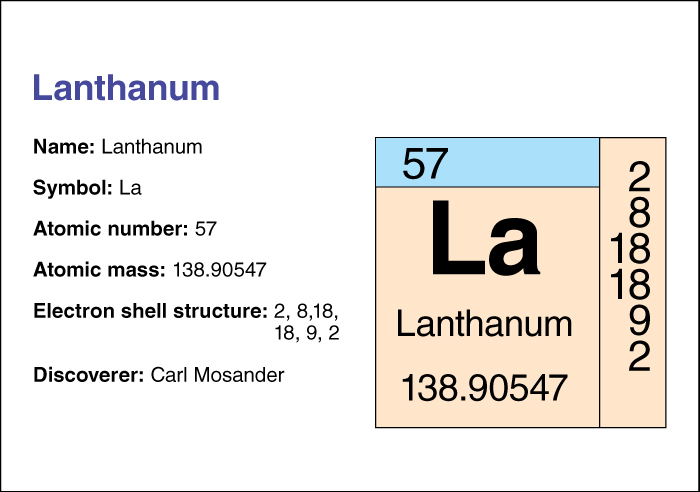
Lanthanum, << LAN thuh nuhm, >> is a soft, silvery-white metallic element. It tarnishes rapidly when exposed to air. Lanthanum is often classified as a lanthanide, although some chemists treat it as a transition metal. Lanthanum is found in lanthanide mineral ores, such as monazite and bastnasite. It also can be produced in nuclear reactors by the fissioning of uranium, thorium, or plutonium. The Swedish chemist Carl Mosander first identified lanthanum in 1839. Its name comes from a Greek word meaning to be hidden or concealed.
Lanthanum forms part of an alloy called misch metal, which is used in making flints for cigarette lighters. Lanthanum oxide is added to the glass used for camera lenses to increase its ability to refract (bend) light.
Lanthanum has an atomic number (number of protons in its nucleus) of 57. Its relative atomic mass is 138.905. An element’s relative atomic mass equals its mass (amount of matter ) divided by 1/12 of the mass of carbon 12, the most abundant form of carbon. The chemical symbol of lanthanum is La. Lanthanum melts at 921 °C and boils at 3457 °C. For information on the position of lanthanum on the periodic table, see the article Periodic table .
