Belladonna, << `behl` uh DON uh, >> is a bushy plant that supplies several drugs. The most important drug obtained from the plant is atropine. Belladonna is sometimes called deadly nightshade to distinguish it from common, or black, nightshade, which is not so dangerous. Belladonna grows in Europe and Asia. Some is now raised in the United States.
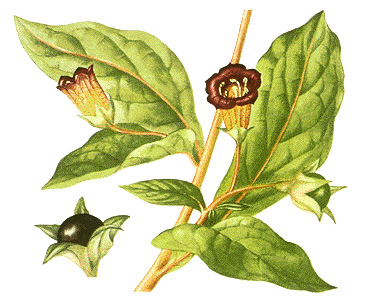
Belladonna bushes are often grown in gardens for their beauty. They are from 2 to 3 feet (61 to 91 centimeters) high and have drooping, bell-shaped flowers that are blue-purple or dull red. People have died from eating the berries, which contain the belladonna drugs. Vinegar is a simple first-aid remedy for belladonna poisoning, but a physician should be called at once.
Belladonna drugs are taken from the roots and leaves, but all parts of the plant contain the drugs. They are an important antidote for poisoning with certain insecticides and mushrooms. They also are sometimes used to relieve colic and various intestinal troubles. Ophthalmologists sometimes use belladonna drugs to relax eye muscles and to cause the pupil to expand. The drugs should be used only under the direction of a physician.
