Baroque, << buh ROHK or buh ROK, >> is a term applied to many forms of art created in western Europe and Latin America. The style first appeared in Rome in the late 1500’s. Baroque art is large in scale and filled with dramatic details. In the 1700’s, Baroque art developed into a more relaxed, intimate style called rococo (see Rococo ).
Loading the player...Baroque music by George Frideric Handel
Three elements in the cultural life of western Europe helped form the Baroque style. First, artists in the late 1500’s rebelled against the art of the Renaissance. Renaissance art was restrained and orderly, and generally symmetrically balanced. Baroque painters, architects, and sculptors achieved balance in a more dramatic and exciting way. For example, a Renaissance architect might use rectangular areas to achieve balance and beauty. The more dramatic Baroque architect would replace the rectangular areas with curved areas.
Second, many rulers wanted an art style that would glorify their reigns. Magnificent Baroque palaces such as Versailles in France and the Zwinger in Germany expressed the power and authority of the head of state.
Third, a movement called the Counter Reformation stirred a sense of religious enthusiasm in Europe during the late 1500’s and the 1600’s. Baroque churches expressed the drama and emotion of this movement.
Baroque architecture
combined in new ways such classical and Renaissance elements as columns, arches, and capitals. Sweeping curved areas replaced orderly rectangular areas. Sculpture and painting played a greater part in building design, helping create an illusion of great space. Interest in the relationship between buildings and their surroundings led to greater emphasis on city planning and landscape design.
One of the highlights of Baroque design was the creation of vast gardens, such as those at Versailles, the French king’s country estate. There, nature was controlled and presented in a formal arrangement of cascades, fountains, terraces, and trees.

Baroque buildings in Austria, Spain, and Latin America were especially ornate and elaborate. Baroque architecture in France was more classical and ordered. Among the finest architects who designed buildings in the Baroque style were the Italian artists Gian Lorenzo Bernini and Francesco Borromini. See Architecture (Baroque) .
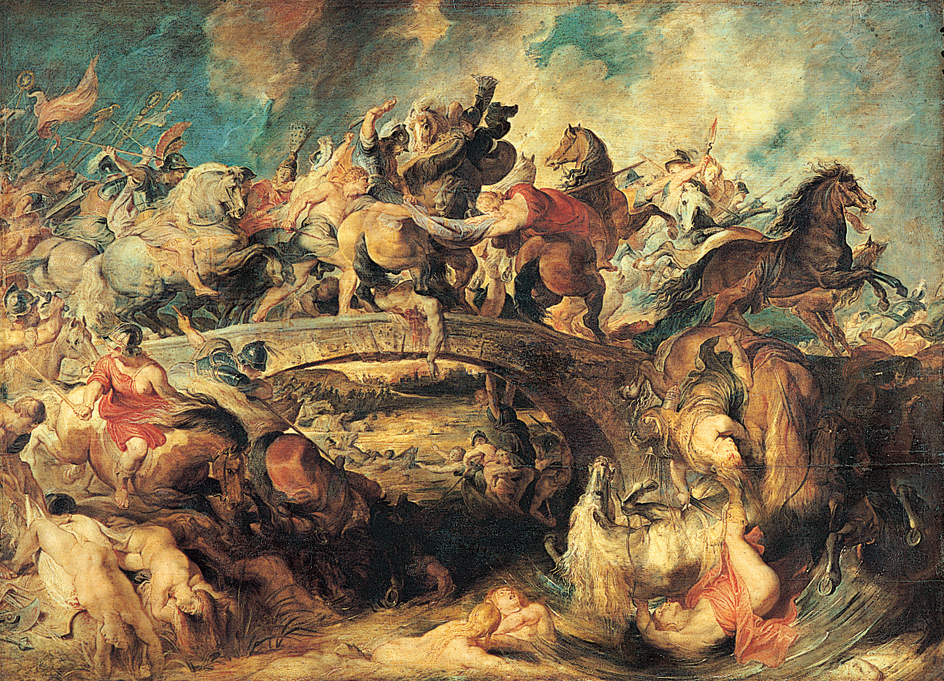
Baroque painting
displays large-scale forms and often freely painted compositions. Artists developed new approaches to traditional subjects. Michelangelo da Caravaggio practiced a revolutionary style depicting earthy, realistic figures in close-up with dramatic contrasts of light and shade. Annibale Carracci established the Italian Baroque taste for ceiling decoration of massive figures in settings that give the illusion of space. In Flanders in northern Europe, Peter Paul Rubens was the chief Baroque artist. He painted large altarpieces, mythological subjects, and decorative compositions of weighty forms in dynamic movement. In Holland, Rembrandt was painting works that were often influenced by Caravaggio and Rubens. But Rembrandt used light effects and free application of paint for greater emotional and psychological insight. Spain’s leading Baroque painter was Diego Velazquez. His many portraits and other works have a somber, brooding quality. See Painting (The 1600’s and 1700’s) .

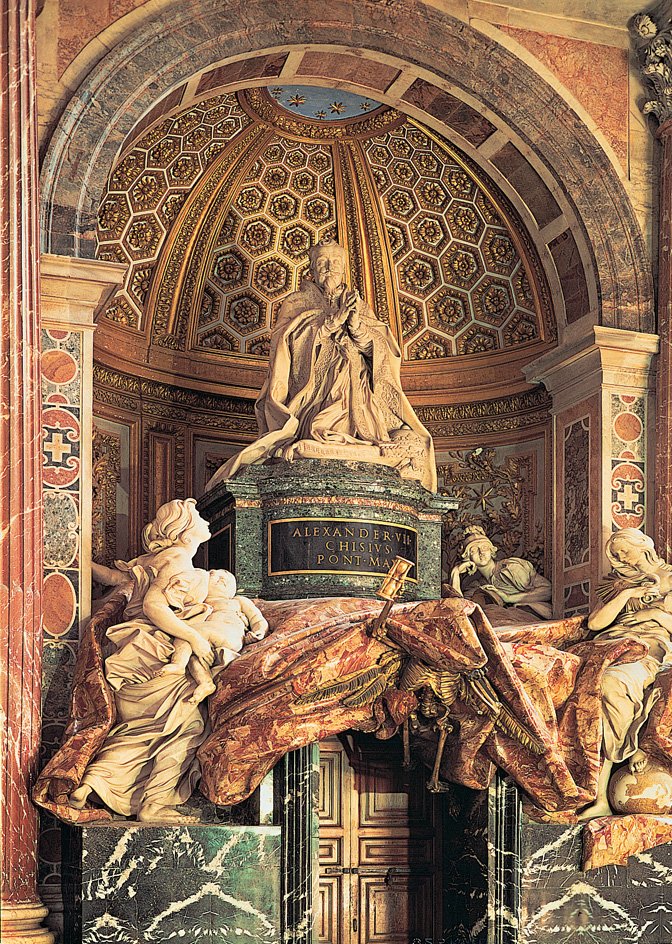
Baroque sculpture
was characterized by a tremendous feeling for movement. This came from the careful intermingling of mass and space as well as the use of new materials such as stucco and plaster. The greatest sculptor of the period was Gian Lorenzo Bernini of Italy. He worked primarily in marble, designing fountains, altarpieces, portrait busts, and free-standing pieces. All had remarkably realistic features and a flamboyant theatrical sense. See Sculpture (Sculpture from 1600 to 1900) .
Baroque music,
like other Baroque art forms, is filled with complex details and contrasts. Baroque music was closely related to church and court life. Baroque religious music became increasingly dramatic and worldly. Opera, with its elaborate stage spectacles, first developed during the Baroque period. The great Baroque composers include Claudio Monteverdi and Alessandro Scarlatti of Italy, and Johann Sebastian Bach and George F. Handel of Germany. See Classical music .
Loading the player...Brandenburg Concerto No. 3, 3rd Movement
