Jumping mouse is a small animal that usually moves by hopping. Jumping mice have long hind legs and unusually long tails. They use their hind legs to hop and their tails for balance. A jumping mouse is about 4 inches (10 centimeters) long, excluding its 5-inch (13-centimeter) tail. The animal’s fur is dark on the back and yellowish-brown on the belly. Most species (kinds) have a line along the sides of their bodies where the dark-colored and the lighter-colored fur meet.
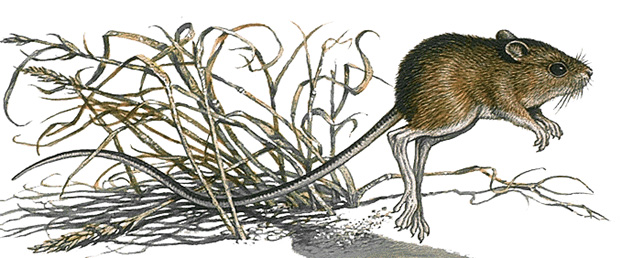
Jumping mice are rodents that live in Asia, Europe, and North America. Scientists have identified several species of the mice. Most North American kinds live in meadows and thickets along the edges of woods in the northern United States and in Canada. They are found most often in damp places. They are closely related to the dormouse and jerboa.
Jumping mice eat insects, leaves and stems, and berries and seeds. The female jumping mouse gives birth to a litter of about five young twice a year. Unlike most other mice, jumping mice hibernate (sleep through the winter).
