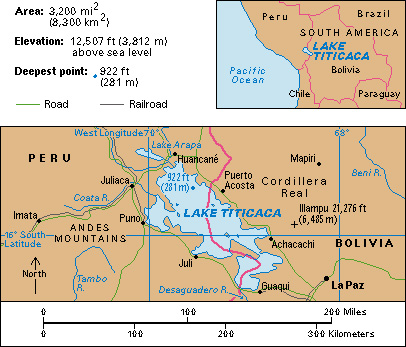
Lake Titicaca, << `tee` tee KAH kah, >> is the highest navigable lake in the world. Located on the border between Peru and Bolivia, it lies 12,507 feet (3,812 meters) above sea level. The lake is 110 miles (180 kilometers) long and about 45 miles (72 kilometers) wide. It covers about 3,200 square miles (8,300 square kilometers) and is more than 900 feet (270 meters) deep in places. The Desaguadero River flows out of its southern end and, when water levels are high enough, empties into the ephemeral Lake Poopó in Bolivia. An ephemeral lake usually is dry but has water during the wet season or for certain periods.
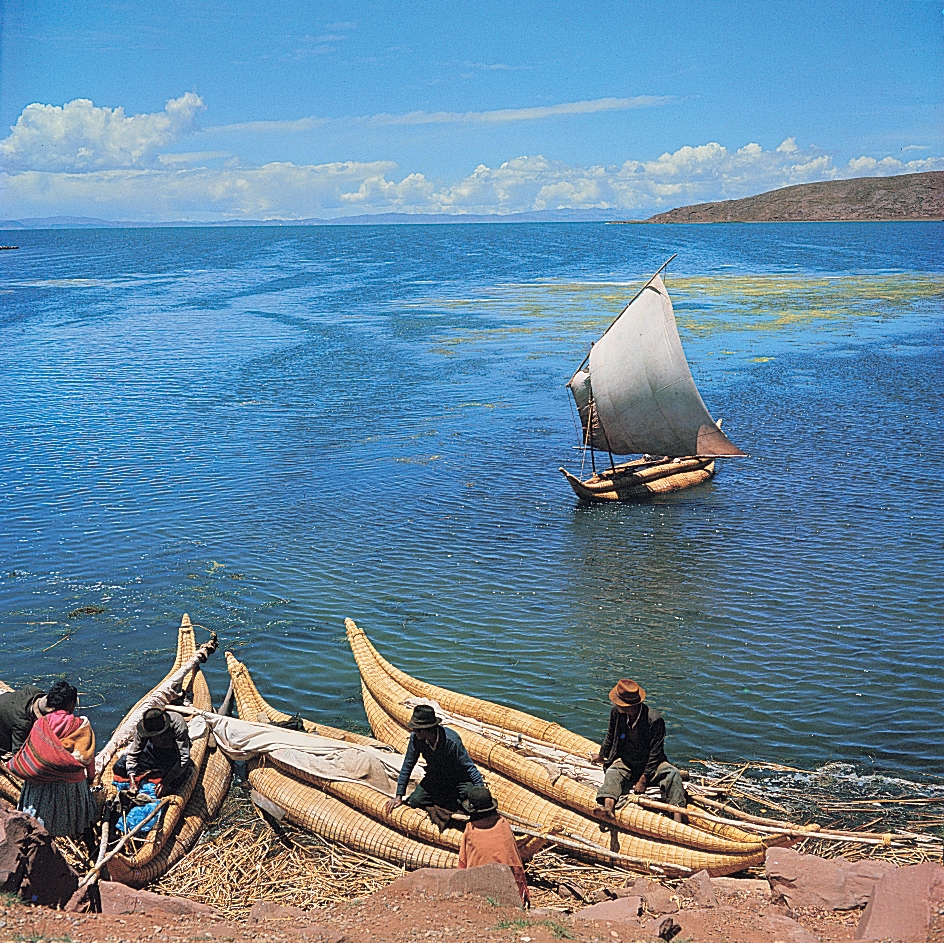
Many islands lie in the lake. Some have ruins of Indian civilizations that existed before the Spanish conquest of South America in the 1500’s. Numerous Indian villages lie near Lake Titicaca’s shore. Many villagers make boats from reeds called totoras, which grow on the shores of the lake. These boats provide transportation for local Indian commerce. Trout are found in Lake Titicaca. Some of these fish are about 3 feet (1 meter) long.

