Blueberry is a small, sweet fruit that grows on a shrub of the same name. People eat blueberries fresh or cook them in such foods as blueberry pie and preserves. Ripe blueberries range in color from light blue to black and have a waxy, powdery-gray coating. They measure from 1/8 inch to more than 1 inch (0.3 to more than 2.5 centimeters) in diameter. Blueberry bushes have green leaves and bear white or pink flowers.
Blueberries grow wild in many parts of the world. However, the United States and Canada supply about 95 percent of the blueberries used by the food industry. North American farmers harvest about 103 million pounds (47 million kilograms) of blueberries annually. Nearly a third of the crop is sold as fresh fruit, and another third is frozen. The rest is canned or goes into bakery goods, ice cream, and other food products.
The food industry uses two main kinds of blueberries, lowbush and highbush. Lowbush blueberry shrubs grow wild and are about 6 to 18 inches (15 to 46 centimeters) tall. Farmers gather the berries and sell them for use in canned and other processed foods. Most lowbush blueberries are supplied by Maine and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and Quebec.
Highbush blueberries make up most of the fresh blueberries sold in groceries. Farmers plant and cultivate the bushes, which reach a height of 3 to 6 feet (0.9 to 1.8 meters). Most highbush blueberries come from Arkansas, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia. The southern highbush is grown in Florida. It is a hybrid developed by crossing the common highbush blueberry and a native Southern variety.
The rabbit-eye blueberry is grown by farmers in some Southern States. This hardy species is the tallest blueberry plant and may reach 15 feet (4.6 meters).
All blueberries grow best in acid soil. To blossom normally, they need a cold, inactive period during the winter. However, most blueberry plants cannot survive temperatures below –20 °F (–29 °C). A healthy plant can produce as many as 20 pints (9 liters) of berries annually and may live longer than 50 years.
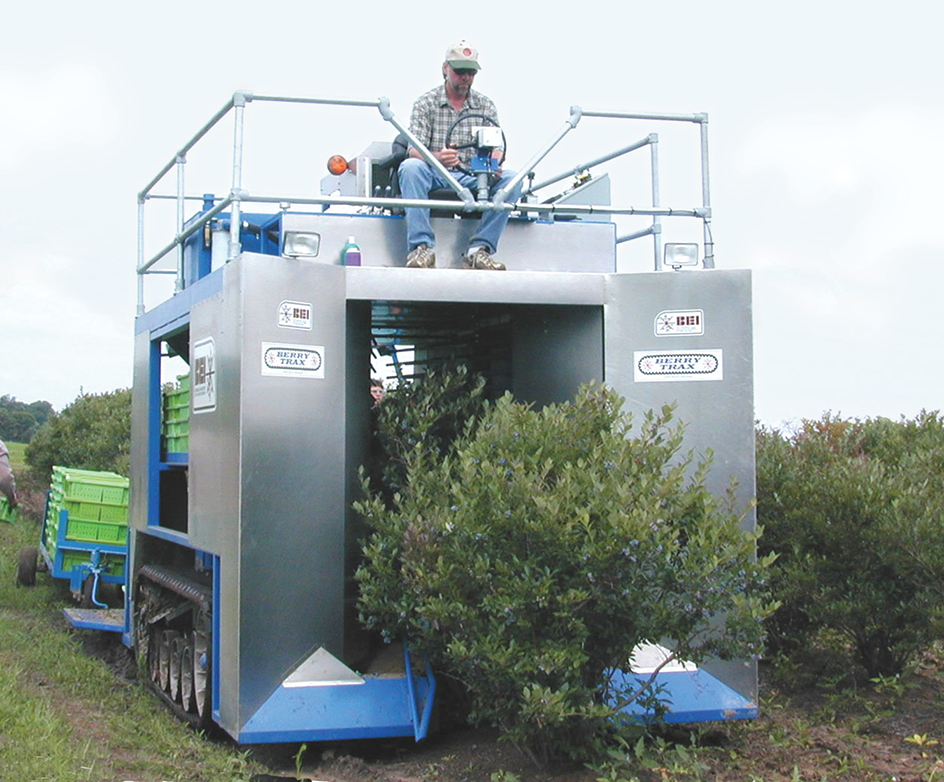

The fresh blueberry season lasts from May through June in the South and from June through September in the North. About 60 percent of the blueberry crop is picked by hand, but many farmers pick highbush and rabbit-eye blueberries with large harvesting machines. The berries are cleaned, packed in boxes, and shipped to stores. Lowbush blueberries are sent to processing plants to be canned or frozen.
