Horn is the general name for musical instruments of the brass family. The most popular horns include the bugle, cornet, flugelhorn, French horn, trombone, trumpet, and tuba. The term horn is often used to refer only to the French horn.
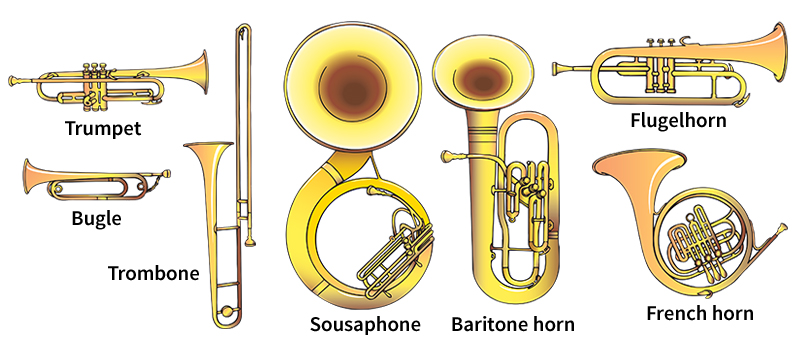
Most horns are made of brass and consist largely of tubing in various shapes and lengths. The differences in tubing produce a variety of tone colors, from the brilliant sound of the trumpet to the warm, mellow sound of the French horn. The pitches of all horns are determined by the tension of the player’s lips in the horn’s mouthpiece and by the use of valves or slides.
The earliest horns were made from natural materials, such as animal horns, tusks, shells, or hollow lengths of wood. People originally used horns to send signals over distances too great to be covered by the human voice. As sophisticated instruments developed, various types of horns became popular in military bands and orchestras. However, in many parts of the world, primitive horns made of natural materials are used today for signaling or to accompany dances or ceremonies. The oldest horn in continual use is the ancient Hebrew shofar, made from a curved ram’s horn. This instrument dates back about 6,000 years and is still used in Jewish religious services.
