Hazel is a group of trees and shrubs known for their edible nuts. There are more than a dozen species (kinds). Hazels grow in temperate (mild) climates of Asia, Europe, and North America. Hazels are often called filberts or cobnuts, as are the nuts. The nuts are also called hazelnuts. Common hazel is cultivated for its nuts. Two other hazels are native to the United States—the beaked hazel and the American hazel.
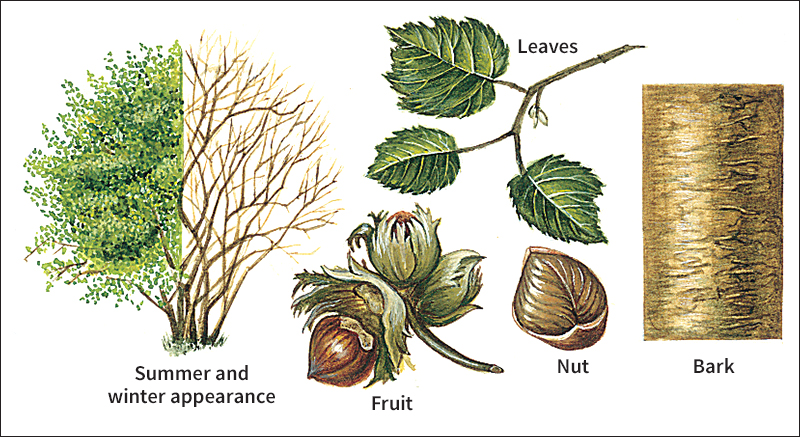
Hazels have large, oval leaves with toothed edges. The leaves turn yellow in the autumn. The plants bear male and female flowers. The male flowers are tassellike clusters called catkins (see Catkin). The female blossoms grow on separate twigs. They are so small that they are hard to see.
Hazels furnish valuable cover and food for wildlife. A species with purple leaves and another with twisted branches are grown as ornamentals.
Although hazels are small, their branches are strong and flexible. People have used them to make baskets, whip handles, hoops, and many similar articles.
In ancient times, many people believed that a forked hazel twig had supernatural powers. Stories tell how divining rods of hazel can be used to find water or minerals underground. Witch hazel does not belong to the group of true hazels.
