Cold frame is a boxlike structure built or placed on the ground to protect plants during cold weather. Gardeners use cold frames in spring to shelter tender seedlings sprouted before the start of the growing season. Cold frames also extend the growing season of plants in fall by protecting them from frost.
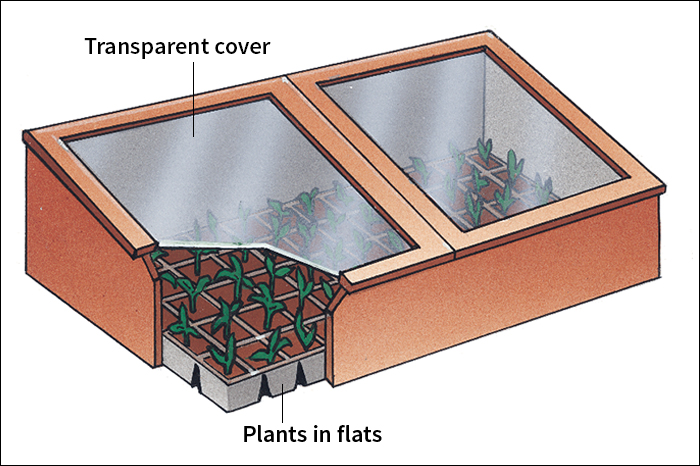
A cold frame consists of a rectangular structure made of wood, concrete, or brick, with a cover of glass or transparent plastic. The cover lets in sunlight and retains heat. Most cold frames have a cover that slants downward toward the south, in order to let in as much sunlight as possible. On warm days, one side of the cover can be raised to cool the frame.
In most cases, gardeners plant seeds indoors in pots or in long boxes called flats. In the spring, they put the pots or flats containing the seedlings into cold frames. They may bury the pots to help the soil in the pots retain moisture. To prepare a growing area for seedlings planted directly inside a cold frame, a gardener replaces about 1 foot (30 centimeters) of soil with equal layers of gravel and richer soil.
In summer, plants that need shade can be protected from bright sunlight by replacing the transparent covering with wooden slats or burlap. A structure similar to a cold frame but heated by electric heat or other means is called a hotbed (see Hotbed ).
