Chayote << chah YOH tay >>, also called mirliton or vegetable pear, is a climbing vine grown chiefly for its fruit. Chayote has thick roots, cream-colored flowers, and large leaves with pointed lobes. A single plant may cover a tree 50 feet (15 meters) tall.
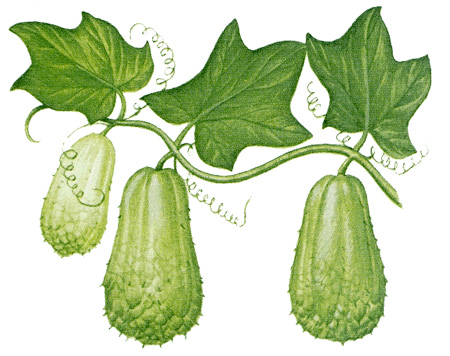
Chayote gourds are round to pear-shaped. These fruits grow as long as 6 inches (15 centimeters) and usually weigh from 6 ounces to 2 pounds (170 to 900 grams). They range in color from ivory-white to dark green and contain one large seed. Immature chayote gourds are usually cooked but can be eaten fresh in salads. The roots, leaves, and young shoots are also edible, and the plant is sometimes used as livestock feed.
Chayote may be native to Mexico, but it now grows throughout Latin America and much of the southern United States. New vines are grown by planting either gourds or cuttings from the stem.
