Coronary thrombosis, also called coronary occlusion, is a condition in which a clot blocks the passage of blood in an artery of the heart. The portion of the heart muscle supplied by the blocked artery then dies. The death of the muscle is called a heart attack or a myocardial infarction.
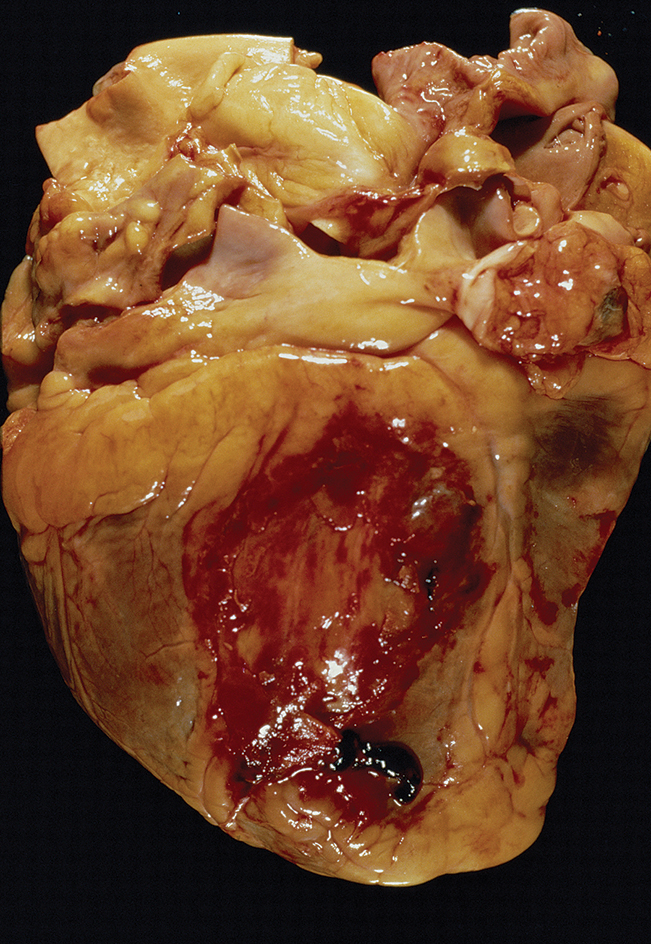
Symptoms of a coronary thrombosis include severe chest pain, shortness of breath, vomiting, and a weak and rapid pulse. A coronary thrombosis can cause death. If the patient survives, the condition leaves scar tissue in the area of the heart muscle supplied by the artery where the clot developed.
See also Heart attack.
