Barracuda, << `bar` uh KOO duh, >> is the name of a family of marine fish with long, slender bodies and forked tail fins. Barracudas have large jaws and sharp teeth. They feed mainly on other fish.
There are 20 species of barracudas worldwide. Five species live off the Atlantic coast of North America, one off the Pacific coast, and two in waters off Hawaii. The great barracuda, found in the Atlantic, Indian, and western Pacific oceans, is the largest species of barracuda. It can grow to about 6 feet (1.8 meters) and 100 pounds (45 kilograms). The great barracuda is called the “tiger of the sea” because it is swift and destructive.
Loading the player...Great barracuda
When young, great barracudas usually live close to shore. They may form schools (groups) of up to several thousand. Adults are often found near coral reefs or artificial structures, such as oil rigs or sunken ships. They are generally solitary.
The Pacific barracuda may grow to a length of 4 feet (1.2 meters). It is found along the west coast of North America but is rare in waters north of California.
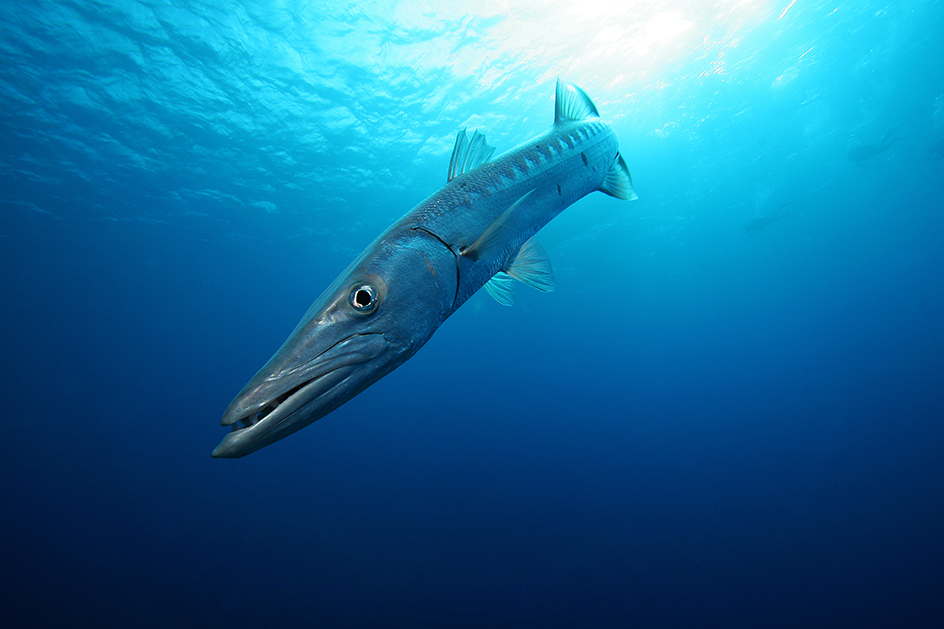
Eating the flesh of the barracuda can result in ciguatera, a disease that can be fatal. The disease is caused by a poison found in some tiny living things called dinoflagellates. Barracudas become poisonous when they eat fish that have fed on dinoflagellates. Barracudas have attacked people, but such attacks are extremely rare.
Loading the player...Great barracuda
