Iridium, << ih RIHD ee uhm, >> is a silvery metallic element. It is one of the hardest metals, and it resists corrosion better than any other metal. Iridium is rare. It occurs in gravel deposits containing platinum ores. It also occurs in alloys (metal mixtures) with osmium. Most iridium comes from Brazil, Canada, Myanmar, Russia, South Africa, and the United States. Iridium is too brittle to use by itself. Its main use is to increase platinum’s strength and resistance to corrosion. Manufacturers use platinum-iridium alloys in containers, machine parts, and electric contacts that are to be exposed to corrosive chemicals and high temperatures. Jewelry and spark-plug electrodes are also made from iridium alloys.
Iridium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth’s crust. But it is found in much higher abundance in meteorites and asteroids . There is also an unusually high abundance of iridium in a clay layer found around the world that dates to about 65 million years ago. This fact has given rise to the idea that the impact of a massive asteroid around this time caused the extinction of the dinosaurs. See Dinosaur (Why dinosaurs died out) .
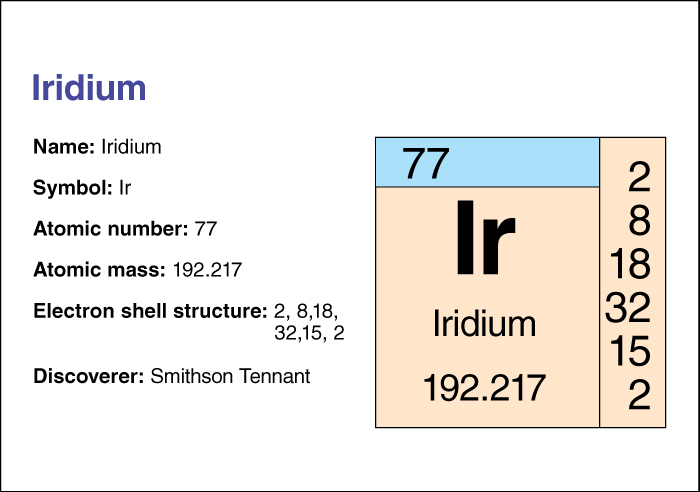
Iridium has the chemical symbol Ir. Its atomic number (number of protons in its nucleus) is 77. Its relative atomic mass is 192.217. An element’s relative atomic mass equals its mass (amount of matter) divided by 1/12 of the mass of carbon 12, the most abundant form of carbon. Iridium melts at 2410 °C and boils at 4130 °C. Iridium is extremely dense. It has a density of 22.65 grams per cubic centimeter at 20 °C.
Iridium belongs to the group of elements called transition metals . For information on the position of iridium on the periodic table, see the article Periodic table .
Smithson Tennant, a British chemist, discovered iridium in 1804.
