Kyoto, << kee OH toh or KYAW taw >> (pop. 1,463,723), is one of Japan’s largest cities. It lies on Honshu Island, about 27 miles (43 kilometers) inland from the industrial center of Osaka. Kyoto was Japan’s capital from A.D. 794 to 1868, and it became the home of many of the country’s cultural treasures.
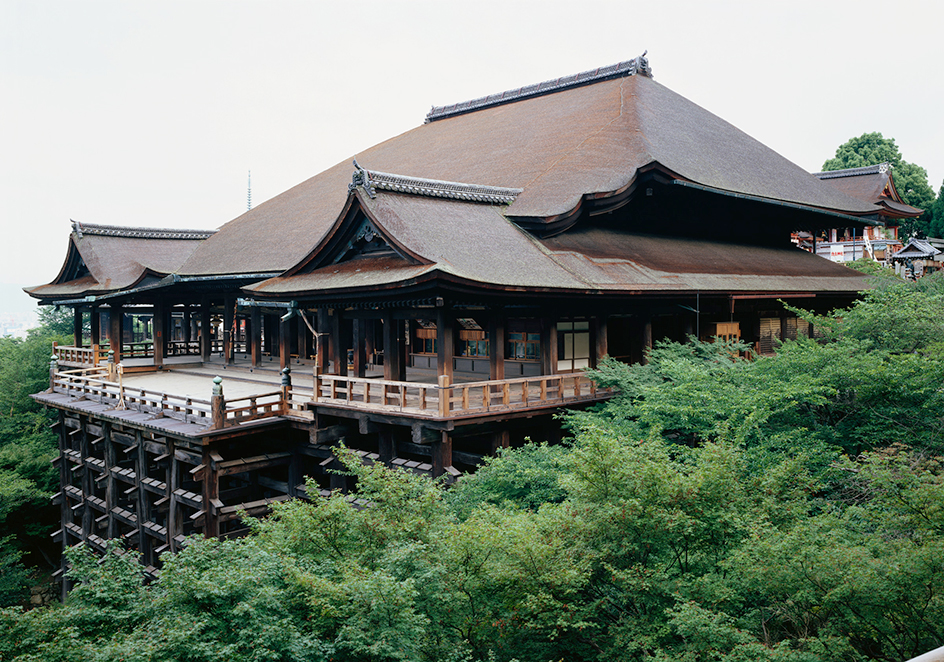
Kyoto is an important religious center, with many Buddhist temples and Shinto shrines housing priceless works of art. One of the most beautiful sights, the Golden Pavilion, was built in 1397 and rebuilt in the 1950’s. Deputies of the Tokugawa shoguns lived in Nijo Castle from the 1600’s to the 1800’s. The Imperial Palace, first erected in A.D. 794, was rebuilt in 1855.
The city has many institutions of higher education, including the government-controlled Kyoto University, and Doshisha University, a private school.
Workers in small factories produce exquisite textile, ceramic, lacquer, and cloisonne goods. Weaving and dyeing silks is an important industry.

Emperor Kammu established Japan’s capital at Kyoto in A.D. 794. He called it Heian-kyo, meaning capital of peace and tranquillity. Many Japanese called it Miyako, meaning imperial city, or Kyoto, meaning capital city. Tokyo replaced Kyoto as the capital in 1868. Kyoto was the only major Japanese city which escaped bombing during World War II (1939-1945).
