salt , the best known such compound, is sodium chloride.
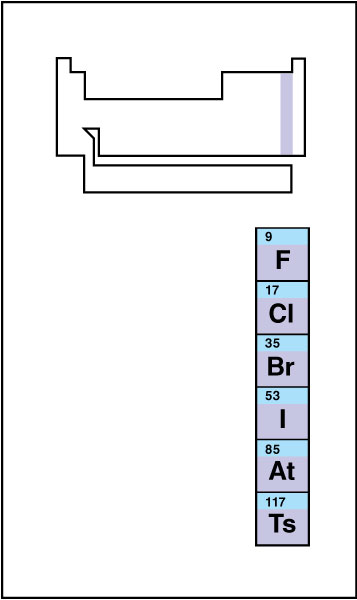
The halogens have a strong, unpleasant odor, and will burn the flesh. They do not dissolve well in water. At ordinary temperatures, fluorine is a pale yellow gas, chlorine a yellowish-green gas, bromine a red liquid, and iodine a bluish-black solid. Fluorine is the lightest halogen; tennessine is the heaviest. The relative atomic mass of fluorine is 18.9984033163; of chlorine, 35.453; of bromine, 79.904; and of iodine, 126.90447. All isotopes (forms) of astatine and tennessine are radioactive; the most stable isotope of astatine has a relative atomic mass of 210, and the most stable isotope of tennessine has a relative atomic mass of 294. The relative atomic mass of an element or an isotope equals the mass of the element or isotope divided by 1/12 of the mass of carbon 12, the most common isotope of carbon.
The elements of the halogen group are electronegative. This means that the atoms of halogens tend to oxidize (take up electrons from) other chemicals and become charged with negative electricity. They are then called negative ions. The salts, called the halides, are compounds formed by these ions. All the halogens are oxidizing agents. However, the heavier the atomic weight of the halogen, the weaker its oxidizing power. Fluorine is the strongest of all oxidizing agents. It is also extremely reactive.
The halogens react with most metals and many nonmetals. Their reactions with hydrogen give the hydrogen halides. The most important of these is hydrogen chloride, which dissolves in water to make hydrochloric acid .
The halogens and their compounds have many uses. Iodine and bromine gases inside halogen light bulbs make the bulb last longer than an ordinary bulb and prevent it from blackening. Fluorides are used to make aluminum, steel, and the nonstick plastic Teflon . Small quantities of fluorides are added to toothpaste and drinking water to help prevent tooth decay. Chlorine and its compounds are important in making paper and plastics, and in purifying drinking water. Bromine is used to make dyes, fire-retardant chemicals, and medicines. The iodine compound silver iodide is used in photographic film. Other iodine compounds are valuable antiseptics and disinfectants . Astatine also has important medical uses.
