Baltic Sea is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean that extends into northern Europe. It separates the Scandinavian Peninsula from the northern coast of Europe. It links Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and Poland with the North Sea and the Atlantic.
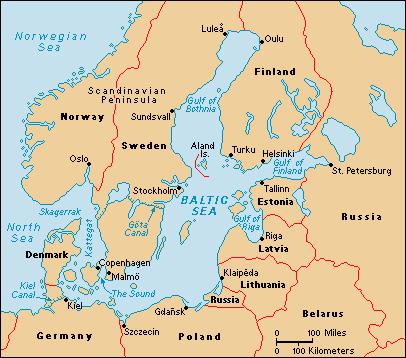
The Baltic Sea has an area of about 160,000 square miles (414,000 square kilometers). It is about 950 miles (1,530 kilometers) long and about 400 miles (640 kilometers) across at its widest part. The Baltic coastline, including that of its gulfs and bays, is about 5,000 miles (8,000 kilometers) long.
There are important harbors at the cities of Copenhagen, Denmark; Gdansk, Poland; Kiel, Germany; Klaipėda, Lithuania; Riga, Latvia; and Stockholm, Sweden. The Gota Canal provides a short cut from Sweden’s Baltic coast to its west coast. The Kiel Canal connects the Baltic with the North Sea. There are narrow straits between Denmark and the Scandinavian Peninsula. These include the Great Belt and the Little Belt, and The Sound (Oresund), leading from the Baltic to the Kattegat.
Two long gulfs extend from the northern and eastern sides of the Baltic Sea. These are the Gulf of Finland and the Gulf of Bothnia. A chain of islands guards the entrance to the Gulf of Riga. The Aland Islands lie across the mouth of the Gulf of Bothnia.
