Lake Superior, one of the five Great Lakes of North America, is the largest body of fresh water in the world. Among the Great Lakes, it is the deepest, the highest above sea level, and the farthest north and west. Lake Superior forms part of an important interior waterway of the United States and Canada. This waterway extends from the Atlantic Ocean through the St. Lawrence Seaway and the Great Lakes. French fur traders gave the name Lac Superieur, French for Upper Lake, to the lake.
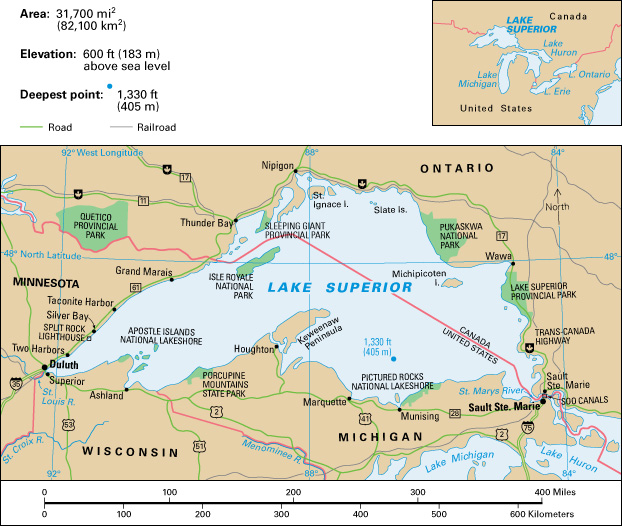
Location and size.
Lake Superior lies across the U.S.-Canadian border. The Canadian province of Ontario is to the north and east of the lake. The U.S. states of Michigan and Wisconsin lie to the south of the lake, and the state of Minnesota to the west.
Lake Superior covers 31,700 square miles (82,100 square kilometers). Its greatest length from east to west is 350 miles (563 kilometers), and its greatest width is 160 miles (257 kilometers). The lake lies 600 feet (183 meters) above sea level and is 1,330 feet (405 meters) deep at its deepest point.
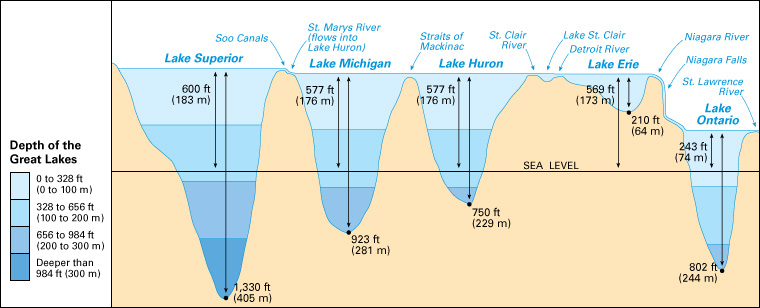
Description.
The coastline of Lake Superior is bold and rocky. In some places, especially along the northern shore, cliffs rise from the water’s edge. Colorful sandstone walls, known as the Pictured Rocks, rise along some areas of the lake’s shore in Michigan. The highway that follows the rocky Minnesota shore is lined with summer resorts, fishing villages, and state parks. Split Rock Lighthouse warns lake shipping from reefs in Beaver Bay along the Minnesota shore.
Forests cover almost all of the land that borders the lake. About 200 rivers, most of them short, empty into Lake Superior. Many of these rivers form waterfalls that plunge over the high, rocky headlands. The largest river emptying into the lake is the St. Louis River, which drains into the lake’s western end. The Keweenaw Peninsula, known for its copper deposits, juts into the lake in Michigan.
Many islands dot the surface of Lake Superior. The largest are Michigan’s Isle Royale and Ontario’s St. Ignace and Michipicoten. Small islands called the Apostle Islands lie off the northern Wisconsin shore.

Recreation and commerce.
There are few people or factories along the shoreline of Lake Superior. As a result, it is the least polluted of the Great Lakes and is popular for fishing and other recreational activity.
For years, lake trout had been fished heavily in Lake Superior. But by the late 1950’s, fish called lampreys had killed almost all the trout. Scientists added a chemical to the lake’s tributaries, where the lampreys breed. The chemical killed the lamprey larvae but did not harm other fish. By the mid-1960’s, the number of lampreys in Lake Superior had been significantly reduced. Wildlife officials then stocked the lake with trout and other fishes. Periodic chemical treatments and other measures keep the lamprey population low.
The lake does not freeze over in winter, but frozen harbors restrict shipping. The shipping season extends from about mid-April to December. Boats carry iron ore, lumber, taconite, wheat, and copper and other minerals to ports along the Great Lakes and farther east. The locks of the Soo Canals in Sault Ste. Marie carry ships around the rapids of the St. Marys River. This river connects Lake Superior and Lake Huron. The chief ports on Lake Superior are Duluth, Two Harbors, Taconite Harbor, Silver Bay, and Grand Marais, all in Minnesota; Superior and Ashland, Wisconsin; Marquette, Michigan; and Thunder Bay, Ontario.

