Labour Party is one of the two main political parties in the United Kingdom. The Conservative Party is the other one. The Labour Party traditionally has received support from working class voters, especially members of trade unions. For most of its history, the party has promoted socialist policies and has brought about many changes in the British economic system. But in the mid-1990’s, the party moved away from its long-held socialist principles in an effort to win wider support among voters.
History.
The number of British working-class voters was increased by the Reform Acts of 1867 and 1884. But unlike the socialist workers on the European continent, British workers did not at first favor independent political action. The Labour Party did not begin to take shape until the late 1800’s. This occurred under the leadership of several groups, particularly the Fabian Society and the Independent Labour Party. The first effective steps were taken in 1900, with the formation of a Labour Representation Committee. It included representatives of trade unions and socialist groups. The Labour Party elected 29 candidates in 1906, but its growth was uneven. In World War I (1914-1918), some of its leaders alarmed the country by their pacifism.
After the war, the party declared itself in favor of socialism. Its membership grew, and, in 1924, James Ramsay MacDonald formed the first Labour government. But the Labour Party still depended on Liberal votes for its majority in the House of Commons, so it had little chance to follow an independent policy. In 1931, MacDonald and other Labour members formed a coalition government to combat a severe depression that had struck the country. They then were expelled from the Labour Party.
In World War II (1939-1945), the Labour Party joined with Winston Churchill’s government to carry the nation to victory. After Germany’s defeat in 1945, cooperation ended, and an election was held. Labour won by a large margin, and Clement Attlee became prime minister. Attlee led the party from 1935 to 1955. From 1945 to 1951, a Labour government under Attlee carried out much of the party’s program. It passed laws nationalizing (placing under government control) about one-fifth of the country’s industry. It also provided more social services. New and revised programs extended insurance and pension coverage. The National Health Service Act provided for free medical and dental care for the entire population.
The Conservatives regained control of Parliament in 1951 and held it until 1964. Labour Party leader Harold Wilson became prime minister in 1964. The party was defeated by the Conservatives in 1970, but it returned to power in 1974, still headed by Wilson. Wilson retired in 1976. James Callaghan became Labour leader and prime minister. In 1979, the Conservatives regained control of Parliament. Callaghan’s term as prime minister ended. Callaghan retired as party leader in 1980.
After its 1979 election defeat, the Labour Party suffered internal conflicts over policy. Several right-wing members left it and formed a party that later merged with the Liberal Party to form the Social and Liberal Democratic Party, now called the Liberal Democrats.
In 1994, Tony Blair became head of the Labour Party. In 1995, party members voted to drop from the party’s constitution a statement of commitment to “common ownership of the means of production, distribution, and exchange.” Dropping this statement of socialist principles was intended to broaden the party’s appeal beyond the working class. In a 1997 national election, the party won by a landslide over the Conservatives, and Blair became prime minister.
Recent developments.
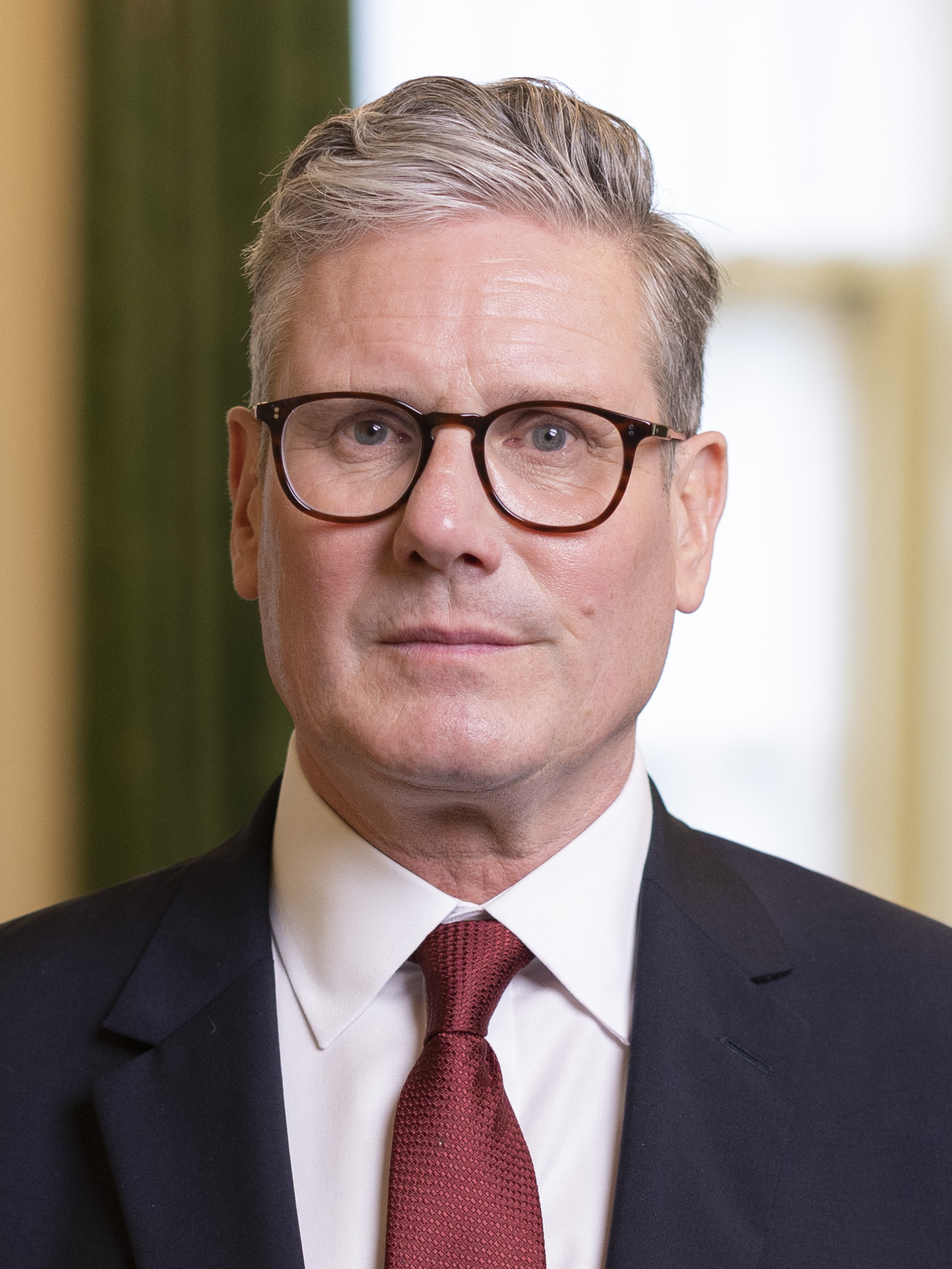
The Labour Party won elections in 2001 and 2005, and Blair continued as prime minister. In 2007, Blair resigned as prime minister and Labour Party leader. The party chose Gordon Brown to replace Blair. Brown served as prime minister until May 2010, when the Labour Party was defeated in general elections. Harriet Harman served as acting party leader until September, when Ed Miliband became the new Labour Party leader. After Labour lost a number of seats in May 2015 elections, Miliband resigned as party leader. Harman served as acting leader until Jeremy Corbyn succeeded her in September. Labour remained a minority party following general elections in 2017 and 2019. Keir Starmer succeeded Corbyn as party leader in 2020. Starmer became prime minister after the Labour Party won a majority of seats in the July 2024 elections.

In other countries.
Other countries that have a Labour (or Labor) Party include Australia, Ireland, Israel, the Netherlands, New Zealand, and Norway. Canada had a farmer-labor party called the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation until 1961. That year, the party united with the Canadian Labour Congress to form the New Democratic Party. Labour (or labor) parties have never been powerful in the United States. But a few had influence in certain areas. The American Labor Party was most active in New York City in the 1930’s. The Farmer-Labor Party of Minnesota was active mostly in the 1920’s and 1930’s.
