Bearing is a part of a machine that supports or guides a moving part. Bearings hold weight, turn with the motion of other parts, and reduce friction and wear by enabling sliding or rotating parts to move smoothly. Bearings are used in a wide variety of machines, including automobile engines, conveyors, elevators, generators, and turbines. They are often classified according to their function. For example, linear bearings guide objects along a track. Journal bearings keep a journal (shaft) turning smoothly.
There are two major types of bearings—plain bearings and rolling element bearings. They differ in how they reduce friction.
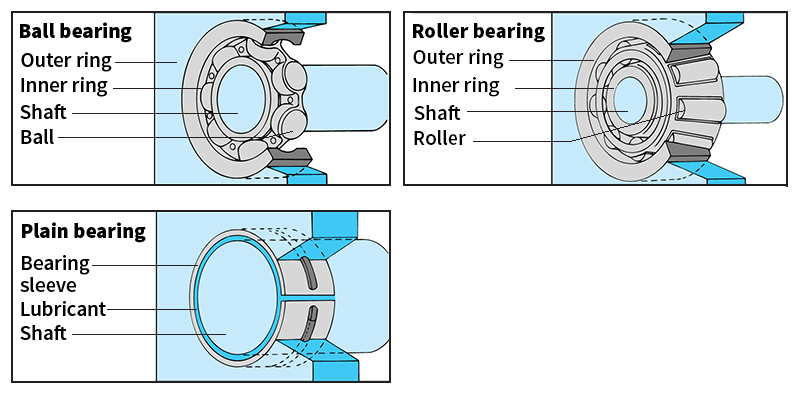
Plain bearings
are sometimes called fluid film bearings because they support moving parts on a thin film of lubricating fluid. Plain bearings form a sleeve around a shaft but are separated from it by the fluid. Many plain bearings are lined with a soft alloy called babbitt metal and are lubricated with grease or oil.
In a common type of plain bearing, the lubricant works only when the shaft is turning at high speeds. The rapid movement of the shaft creates high pressures in the lubricant, which keeps the metal surfaces from touching each other. When the machine is starting or stopping and the shaft is rotating slowly, however, the surfaces touch, producing more friction and wear.
In another type of plain bearing, lubricant is pumped in beneath the shaft at high pressure. The lubricant lifts the shaft and prevents it from touching any other surface, even during periods of slow rotation. As a result, there is almost no friction.
Some plain bearings require no lubrication because they are made of plastic or have nonmetallic liners. Self-lubricating bearings made of sintered (compressed and heated) metal powder are used in the electric motors in vacuum cleaners and other appliances. These bearings have many tiny pores that can be filled with lubricating oil.
Rolling element bearings
use rolling motion between parts. Thus, they reduce friction better than plain bearings do. Rolling element bearings are identified by the shape of the rolling element and include ball bearings and roller bearings. Ball bearings have several steel or ceramic balls that roll between two grooved steel rings. In most ball bearings, the balls are separated and held in place by a cage or spacer made of bronze, soft steel, or plastic. Roller bearings use cylindrical, spherical, or tapered rollers instead of balls. Bearings may also be manufactured in brackets or housings.
