Denver is the capital and largest city of Colorado. It is the distribution, manufacturing, and transportation center for the Rocky Mountain region of the United States. The city is also a center for snow sports and serves as a gateway to nearby mountain vacation spots.
Denver lies in the north-central part of Colorado on the South Platte River, 10 miles (16 kilometers) east of the Rocky Mountains. It is called the Mile High City because the Colorado State Capitol stands in the city on land 1 mile (1.6 kilometers) above sea level.
When gold prospectors founded Denver in 1858, it formed part of the Kansas Territory. The town was named after James W. Denver, governor of the territory. The town became the capital of the Colorado Territory in 1867 and the state capital when Colorado became a state in 1876.
From 1860 to 1945, Denver was a mining and agricultural community. The city’s population increased greatly before and during World War II (1939-1945). After the war, Denver became known for its industries. Between 1945 and 1980, the city’s continued expansion in industry and population made it one of the nation’s fastest-growing cities. Denver’s population decreased during the 1980’s, but began growing again during the 1990’s and first two decades of the 2000’s.
The city
has the same boundaries as Denver County. The U.S. Census Bureau defines the Denver-Aurora-Centennial metropolitan area as 10 counties—Adams, Arapahoe, Broomfield, Clear Creek, Denver, Douglas, Elbert, Gilpin, Jefferson, and Park counties.
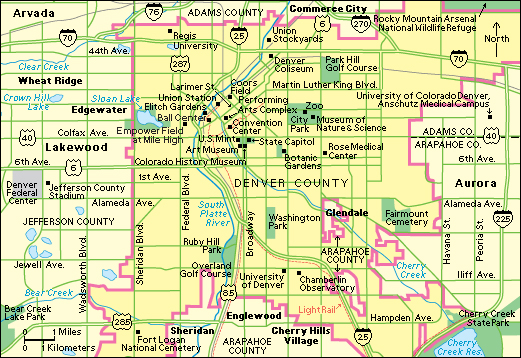
Broadway, Colfax Avenue, and Larimer Street form a triangle around Denver’s downtown business district. Cherry Creek joins the South Platte River northwest of the triangle. Skyscrapers with banks and investment firms make 17th Street the “Wall Street of the West.”
The 16th Street Mall, a 16-block-long pedestrian mall, is in downtown Denver. During the day, downtown office workers and shoppers mingle among the mall’s colorful pushcarts, street musicians, and old-fashioned horse-drawn carriages. Many apartment buildings stand near the west end of the mall.
Southeast of the city’s main business district, the Civic Center includes the City and County Building, the Colorado State Capitol, the Denver Art Museum, and the Denver Public Library. West of the business district stand the city’s sports complex; an amusement park; the Colorado Convention Center; and the sprawling Denver Performing Arts Complex, which includes an opera house, concert hall, and several theaters.

The people.
About 30 percent of Denver’s people are of Hispanic ancestry. African Americans make up about 10 percent of the population. Denver also has a small number of American Indians and people of Asian descent.
Economy.
The federal government and the state government are among Denver’s major employers. The city serves as the national or regional headquarters of more federal agencies than any other city in the United States except Washington, D.C. The Denver Mint, which is near the Capitol, makes millions of U.S. coins every year.
The Denver area has a number of telecommunications and high-technology companies as well as manufacturing plants. Food processing ranks among the top manufacturing activities. Other manufactured products include beverages, computer and electronic components, fabricated metal products, and transportation equipment.
A large number of warehouses help make Denver the distribution center of the Rocky Mountain region. The city also serves as the region’s transportation center. Airlines use Denver International Airport. Railroad passenger trains, freight lines, and several highways also serve the city. Light rail lines serve downtown Denver and communities south, southeast, and west of the city. Denver has one daily newspaper, The Denver Post.
Education.
An elected Board of Education runs Denver’s public school system. The city is the home of several colleges and universities. The schools include the University of Colorado Denver, the University of Denver, the Iliff School of Theology, Metropolitan State University of Denver, and Regis University.
Cultural life and recreation.
The Denver Art Museum owns one of the country’s finest collections of American Indian art. The History Colorado Center, which is located in Denver, has many fine exhibits on the history of the area. The Denver Public Library is the largest public library in the Rocky Mountain region.
The Denver Performing Arts Complex covers four city blocks and includes the Ellie Caulkins Opera House, Boettcher Concert Hall, the Temple Hoyne Buell Theatre, and several other performance spaces. Opera Colorado and the Colorado Ballet perform in the opera house. The Colorado Symphony Orchestra performs in the concert hall.
Denver maintains numerous parks in the city and more than 20 square miles (50 square kilometers) of parkland in the Rocky Mountains. Winter Park, a city-owned ski resort, lies in the mountains.
Denver has several professional sports teams. The teams include the Colorado Rockies baseball team of the National League, the Denver Nuggets of the National Basketball Association, the Denver Broncos of the National Football League, and the Colorado Avalanche of the National Hockey League.

Government.
Denver has a mayor-council form of government. The people elect the mayor and 13 City Council members—all to four-year terms.
In 1902, Denver led a home-rule movement among the cities of Colorado. As a result of this movement, an amendment to the state Constitution made Denver both a city and a county. Denver gets most of its income from taxes on personal property, real estate, and general sales.
History.
Denver was founded in 1858, after prospectors found gold in the area. The community became a supply point for mining settlements during the “Pikes Peak or Bust” gold rush of 1859. Denver and nearby Auraria merged in April 1860. The next year, Denver was incorporated as a city. The city became the capital of the Colorado Territory in 1867 and the capital of Colorado when it became a state in 1876.
Denver expanded with completion of the Denver Pacific Railway in 1870. A silver-mining boom gave the city additional wealth during the 1880’s and 1890’s.
During the early 1900’s, Denver changed from a prairie town to a beautiful city. The city’s government established many parkways and planted trees throughout Denver. By 1910, the city had become the commercial center of the Rocky Mountain region. The Moffat Tunnel, a mountain railway route from Denver through James Peak, was completed in 1927.
The population of the Denver area soared during and after World War II (1939-1945). Many members of the U.S. armed forces who had been stationed in the area moved there after the war. During the 1970’s, Denver faced the problem of preserving its natural beauty while continuing to expand its industry. In 1968, Denver prohibited open burning of wastes by city agencies to lessen air pollution.
The Denver Urban Renewal Authority began the Skyline Project in 1968 to replace and restore old, run-down buildings in the city’s downtown area. The project included apartment and office buildings and a performing arts complex. The Skyline Project was completed in 1985. In 1990, the Colorado Convention Center opened.
One of Denver’s most successful suburban business developments is the Denver Technological Center (DTC), an office park southeast of the city. Development began in the 1960’s and continues. Today, the DTC is the home of hundreds of companies.
Tragedy struck Columbine High School in the Denver suburb of Littleton in April 1999. Two students at the school, armed with guns and bombs, killed 13 people and wounded more than 20 others before killing themselves. The incident helped fuel a nationwide effort to prevent violence in schools. See also Columbine High School shooting.
Tragedy again struck a Denver suburb in July 2012. A man armed with guns and tear gas shot 70 people, killing 12 of them, at a movie theater in Aurora, just east of Denver. In 2015, a jury found the man—James E. Holmes—guilty of the crimes and sentenced him to life in prison without the possibility of parole.
