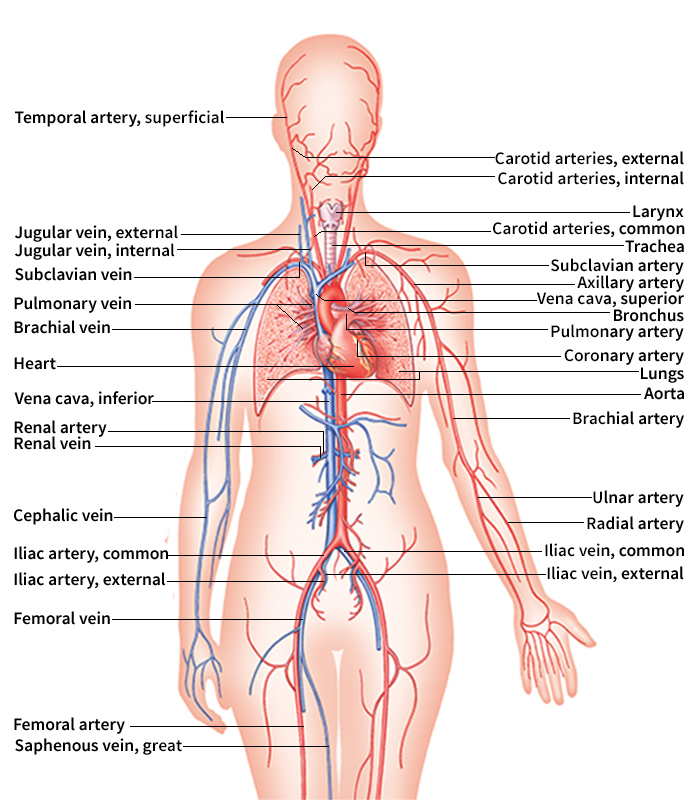
Aorta, << ay AWR tuh, >> is the body’s longest and largest artery. Its many branches distribute purified blood to all parts of the body. The first part of the aorta is the ascending aorta. It rises from the left ventricle of the heart almost to the top of the breastbone. The aorta’s first branches are the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. From near the top of the breastbone, the aorta arches backward and slightly to the left to form the arch of the aorta. Branches from the arch supply blood to the head and neck. The section after the arch, the descending aorta, passes downward through the chest and abdomen. It supplies the bones, organs, and muscles with blood. In the chest, or thorax, the aorta is called the thoracic aorta; in the abdomen, the abdominal aorta. At the hips, the aorta divides into two large arteries, the common iliac arteries, which carry blood to the pelvis and legs.